Abstract
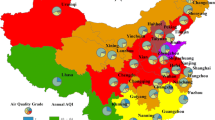
Daily air quality index (AQI) of 161 Chinese cities obtained from the Ministry of Environmental Protection of China in 2015 is conducted. In this study, to better explore spatial distribution and regional characteristic of AQI, global and local spatial autocorrelation is utilized. Pearson’s correlation is introduced to determine the influence of single urban indicator on AQI value. Meanwhile, multiple linear stepwise regression is chosen to estimate quantitatively the most influential urban indicators on AQI. The spatial autocorrelation analysis indicates that the AQI value of Chinese 161 cities shows a spatial dependency. Higher AQI is mainly located in north and northwest regions, whereas low AQI is concentrated in the south and the Qinghai-Tibet regions. The low AQI and high AQI values in China both exhibit relative immobility through seasonal variation. The influence degree of three adverse urban driving factors on AQI value is ranked from high to low: coal consumption of manufacturing > building area > coal consumption of the power industry. It is worth noting that the risk of exposed population to poor quality is greater in the northern region than in other regions. The results of the study provide a reference for the formulation of urban policy and improvement of air quality in China.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ang BW, Xu XY (2013) Tracking industrial energy efficiency trends using index decomposition analysis. Energy Econ 40:1014–1021. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2013.05.014
Bai-Chen X, Ying F, Qian-Qian Q (2012) Does generation form influence environmental efficiency performance? An analysis of China’s power system. Appl Energy 96:261–271. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2011.11.011
Bertazzon S, Johnson M, Eccles K, Kaplan GG (2015) Accounting for spatial effects in land use regression for urban air pollution modeling. Spatial Spatio-temporal Epidemiol 14–15:9–21. doi:10.1016/j.sste.2015.06.002
Bone C, Wulder MA, White JC, Robertson C, Nelson TA (2013) A GIS-based risk rating of forest insect outbreaks using aerial overview surveys and the local Moran’s I statistic. Appl Geogr 40:161–170. doi:10.1016/j.apgeog.2013.02.011
Cai WG, Wu Y, Zhong Y, Ren H (2009) China building energy consumption: situation, challenges and corresponding measures. Energy Policy 37:2054–2059. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2008.11.037
Cárdenas Rodríguez M, Dupont-Courtade L, Oueslati W (2016) Air pollution and urban structure linkages: evidence from European cities. Renew Sust Energ Rev 53:1–9. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2015.07.190
Carvalho A, Monteiro A, Flannigan M, Solman S, Miranda AI, Borrego C (2011) Forest fires in a changing climate and their impacts on air quality. Atmos Environ 45:5545–5553. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.05.010
Chan CK, Yao X (2008) Air pollution in mega cities in China. Atmos Environ 42:1–42. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.09.003
Dominick D, Juahir H, Latif MT, Zain SM, Aris AZ (2012) Spatial assessment of air quality patterns in Malaysia using multivariate analysis. Atmos Environ 60:172–181. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2012.06.021
Gao H et al (2011) A study of air pollution of city clusters. Atmos Environ 45:3069–3077. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.03.018
Gordon T, Stanek LW, Brown J (2014) Pollution, air in encyclopedia of toxicology. In: Wexler P (ed) Encyclopedia of toxicology (third edition). Academic Press, Oxford, pp. 995–1002. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-386454-3.00530-3
Griffith DA (2009) Spatial autocorrelation. In: Thrift RK (ed) International encyclopedia of human geography. Elsevier, Oxford, pp. 308–316. doi:10.1016/B978-008044910-4.00522-8
Grundström M, Hak C, Chen D, Hallquist M, Pleijel H (2015) Variation and co-variation of PM10, particle number concentration, NOx and NO2 in the urban air—relationships with wind speed, vertical temperature gradient and weather type. Atmos Environ. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.08.057
Jiang H-y, Li H-r, Yang L-s, Li Y-h, Wang W-y, Yan Y-c (2014) Spatial and seasonal variations of the air pollution index and a driving factors analysis in China. J Environ Qual 43:1853–1863. doi:10.2134/jeq2014.06.0254
Khan MM et al. (2016) Triangular relationship among energy consumption, air pollution and water resources in Pakistan. J Clean Prod. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.01.094
Kim SE, Lim Y-H, Kim H (2015) Temperature modifies the association between particulate air pollution and mortality: a multi-city study in South Korea. Sci Total Environ 524–525:376–383. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.03.137
Künzli N et al (2000) Public-health impact of outdoor and traffic-related air pollution: a European assessment. Lancet 356:795–801. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02653-2
Lee M (2005) The shadow price of substitutable sulfur in the US electric power plant: a distance function approach. J Environ Manag 77:104–110. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2005.02.013
Lee YC, Calori G, Hills P, Carmichael GR (2002) Ozone episodes in urban Hong Kong 1994–1999. Atmos Environ 36:1957–1968. doi:10.1016/S1352-2310(02)00150-4
Li L, Qian J, Ou C-Q, Zhou Y-X, Guo C, Guo Y (2014) Spatial and temporal analysis of air pollution index and its timescale-dependent relationship with meteorological factors in Guangzhou, China, 2001–2011. Environ Pollut 190:75–81. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2014.03.020
Matus K, Nam K-M, Selin NE, Lamsal LN, Reilly JM, Paltsev S (2012) Health damages from air pollution in China. Glob Environ Chang 22:55–66. doi:10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2011.08.006
Murty MN, Kumar S, Dhavala KK (2007) Measuring environmental efficiency of industry: a case study of thermal power generation in India. Environ Resour Econ 38:31–50. doi:10.1007/s10640-006-9055-6
NBS (National Bureau of Statistics) (1994–2012). China statistical yearbook. China Statistics Press, Beijing, China (in Chinese).
Nematchoua MK, Tchinda R, Orosa JA, Andreasi WA (2015) Effect of wall construction materials over indoor air quality in humid and hot climate. J Build Eng 3:16–23. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2015.05.002
Niu H, Hu W, Wei P, Fan J, Wang J (2015) Evolution of atmospheric aerosol particles during a pollution accumulation process: a case study. World J Eng 12:51–60
Nowak DJ, Hirabayashi S, Bodine A, Greenfield E (2014) Tree and forest effects on air quality and human health in the United States. Environ Pollut 193:119–129. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2014.05.028
Papamanolis N (2015) The main characteristics of the urban climate and the air quality in Greek cities. Urban Clim 12:49–64. doi:10.1016/j.uclim.2014.11.003
Root HT, Geiser LH, Jovan S, Neitlich P (2015) Epiphytic macrolichen indication of air quality and climate in interior forested mountains of the Pacific Northwest, USA. Ecol Indic 53:95–105. doi:10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.01.029
Schucht S et al (2015) Moving towards ambitious climate policies: monetised health benefits from improved air quality could offset mitigation costs in Europe. Environ Sci Pol 50:252–269. doi:10.1016/j.envsci.2015.03.001
Sekki T, Airaksinen M, Saari A (2015) Impact of building usage and occupancy on energy consumption in Finnish daycare and school buildings. Energy Build 105:247–257. doi:10.1016/j.enbuild.2015.07.036
Sueyoshi T, Goto M (2013) A comparative study among fossil fuel power plants in PJM and California ISO by DEA environmental assessment. Energy Econ 40:130–145. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2013.06.004
Tan Q, Wei Y, Wang M, Liu Y (2014) A cluster multivariate statistical method for environmental quality management. Eng Appl Artif Intell 32:1–9. doi:10.1016/j.engappai.2014.02.007
Tanaka S (2015) Environmental regulations on air pollution in China and their impact on infant mortality. J Health Econ 42:90–103. doi:10.1016/j.jhealeco.2015.02.004
Tian G, Qiao Z, Xu X (2014) Characteristics of particulate matter (PM10) and its relationship with meteorological factors during 2001–2012 in Beijing. Environ Pollut 192:266–274. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2014.04.036
Tie X et al (2006) Chemical characterization of air pollution in Eastern China and the Eastern United States. Atmos Environ 40:2607–2625. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.11.059
Torres-Roldán M, López-Luque R, Varo-Martínez M (2015) Design of an innovative and simplified polar heliostat for integration in buildings and urban environments. Sol Energy 119:159–168. doi:10.1016/j.solener.2015.06.041
Vos PEJ, Maiheu B, Vankerkom J, Janssen S (2013) Improving local air quality in cities: to tree or not to tree? Environ Pollut 183:113–122. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2012.10.021
Wang Y, Ying Q, Hu J, Zhang H (2014) Spatial and temporal variations of six criteria air pollutants in 31 provincial capital cities in China during 2013–2014. Environ Int 73:413–422. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2014.08.016
Zhang F, Wang L, Yang J, Chen M, Wei Z, Su J (2015a) The characteristics of air pollution episodes in autumn over the southern Hebei, China. World J Eng 12:221–236
Zhang X, Cao J, Li J, Deng S, Zhang Y, Wu J (2015b) Influence of sewage treatment on China′s energy consumption and economy and its performances. Renew Sust Energ Rev 49:1009–1018. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2015.04.182
Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Shi W, Shang R, Cheng R, Wang X (2015c) A new approach, based on the inverse problem and variation method, for solving building energy and environment problems: preliminary study and illustrative examples. Build Environ 91:204–218. doi:10.1016/j.buildenv.2015.02.016
Zhang Z, Zhang X, Gong D, Quan W, Zhao X, Ma Z, Kim S-J (2015d) Evolution of surface O3 and PM2.5 concentrations and their relationships with meteorological conditions over the last decade in Beijing. Atmos Environ 108:67–75. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2015.02.071
Zhao J et al (2012) Quantifying the impacts of socio-economic factors on air quality in Chinese cities from 2000 to 2009. Environ Pollut 167:148–154. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2012.04.007
Zheng S, Yi H, Li H (2015) The impacts of provincial energy and environmental policies on air pollution control in China. Renew Sust Energ Rev 49:386–394. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2015.04.088
Zhou P, Ang BW, Wang H (2012) Energy and CO2 emission performance in electricity generation: a non-radial directional distance function approach. Eur J Oper Res 221:625–635. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2012.04.022
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to Xiaojuan Li from Nanjing University for support and assistance during data collection. We thank Ran Xu from the National Geographic Information Bureau of Surveying and Mapping for data arrangement. This research was supported by the National Key Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (No. 2014CB238906) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41472322, 41172310).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Gerhard Lammel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pu, H., Luo, K., Wang, P. et al. Spatial variation of air quality index and urban driving factors linkages: evidence from Chinese cities. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24, 4457–4468 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8181-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-8181-0