Abstract
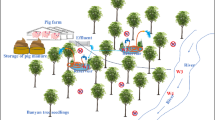
Duck/fish polyculture farming is a typical farming model in the Pearl River delta in southern China. We examined soil, water, and sediment samples from three duck-fish farms in Guangdong Province in September and December 2014. We determined the abundance of three metal resistance genes, 16S rDNA, and 23 antibiotic resistance genes encoding resistance to tetracycline, sulfonamides, quinolones, chloramphenicol, and β-lactamases. Microbial community structure was quantified by Illumina high-throughput sequencing of 16S rDNA genes. We found a prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes and the sul1, sul2, tetA, tetM, aac(6′)-Ib, and floR genes were the most abundant. Levels of Cu and Zn were significantly correlated with numerous ARG types and sul2, floR, and tetM were identified as potential antibiotic resistance gene indicators. Cu levels were significantly and positively correlated with the relative abundance of sul3, tetT, tetW, qnrB, qnrS, fexB, sul1, sul2, tetM, and qnrA. Zn was significantly correlated to relative abundance of sul2, sul3, tetM, tetA, tetT, tetW, qnrA, qnrB, qnrS, aac(6′)-Ib, qepA, blaSHV, cmlA, floR, fexA, cfr, and fexB. The levels of Acinetobacter, Brevibacillus, and Wautersiella showed significant positive correlations with metal resistance genes as well as qnrB, oqxA, oqxB, and blaSHV (p > 0.8). Sphingobacterium, Flavobacterium, Acidothermus, and Corynebacterium had significant correlations with abundance of tetracycline resistance genes, sulfonamide resistance genes, blaTEM, blaCTX, and cfr (p > 0.8). Sphingobacterium, Flavobacterium, Acidothermus, and Corynebacterium were most abundant in soil samples while Acinetobacter, Brevibacillus, and Wautersiella were most abundant in water samples. Dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes in aquaculture environments is extensive and tracing their origins is necessary to establish risk assessment methods required for aquatic environmental protection.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aminov RI, Garrigues-Jeanjean N, Mackie RI (2001) Molecular ecology of tetracycline resistance:development and validation of primers for detection of tetracycline resistance genes encoding ribosomal protection proteins [J]. Appl Environ Microbiol 67(1):22–32
Aminov RI, Chee-Sanford JC, Garrigues N, Teferedegne B, Krapac IJ, White BA, Mackie RI (2002) Development, validation, and application of PCR primers for detection of tetracycline efflux genes of gram-negative bacteria [J]. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(4):1786–1793
Bach HJ, Tomanova J, Schloter M, Munch JC (2002) Enumeration of total bacteria and bacteria with genes for proteolytic activity in pure cultures and in environmental samples by quantitative PCR mediated amplification [J]. J Microbiol Methods 49(3):235–245
Baker-Austin C, Wright MS, Stepanauskas R, McArthur JV (2006) Co-selection of antibiotic and metal resistance. Trends Microbiol 14:176–182
Bengtsson-Palme J, Larsson DGJ (2015) Antibiotic resistance genes in the environment: Prioritizing risks [J]. Nat Rev Microbiol 13(6):396
Bengtsson-Palme J, Boulund F, Fick J, Kristiansson E, Larsson DG (2014) Shotgun metagenomics reveals a wide array of antibiotic resistance genes and mobile elements in a polluted lake in India. Front Microbiol 5:648
Cattoir V, Poirel L, Rotimi V (2007) Multiplex PCR for detection of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance qnr genes in ESBL-producing enterobacterial isolates. J Antimicrob Chemother 60(2):394–397
Chapman JS (2003) Disinfectant resistance mechanisms, cross-resistance, and co-resistance. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation 51:271–276
Chen H, Chen R, Jing L et al (2019) A metagenomic analysis framework for characterization of antibiotic resistomes in river environment: application to an urban river in Beijing [J]. Environ Pollut 245:398–407
Chen B, Hao L, Guo X, Wang N, Ye B (2015) Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes of wastewater and surface water in livestock farms of Jiangsu Province. China Environmental science and pollution research international 22:13950–13959
Cheng W, Chen H, Su C, Yan S (2013) Abundance and persistence of antibiotic resistance genes in livestock farms: a comprehensive investigation in eastern China. Environ Int 61(1–7):1–7
Di Cesare A, Eckert E M, D’Urso S, et al. Co-occurrence of integrase 1, antibiotic and heavy metal resistance genes in municipal wastewater treatment plants [J]. Water Research, 2016,94:208-214.
Fang L, Li X, Li L, Li S, Liao X, Sun J, Liu Y (2016) Co-spread of metal and antibiotic resistance within ST3-IncHI2 plasmids from E. coli isolates of food-producing animals. Sci Rep 6:25312
Ferjani S, Saidani M, Amine FS, Boutiba-Ben Boubaker I (2015) Prevalence and characterization of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes in extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in a Tunisian hospital. Microb Drug Resist 21:158–166
Gao P, Mao D, Luo Y, Wang L, Xu B, Xu L (2012) Occurrence of sulfonamide and tetracycline-resistant bacteria and resistance genes in aquaculture environment [J]. Water Res 46(7):2355–2364
Gao P, He S, Huang S, Li K, Liu Z, Xue G, Sun W (2015) Impacts of coexisting antibiotics, antibacterial residues, and heavy metals on the occurrence of erythromycin resistance genes in urban wastewater [J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(9):3971–3980
Harrison JJ, Tremaroli V, Stan MA, Chan CS, Vacchi-Suzzi C, Heyne BJ, Parsek MR, Ceri H, Turner RJ (2009) Chromosomal antioxidant genes have metal ion-specific roles as determinants of bacterial metal tolerance. Environ Microbiol 11:2491–2509
Hasman H, Aarestrup FM (2002) tcrB, a gene conferring transferable copper resistance in enterococcus faecium: occurrence, transferability, and linkage to macrolide and glycopeptide resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 46:1410–1416
He LY, Liu YS, Su HC, Zhao JL, Liu SS, Chen J, Liu WR, Ying GG (2014) Dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes in representative broiler feedlots environments: identification of indicator ARGs and correlations with environmental variables. Environmental science & technology 48:13120–13129
Kim HB, Wang M, Park CH, Kim E-C, Jacoby GA, Hooper DC (2009) oqxAB encoding a multidrug efflux pump in human clinical isolates of enterobacteriaceae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53(8):3582–3584
Lapara TM, Burch TR, Mcnamara PJ et al (2011) Tertiary-treated municipal wastewater is a significant point source of antibiotic resistance genes into Duluth-Superior Harbor [J]. Environmental Science & Technology 45(22):9543–9549
Li J, Shao B, Shen J, Wang S, Wu Y (2013) Occurrence of chloramphenicol-resistance genes as environmental pollutants from swine feedlots. Environmental science & technology 47:2892–2897
Mao D, Yu S, Rysz M, Luo Y, Yang F, Li F, Hou J, Mu Q, Alvarez PJJ (2015) Prevalence and proliferation of antibiotic resistance genes in two municipal wastewater treatment plants [J]. Water Res 85:458–466
Marti R, Scott A, Tien YC, Murray R, Sabourin L, Zhang Y, Topp E (2013) Impact of manure fertilization on the abundance of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and frequency of detection of antibiotic resistance genes in soil and on vegetables at harvest. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:5701–5709
Mieszkin S, Furet JP, Corthier G, Gourmelon M (2009) Estimation of pig fecal contamination in a river catchment by real-time PCR using two pig-specific Bacteroidales 16S rRNA genetic markers. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:3045–3054
Ng LK, Martin I, Alfa M (2001) Multiplex PCR for the detection of tetracycline resistant genes. Mol Cell Probes 15(4):209–215
Oktem IMA, Gulay Z, Bicmen M, Gur D, Grp HPS (2008) qnrA prevalence in extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-positive Enterobacteriaceae isolates from Turkey. Jpn J Infect Dis 61:13–17
Park CH, Robicsek A, Jacoby GA (2006) Prevalence in the United States of aac(6')-Ib-cr encoding a ciprofloxacin-modifying enzyme[J]. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50(11):3953–3955
Pei R, Kim SC, Carlson KH (2006) Effect of river landscape on the sediment concentrations of antibiotics and corresponding antibiotic resistance genes (ARG). Water Research 40(12):2427–2435
Pruden A, Pei RT, Storteboom H, Carlson KH (2006) Antibiotic resistance genes as emerging contaminants: studies in northern Colorado. Environmental science & technology 40:7445–7450
Seiler C, Berendonk TU (2012) Metal driven co-selection of antibiotic resistance in soil and water bodies impacted by agriculture and aquaculture. Front Microbiol 3:399
Silveira E, Freitas AR, Antunes P, Barros M, Campos J, Coque TM, Peixe L, Novais C (2014) Co-transfer of resistance to high concentrations of copper and first-line antibiotics among Enterococcus from different origins (humans, animals, the environment and foods) and clonal lineages. J Antimicrob Chemother 69:899–906
Wales A, Davies R (2015) Co-selection of resistance to antibiotics, biocides and heavy metals, and its relevance to foodborne pathogens [J]. Antibiotics 4(4):567–604
Wang R, Zhang J, Sui Q, Wan H, Tong J, Chen M, Wei Y, Wei D (2016) Effect of red mud addition on tetracycline and copper resistance genes and microbial community during the full scale swine manure composting [J]. Bioresour Technol 216:1049–1057
Wang R, Chen M, Feng F, Zhang J, Sui Q, Tong J, Wei Y, Wei D (2017) Effects of chlortetracycline and copper on tetracyclines and copper resistance genes and microbial community during swine manure anaerobic digestion [J]. Bioresour Technol 238:57–69
Wang M, Liu P, Xiong W, Zhou Q, Wangxiao J, Zeng Z, Sun Y (2018) Fate of potential indicator antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs) and bacterial community diversity in simulated manure-soil microcosms [J]. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:817–823
Wilkinson D, Newman W, Reid A, Squire SB, Sturm AW, Gilks CF (2000) Trial-of-antibiotic algorithm for the diagnosis of tuberculosis in a district hospital in a developing country with high HIV prevalence [J]. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 4(6):513–518
Wright MS, Baker-Austin C, Lindell AH, Stepanauskas R, Stokes HW, McArthur JV (2008) Influence of industrial contamination on mobile genetic elements: class 1 integron abundance and gene cassette structure in aquatic bacterial communities. Isme J 2:417–428
Xi C, Zhang Y, Marrs CF, Ye W, Simon C, Foxman B, Nriagu J (2009) Prevalence of antibiotic resistance in drinking water treatment and distribution systems [J]. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(17):5714–5718
Xia LN, Li L, Wu CM et al (2010) A survey of plasmid-mediated fluoroquinolone resistance genes from Escherichia coli isolates and their dissemination in Shandong, China [J]. Foodborne Pathog Dis 7(2):207–215
Yao L, Wang Y, Tong L, Deng Y, Li Y, Gan Y, Guo W, Dong C, Duan Y, Zhao K (2017) Occurrence and risk assessment of antibiotics in surface water and groundwater from different depths of aquifers: a case study at Jianghan Plain, central China [J]. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 135:236–242
Zhao X, Wang J, Zhu L et al (2019) Field-based evidence for enrichment of antibiotic resistance genes and mobile genetic elements in manure-amended vegetable soils [J]. Sci Total Environ 654:906–913
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31772803), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China [2016A030311029], and National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD0501300).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Robert Duran
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Q., Wang, M., Zhong, X. et al. Dissemination of resistance genes in duck/fish polyculture ponds in Guangdong Province: correlations between Cu and Zn and antibiotic resistance genes. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26, 8182–8193 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-04065-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-04065-2