Abstract
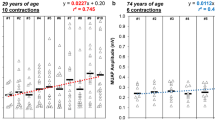
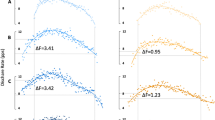
Age-related changes in motor unit activation properties remain unclear for locomotor muscles such as quadriceps muscles, although these muscles are preferentially atrophied with aging and play important roles in daily living movements. The present study investigated and compared detailed motor unit firing characteristics for the vastus lateralis muscle during isometric contraction at low to moderate force levels in the elderly and young. Fourteen healthy elderly men and 15 healthy young men performed isometric ramp-up contraction to 70 % of the maximal voluntary contractions (MVC) during knee extension. Multichannel surface electromyograms were recorded from the vastus lateralis muscle using a two-dimensional grid of 64 electrodes and decomposed with the convolution kernel compensation technique to extract individual motor units. Motor unit firing rates in the young were significantly higher (~+29.7 %) than in the elderly (p < 0.05). There were significant differences in firing rates among motor units with different recruitment thresholds at each force level in the young (p < 0.05) but not in the elderly (p > 0.05). Firing rates at 60 % of the MVC force level for the motor units recruited at <20 % of MVC were significantly correlated with MVC force in the elderly (r = 0.885, p < 0.0001) but not in the young (r = 0.127, p > 0.05). These results suggest that the motor unit firing rate in the vastus lateralis muscle is affected by aging and muscle strength in the elderly and/or age-related strength loss is related to motor unit firing/recruitment properties.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EMG:
-
Electromyography
- MVC:
-
Maximal voluntary contraction
- PNR:
-
Pulse-to-noise ratio
- SEMG:
-
Surface electromyography
- VL:
-
Vastus lateralis
References
Abe T, Kawakami Y, Bemben MG, Fukunaga T (2011a) Comparison of age-related, site-specific muscle loss between young and old active and inactive Japanese women. J Geriatr Phys Ther 34:168–173. doi:10.1519/JPT.0b013e31821c9294
Abe T, Sakamaki M, Yasuda T, Bemben MG, Kondo M, Kawakami Y, Fukunaga T (2011b) Age-related, site-specific muscle loss in 1507 Japanese men and women aged 20 to 95 years. J Sports Sci Med 10:145–150
Abe T, Loenneke JP, Thiebaud RS, Fukunaga T (2014) Age-related site-specific muscle wasting of upper and lower extremities and trunk in Japanese men and women. Age (Dordr) 36:813–821. doi:10.1007/s11357-013-9600-5
Adam A, de Luca CJ (2005) Firing rates of motor units in human vastus lateralis muscle during fatiguing isometric contractions. J Appl Physiol 99:268–280
Christie A, Kamen G (2010) Short-term training adaptations in maximal motor unit firing rates and afterhyperpolarization duration. Muscle Nerve 41:651–660. doi:10.1002/mus.21539
De Luca CJ, Hostage EC (2010) Relationship between firing rate and recruitment threshold of motoneurons in voluntary isometric contractions. J Neurophysiol 104:1034–1046
De Luca CJ, LeFever RS, McCue MP, Xenakis AP (1982) Behaviour of human motor units in different muscles during linearly varying contractions. J Physiol Lond 329:113–128
Deschenes MR (2004) Effects of aging on muscle fibre type and size. Sports Med 34:809–824
Erim Z, De Luca CJ, Mineo K, Aoki T (1996) Rank-ordered regulation of motor units. Muscle Nerve 19:563–573
Erim Z, Beg MF, Burke DT, de Luca CJ (1999) Effects of aging on motor-unit control properties. J Neurophysiol 82:2081–2091
Farina D, Enoka RM (2011) Surface EMG decomposition requires an appropriate validation. J Neurophysiol 105:981–982 . doi:10.1152/jn.00855.2010author reply 983-984
Farina D, Merletti R, Enoka RM (2004) The extraction of neural strategies from the surface. EMG J Appl Physiol 96:1486–1495
Farina D, Holobar A, Merletti R, Enoka RM (2010) Decoding the neural drive to muscles from the surface electromyogram. Clin Neurophysiol 121:1616–1623
Fuglevand AJ, Winter DA, Patla AE (1993) Models of recruitment and rate coding organization in motor-unit pools. J Neurophysiol 70:2470–2488
Gallego JA et al. (2015a) The phase difference between neural drives to antagonist muscles in essential tremor is associated with the relative strength of supraspinal and afferent input. J Neurosci 35:8925–8937. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0106-15.2015
Gallego JA et al. (2015b) Influence of common synaptic input to motor neurons on the neural drive to muscle in essential tremor. J Neurophysiol 113:182–191. doi:10.1152/jn.00531.2014
Holobar A, Farina D (2014) Blind source identification from the multichannel surface electromyogram. Physiol Meas 35:R143–R165. doi:10.1088/0967-3334/35/7/R143
Holobar A, Zazula D (2004) Correlation-based decomposition of surface electromyograms at low contraction forces. Med Biol Eng Comput 42:487–495
Holobar A, Zazula D (2008) On the selection of the cost function for gradient-based decomposition of surface electromyograms. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2008:4668–4671
Holobar A, Farina D, Gazzoni M, Merletti R, Zazula D (2009) Estimating motor unit discharge patterns from high-density surface electromyogram. Clin Neurophysiol 120:551–562
Holobar A, Glaser V, Gallego JA, Dideriksen JL, Farina D (2012) Non-invasive characterization of motor unit behaviour in pathological tremor. J Neural Eng 9:056011. doi:10.1088/1741-2560/9/5/056011
Holobar A, Minetto MA, Farina D (2014) Accurate identification of motor unit discharge patterns from high-density surface EMG and validation with a novel signal-based performance metric. J Neural Eng 11:016008
Hourigan ML, McKinnon NB, Johnson M, Rice CL, Stashuk DW, Doherty TJ (2015) Increased motor unit potential shape variability across consecutive motor unit discharges in the tibialis anterior and vastus medialis muscles of healthy older subjects. Clin Neurophysiol 126:2381–2389. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2015.02.002
Kamen G, Sison SV, Du CC, Patten C (1995) Motor unit discharge behavior in older adults during maximal-effort contractions. J Appl Physiol (1985) 79:1908–1913
Knight CA, Kamen G (2007) Modulation of motor unit firing rates during a complex sinusoidal force task in young and older adults. J Appl Physiol (1985) 102:122–129. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00455.2006
Knight CA, Kamen G (2008) Relationships between voluntary activation and motor unit firing rate during maximal voluntary contractions in young and older adults. Eur J Appl Physiol 103:625–630
Lexell J, Downham D, Sjostrom M (1986) Distribution of different fibre types in human skeletal muscles. Fibre type arrangement in m. vastus lateralis from three groups of healthy men between 15 and 83 years. J Neurol Sci 72:211–222
Ling SM, Conwit RA, Ferrucci L, Metter EJ (2009) Age-associated changes in motor unit physiology: observations from the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 90:1237–1240. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2008.09.565
Merletti R, Holobar A, Farina D (2008) Analysis of motor units with high-density surface electromyography. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 18:879–890
Minetto MA, Holobar A, Botter A, Farina D (2009) Discharge properties of motor units of the abductor hallucis muscle during cramp contractions. J Neurophysiol 102:1890–1901
Minetto MA, Holobar A, Botter A, Ravenni R, Farina D (2011) Mechanisms of cramp contractions: peripheral or central generation? J Physiol 589:5759–5773. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2011.212332
Minetto MA, Botter A, Sprager S, Agosti F, Patrizi A, Lanfranco F, Sartorio A (2013) Feasibility study of detecting surface electromyograms in severely obese patients. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 23:285–295. doi:10.1016/j.jelekin.2012.09.008
Mitchell WK, Williams J, Atherton P, Larvin M, Lund J, Narici M (2012) Sarcopenia, dynapenia, and the impact of advancing age on human skeletal muscle size and strength: a quantitative review. Front Physiol 3:260. doi:10.3389/fphys.2012.00260
Moritani T, deVries HA (1980) Potential for gross muscle hypertrophy in older men. J Gerontol 35:672–682
Moritani T, Muro M, Kijima A (1985) Electromechanical changes during electrically induced and maximal voluntary contractions: electrophysiologic responses of different muscle fiber types during stimulated contractions. Exp Neurol 88:471–483
Moritani T, Muramatsu S, Muro M (1987) Activity of motor units during concentric and eccentric contractions. Am J Phys Med 66:338–350
Narici MV, Bordini M, Cerretelli P (1991) Effect of aging on human adductor pollicis muscle function. J Appl Physiol (1985) 71:1277–1281
Nelson RM, Soderberg GL, Urbscheit NL (1983) Comparison of skeletal muscle motor unit discharge characteristics in young and aged humans. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 2:255–264
Nelson RM, Soderberg GL, Urbscheit NL (1984) Alteration of motor-unit discharge characteristics in aged humans. Phys Ther 64:29–34
Oya T, Riek S, Cresswell AG (2009) Recruitment and rate coding organisation for soleus motor units across entire range of voluntary isometric plantar flexions. J Physiol 587:4737–4748. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2009.175695
Patten C, Kamen G, Rowland DM (2001) Adaptations in maximal motor unit discharge rate to strength training in young and older adults. Muscle Nerve 24:542–550
Piasecki M, Ireland A, Stashuk D, Hamilton-Wright A, Jones DA, McPhee JS (2015) Age-related neuromuscular changes affecting human vastus lateralis. J Physiol. doi:10.1113/JP271087
Purves-Smith FM, Sgarioto N, Hepple RT (2014) Fiber typing in aging muscle. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 42:45–52. doi:10.1249/JES.0000000000000012
Roos MR, Rice CL, Vandervoort AA (1997) Age-related changes in motor unit function. Muscle Nerve 20:679–690
Roos MR, Rice CL, Connelly DM, Vandervoort AA (1999) Quadriceps muscle strength, contractile properties, and motor unit firing rates in young and old men. Muscle Nerve 22:1094–1103
Sjostrom M, Downham DY, Lexell J (1986) Distribution of different fiber types in human skeletal muscles: why is there a difference within a fascicle? Muscle Nerve 9:30–36
Soderberg GL, Minor SD, Nelson RM (1991) A comparison of motor unit behaviour in young and aged subjects. Age Ageing 20:8–15
Watanabe K, Akima H (2011) Validity of surface electromyography for vastus intermedius muscle assessed by needle electromyography. J Neurosci Methods 198:332–335
Watanabe K, Kouzaki M, Fujibayashi M, Merletti R, Moritani T (2012a) Spatial EMG potential distribution pattern of vastus lateralis muscle during isometric knee extension in young and elderly men. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 22:74–79
Watanabe K, Miyamoto T, Tanaka Y, Fukuda K, Moritani T (2012b) Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients manifest characteristic spatial EMG potential distribution pattern during sustained isometric contraction. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 97:468–473. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2012.03.004
Watanabe K, Gazzoni M, Holobar A, Miyamoto T, Fukuda K, Merletti R, Moritani T (2013) Motor unit firing pattern of vastus lateralis muscle in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Muscle Nerve 48:806–813
Welsh SJ, Dinenno DV, Tracy BL (2007) Variability of quadriceps femoris motor neuron discharge and muscle force in human aging. Exp Brain Res 179:219–233
Yavuz US, Negro F, Sebik O, Holobar A, Frommel C, Turker KS, Farina D (2015) Estimating reflex responses in large populations of motor units by decomposition of the high-density surface electromyogram. J Physiol 593:4305–4318. doi:10.1113/JP270635
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Japanese Council for Science, Technology and Innovation (CSTI), Cross-ministerial Strategic Innovation Promotion Program (SIP Project ID 14533567 Funding agency: Bio-oriented Technology Research Advancement Institution, NARO), by JSPS KAKENHI, a Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (B) (No. 26750309), and by the Slovenian Research Agency (No. L5-5550).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The subjects in both groups gave written informed consent for the study after receiving a detailed explanation of the purposes, potential benefits, and risks associated with participation. All procedures used in this study were approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Chukyo University (2014–001) and were in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
About this article
Cite this article
Watanabe, K., Holobar, A., Kouzaki, M. et al. Age-related changes in motor unit firing pattern of vastus lateralis muscle during low-moderate contraction. AGE 38, 48 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-016-9915-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-016-9915-0