Abstract
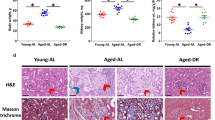
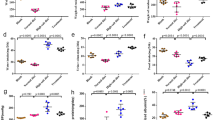
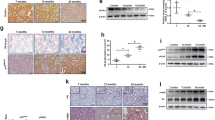
Aging is associated with replacement of normal kidney parenchyma by fibrosis. Because hydrogen sulfide (H2S) ameliorates kidney fibrosis in disease models, we examined its status in the aging kidney. In the first study, we examined kidney cortical H2S metabolism and signaling pathways related to synthesis of proteins including matrix proteins in young and old male C57BL/6 mice. In old mice, increase in renal cortical content of matrix protein involved in fibrosis was associated with decreased H2S generation and AMPK activity, and activation of insulin receptor (IR)/IRS-2-Akt-mTORC1-mRNA translation signaling axis that can lead to increase in protein synthesis. In the second study, we randomized 18–19 month-old male C57BL/6 mice to receive 30 μmol/L sodium hydrosulfide (NaHS) in drinking water vs. water alone (control) for 5 months. Administration of NaHS increased plasma free sulfide levels. NaHS inhibited the increase in kidney cortical content of matrix proteins involved in fibrosis and ameliorated glomerulosclerosis. NaHS restored AMPK activity and inhibited activation of IR/IRS-2-Akt-mTORC1-mRNA translation axis. NaHS inhibited age-related increase in kidney cortical content of p21, IL-1β, and IL-6, components of the senescence-associated secretory phenotype. NaHS abolished increase in urinary albumin excretion seen in control mice and reduced serum cystatin C levels suggesting improved glomerular clearance function. We conclude that aging-induced changes in the kidney are associated with H2S deficiency. Administration of H2S ameliorates aging-induced kidney changes probably by inhibiting signaling pathways leading to matrix protein synthesis.







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
28 January 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-021-00326-0
References
Abe K, Kimura H (1996) The possible role of hydrogen sulfide as an endogenous neuromodulator. J Neurosci 16(3):1066–1071
Acosta JC, Banito A, Wuestefeld T, Georgilis A, Janich P, Morton JP et al (2013) A complex secretory program orchestrated by the inflammasome controls paracrine senescence. Nat Cell Biol 15(8):978–990
Baar MP, Brandt RM, Putavet DA, Klein JD, Derks KW, Bourgeois BR et al (2017) Targeted apoptosis of senescent cells restores tissue homeostasis in response to chemotoxicity and aging. Cell 169(1):132–147 e116
Baker DJ, Childs BG, Durik M, Wijers ME, Sieben CJ, Zhong J et al (2016) Naturally occurring p16(Ink4a)-positive cells shorten healthy lifespan. Nature 530(7589):184–189
Barsha G, Denton KM, Mirabito Colafella KM (2016) Sex- and age-related differences in arterial pressure and albuminuria in mice. Biol Sex Differ 7:57
Bartke A, Sun LY, Longo V (2013) Somatotropic signaling: trade-offs between growth, reproductive development, and longevity. Physiol Rev 93(2):571–598
Bhandari BK, Feliers D, Duraisamy S, Stewart JL, Gingras AC, Abboud HE et al (2001) Insulin regulation of protein translation repressor 4E-BP1, an eIF4E-binding protein, in renal epithelial cells. Kidney Int 59(3):866–875
Bluher M, Kahn BB, Kahn CR (2003) Extended longevity in mice lacking the insulin receptor in adipose tissue. Science 299(5606):572–574
Bos EM, Wang R, Snijder PM, Boersema M, Damman J, Fu M et al (2013) Cystathionine gamma-lyase protects against renal ischemia/reperfusion by modulating oxidative stress. J Am Soc Nephrol 24(5):759–770
Childs BG, Durik M, Baker DJ, van Deursen JM (2015) Cellular senescence in aging and age-related disease: from mechanisms to therapy. Nat Med 21(12):1424–1435
Dugbartey GJ, Peppone LJ, de Graaf IA (2016) An integrative view of cisplatin-induced renal and cardiac toxicities: molecular mechanisms, current treatment challenges and potential protective measures. Toxicology 371:58–66
Eid AA, Ford BM, Block K, Kasinath BS, Gorin Y, Ghosh-Choudhury G et al (2010) AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) negatively regulates Nox4-dependent activation of p53 and epithelial cell apoptosis in diabetes. J Biol Chem 285(48):37503–37512
Feliers D, Lee HJ, Kasinath BS (2016) Hydrogen sulfide in renal physiology and disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 25(13):720–731
Ha TS, Barnes JL, Stewart JL, Ko CW, Miner JH, Abrahamson DR et al (1999) Regulation of renal laminin in mice with type II diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol 10(9):1931–1939
Hawley SA, Ross FA, Gowans GJ, Tibarewal P, Leslie NR, Hardie DG (2014) Phosphorylation by Akt within the ST loop of AMPK-alpha1 down-regulates its activation in tumour cells. Biochem J 459(2):275–287
Hine C, Harputlugil E, Zhang Y, Ruckenstuhl C, Lee BC, Brace L et al (2015) Endogenous hydrogen sulfide production is essential for dietary restriction benefits. Cell 160(1–2):132–144
Hodgin JB, Bitzer M, Wickman L, Afshinnia F, Wang SQ, O’Connor C et al (2015) Glomerular aging and focal global glomerulosclerosis: a podometric perspective. J Am Soc Nephrol 26(12):3162–3178
Holz MK, Ballif BA, Gygi SP, Blenis J (2005) mTOR and S6K1 mediate assembly of the translation preinitiation complex through dynamic protein interchange and ordered phosphorylation events. Cell 123(4):569–580
Hou CL, Wang MJ, Sun C, Huang Y, Jin S, Mu XP et al (2016) Protective effects of hydrogen sulfide in the ageing kidney. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2016:7570489
Iglesias-Bartolome R, Patel V, Cotrim A, Leelahavanichkul K, Molinolo AA, Mitchell JB, Gutkind JS (2012) mTOR inhibition prevents epithelial stem cell senescence and protects from radiation-induced mucositis. Cell Stem Cell 11(3):401–414
Kasinath BS, Feliers D, Sataranatarajan K, Ghosh Choudhury G, Lee MJ, Mariappan MM (2009) Regulation of mRNA translation in renal physiology and disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 297(5):F1153–F1165
Kume S, Uzu T, Horiike K, Chin-Kanasaki M, Isshiki K, Araki S et al (2010) Calorie restriction enhances cell adaptation to hypoxia through Sirt1-dependent mitochondrial autophagy in mouse aged kidney. J Clin Invest 120(4):1043–1055
Lee MJ, Feliers D, Mariappan MM, Sataranatarajan K, Mahimainathan L, Musi N et al (2007) A role for AMP-activated protein kinase in diabetes-induced renal hypertrophy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 292(2):F617–F627
Lee HJ, Mariappan MM, Feliers D, Cavaglieri RC, Sataranatarajan K, Abboud HE et al (2012) Hydrogen sulfide inhibits high glucose-induced matrix protein synthesis by activating AMP-activated protein kinase in renal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 287(7):4451–4461
Lee HJ, Feliers D, Mariappan MM, Sataranatarajan K, Choudhury GG, Gorin Y, Kasinath BS (2015) Tadalafil integrates nitric oxide-hydrogen sulfide signaling to inhibit high glucose-induced matrix protein synthesis in podocytes. J Biol Chem 290(19):12014–12026
Mariappan MM, Feliers D, Mummidi S, Choudhury GG, Kasinath BS (2007) High glucose, high insulin, and their combination rapidly induce laminin-beta1 synthesis by regulation of mRNA translation in renal epithelial cells. Diabetes 56(2):476–485
Miller DL, Roth MB (2007) Hydrogen sulfide increases thermotolerance and lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(51):20618–20622
Miller DL, Budde MW, Roth MB (2011) HIF-1 and SKN-1 coordinate the transcriptional response to hydrogen sulfide in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS One 6(9):e25476
Nelson G, Wordsworth J, Wang C, Jurk D, Lawless C, Martin-Ruiz C, von Zglinicki T (2012) A senescent cell bystander effect: senescence-induced senescence. Aging Cell 11(2):345–349
Paul BD, Snyder SH (2012) H(2)S signalling through protein sulfhydration and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13(8):499–507
Redpath NT, Foulstone EJ, Proud CG (1996) Regulation of translation elongation factor-2 by insulin via a rapamycin-sensitive signalling pathway. EMBO J 15(9):2291–2297
Roncal-Jimenez CA, Ishimoto T, Lanaspa MA, Milagres T, Hernando AA, Jensen T et al (2016) Aging-associated renal disease in mice is fructokinase dependent. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 311(4):F722–F730
Sancak Y, Thoreen CC, Peterson TR, Lindquist RA, Kang SA, Spooner E et al (2007) PRAS40 is an insulin-regulated inhibitor of the mTORC1 protein kinase. Mol Cell 25(6):903–915
Sataranatarajan K, Mariappan MM, Lee MJ, Feliers D, Choudhury GG, Barnes JL, Kasinath BS (2007) Regulation of elongation phase of mRNA translation in diabetic nephropathy: amelioration by rapamycin. Am J Pathol 171(6):1733–1742
Sataranatarajan K, Feliers D, Mariappan MM, Lee HJ, Lee MJ, Day RT et al (2012) Molecular events in matrix protein metabolism in the aging kidney. Aging Cell 11(6):1065–1073
Sataranatarajan K, Ikeno Y, Bokov A, Feliers D, Yalamanchili H, Lee HJ et al (2016) Rapamycin increases mortality in db/db mice, a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 71(7):850–857
Sen U, Pushpakumar S (2016) Mini-review: diabetic renal complications, a potential stinky remedy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 310(2):F119–F122
Sen U, Basu P, Abe OA, Givvimani S, Tyagi N, Metreveli N, Shah KS, Passmore JC, Tyagi SC (2009) Hydrogen sulfide ameliorates hyperhomocysteinemia-associated chronic renal failure. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 297(2):F410–F419
Sen U, Sathnur PB, Kundu S, Givvimani S, Coley DM, Mishra PK et al (2012) Increased endogenous H2S generation by CBS, CSE, and 3MST gene therapy improves ex vivo renovascular relaxation in hyperhomocysteinemia. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 303(1):C41–C51
Sharma K, Ramachandrarao S, Qiu G, Usui HK, Zhu Y, Dunn SR et al (2008) Adiponectin regulates albuminuria and podocyte function in mice. J Clin Invest 118(5):1645–1656
Shen X, Pattillo CB, Pardue S, Bir SC, Wang R, Kevil CG (2011) Measurement of plasma hydrogen sulfide in vivo and in vitro. Free Radic Biol Med 50(9):1021–1031
Song S, Meyer M, Turk TR, Wilde B, Feldkamp T, Assert R et al (2009) Serum cystatin C in mouse models: a reliable and precise marker for renal function and superior to serum creatinine. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24(4):1157–1161
Song K, Wang F, Li Q, Shi YB, Zheng HF, Peng H et al (2014) Hydrogen sulfide inhibits the renal fibrosis of obstructive nephropathy. Kidney Int 85(6):1318–1329
Sweetwyne MT, Pippin JW, Eng DG, Hudkins KL, Chiao YA, Campbell MD et al (2017) The mitochondrial-targeted peptide, SS-31, improves glomerular architecture in mice of advanced age. Kidney Int 91(5):1126–1145
Taguchi A, Wartschow LM, White MF (2007) Brain IRS2 signaling coordinates life span and nutrient homeostasis. Science 317(5836):369–372
van den Born JC, Hammes HP, Greffrath W, van Goor H, Hillebrands JL et al (2016) Gasotransmitters in vascular complications of diabetes. Diabetes 65(2):331–345
Wallace JL, Wang R (2015) Hydrogen sulfide-based therapeutics: exploiting a unique but ubiquitous gasotransmitter. Nat Rev Drug Discov 14(5):329–345
Wang R (2012) Shared signaling pathways among gasotransmitters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109(23):8801–8802
Wang R, Yu Z, Sunchu B, Shoaf J, Dang I, Zhao S et al (2017) Rapamycin inhibits the secretory phenotype of senescent cells by a Nrf2-independent mechanism. Aging Cell 16(3):564–574
Weber GJ, Pushpakumar SB, Sen U (2017) Hydrogen sulfide alleviates hypertensive kidney dysfunction through an epigenetic mechanism. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 312(5):H874–H885
Yang G, Wu L, Jiang B, Yang W, Qi J, Cao K et al (2008) H2S as a physiologic vasorelaxant: hypertension in mice with deletion of cystathionine gamma-lyase. Science 322(5901):587–590
Yuan P, Xue H, Zhou L, Qu L, Li C, Wang Z et al (2011) Rescue of mesangial cells from high glucose-induced over-proliferation and extracellular matrix secretion by hydrogen sulfide. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26(7):2119–2126
Zhou X, Feng Y, Zhan Z, Chen J (2014) Hydrogen sulfide alleviates diabetic nephropathy in a streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat model. J Biol Chem 289(42):28827–28834
Funding
A Pilot Study Grant to BSK from the Nathan Shock Center of Excellence in Basic Biology of Aging (NIH 1P30-AG013319) supported this work. This work was also supported by grants from the Veterans Affairs Biomedical Laboratory Research and Development Service (I01BX001340 to BSK, 5I01BX000926 to GGC, I01BX002211 to VG, II01BX001641 to RS) and the NIH (DK50190 to GGC, HL113303 to CGK, AG050797 to ABS). DF is supported by the American Heart Association (15GRNT25700363). GGC is a recipient of a Veterans Affairs Senior Research Career Scientist Award (IK6BX003611).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BSK, VG, JN, AS, and RS designed the study and analyzed the data. HJL, DF, SO, JB, and CK performed the experiments. All authors participated in data analysis and interpretation. BSK wrote the manuscript; all authors approved it.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The Institutional Animal Care and Utilization Committee of the University of Texas Health at San Antonio approved the animal studies.
Conflict of interest
CGK has intellectual property for hydrogen sulfide measurement and biomarker and also has equity interest in Innolyzer LLC and Theravasc Inc. J.L.B. is a consultant and co-founder of Probetex, Inc. with ownership interests. All other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PPTX 590 kb)
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, H.J., Feliers, D., Barnes, J.L. et al. Hydrogen sulfide ameliorates aging-associated changes in the kidney. GeroScience 40, 163–176 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-018-0018-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-018-0018-y