Abstract
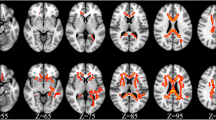
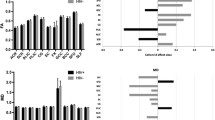
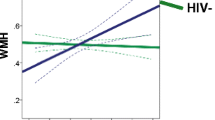
Chronic infection with HIV is associated with neuroinflammation. Prior diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) studies demonstrated increased mean diffusion (MD) and decreased fractional anisotropy (FA) in the white matter (WM) and subcortical brain regions of HIV patients. The current study aims to detect whether there are greater than age-related brain changes in HIV patients after a 1-year follow-up period using DTI. Thirty-nine antiretroviral-stable HIV subjects and 32 HIV-seronegative (SN) controls were evaluated, with neuropsychological tests and DTI, at baseline and after 1 year. MD and FA in the genu and splenium of the corpus callosum and in six other subcortical and white matter regions were evaluated bilaterally. Compared to SN controls, HIV subjects had significantly higher MD in the frontal WM (p = 0.0104) and lower FA in the parietal WM (p = 0.006). After 1 year, HIV subjects showed increase in MD in frontal and parietal WM, putamen, and genu; HIV subjects also showed greater increased genu diffusion than SN controls (p = 0.005). Changes in global cognitive deficit score correlated with changes in MD in the genu and FA in the parietal and frontal WM and putamen (multiple regression, p = 0.0008). Lastly, normal age-dependent changes in frontal WM diffusion and FA in genu and putamen were not observed in HIV subjects. Since increased MD may reflect increased neuroinflammation, our findings suggest greater than normal age-related inflammatory changes in the genu of these HIV patients, which may contribute to the cognitive deficits. Measurements of MD in the genu may be useful for monitoring disease progression in HIV brain infection.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson DC, Wildemann B, Sasaki M, Glass JD, McArthur JC, Christov VI et al (1996) Immunologic NO synthase: elevation in severe AIDS dementia and induction by HIV-1 gp41. Science 274:1917–1921 doi:10.1126/science.274.5294.1917
Banks WA, Ercal N, Price TO (2006) The blood–brain barrier in neuroAIDS. Curr HIV Res 4:259–266 doi:10.2174/157016206777709447
Bartzokis G, Tishler TA, Lu PH, Villablanca P, Altshuler LL, Carter M et al (2007) Brain ferritin iron may influence age- and gender-related risks of neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Aging 28:414–423 doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2006.02.005
Benedict RH, Bruce J, Dwyer MG, Weinstock-Guttman B, Tjoa C, Tavazzi E et al (2007) Diffusion-weighted imaging predicts cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 13:722–730 doi:10.1177/1352458507075592
Blair J, Spreen O (1989) The new adult reading test—Revised manual. University of Victoria, Vol Victoria, Canada
Brand A, Richter-Landsberg C, Leibfritz D (1993) Multinuclear NMR studies on the energy metabolism of glial and neuronal cells. Dev Neurosci 15:289–298 doi:10.1159/000111347
Chang L, Ernst T, Leonido-Yee M, Walot I, Singer E (1999a) Cerebral metabolite abnormalities correlate with clinical severity of HIV-cognitive motor complex. Neurology 52:100–108
Chang L, Ernst T, Leonido-Yee M, Witt M, Speck O, Walot I et al (1999b) Highly active antiretroviral therapy reverses brain metabolite abnormalities in mild HIV dementia. Neurology 53:782–789
Chang L, Ernst T, Witt M, Ames N, Jocivich J, Speck O et al (2002) Relationships among cerebral metabolites, cognitive function and viral loads in antiretroviral-naïve HIV patients. Neuroimage 17:1638–1648 doi:10.1006/nimg.2002.1254
Chang L, Tomasi D, Yakupov R, Lozar C, Arnold S, Caparelli E et al (2004) Adaptation of the attention network in human immunodeficiency virus brain injury. Ann Neurol 56:259–272 doi:10.1002/ana.20190
Chang L, Ernst T, Speck O, Grob C (2005) Additive effects of HIV and chronic methamphetamine use on brain metabolite abnormalities. Am J Psychiatry 162:361–369 doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.162.2.361
Chen ZG, Li TQ, Hindmarsh T (2001) Diffusion tensor trace mapping in normal adult brain using single-shot EPI technique. A methodological study of the aging brain. Acta Radiol 42:447–458 doi:10.1034/j.1600-0455.2001.420504.x
Cloak CC, Chang L, Ernst T (2004) Increased frontal white matter diffusion is associated with glial metabolites and psychomotor slowing in HIV. J Neuroimmunol 157:147–152 doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2004.08.043
Conant K, St Hillaire C, Anderson C, Galey D, Wang J, Nath A (2004) Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat and methamphetamine affect the release and activation of matrix-degrading proteinases. J Neurovirol 10:21–28 doi:10.1080/13550280490261699
Connolly NC, Riddler SA, Rinaldo CR (2005) Proinflammatory cytokines in HIV disease—a review and rationale for new therapeutic approaches. AIDS Rev 7:168–180
Dik MG, Jonker C, Hack CE, Smit JH, Comijs HC, Eikelenboom P (2005) Serum inflammatory proteins and cognitive decline in older persons. Neurology 64:1371–1377
El-Hage N, Wu G, Wang J, Ambati J, Knapp PE, Reed JL et al (2006) HIV-1 Tat and opiate-induced changes in astrocytes promote chemotaxis of microglia through the expression of MCP-1 and alternative chemokines. Glia 53:132–146 doi:10.1002/glia.20262
Ernst T, Chang L, Arnold S (2003) Increased glial markers predict increased working memory network activation in HIV patients. Neuroimage 19:1686–1693 doi:10.1016/S1053-8119(03)00232-5
Filippi C, Ulug A, Ryan E, Ferrando S, van Gorp W (2001) Diffusion tensor imaging of patients with HIV and normal-appearing white matter on MR images of the brain. Am J Neuroradiol 22:277–283
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) Mini-mental state: a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12:189–198 doi:10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6
Gemma C, Bickford PC (2007) Interleukin-1beta and caspase-1: players in the regulation of age-related cognitive dysfunction. Rev Neurosci 18:137–148
Hallgren B, Sourander P (1958) The effect of age on the non-haemin iron in the human brain. J Neurochem 3:41–51 doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.1958.tb12607.x
Hauser KF, El-Hage N, Stiene-Martin A, Maragos WF, Nath A, Persidsky Y et al (2007) HIV-1 neuropathogenesis: glial mechanisms revealed through substance abuse. J Neurochem 100:567–586 doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04227.x
Jernigan T, Gamst A, Archibald S, Fennema-Notestine C, Mindt M, Marcotte T et al (2005) Effects of methamphetamine dependence and HIV infection on cerebral morphology. Am J Psychiatry 162:1461–1472 doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.162.8.1461
Jiang H, van Zijl PC, Kim J, Pearlson GD, Mori S (2006) DtiStudio: resource program for diffusion tensor computation and fiber bundle tracking. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 81:106–116 doi:10.1016/j.cmpb.2005.08.004
Kraus MF, Susmaras T, Caughlin BP, Walker CJ, Sweeney JA, Little DM (2007) White matter integrity and cognition in chronic traumatic brain injury: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Brain 130:2508–2519 doi:10.1093/brain/awm216
Laubenberger J, Haussinger D, Bayer S, Thielemann S, Schneider B, Mundinger A et al (1996) HIV-related metabolic abnormalities in the brain: Depiction with proton MR spectroscopy with short echo times. Radiology 199:805–810
Nath A (2002) Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) proteins in neuropathogenesis of HIV dementia. J Infect Dis 186(Suppl 2):S193–S198 doi:10.1086/344528
Paul RH, Yiannoutsos CT, Miller EN, Chang L, Marra CM, Schifitto G et al (2007) Proton MRS and neuropsychological correlates in AIDS dementia complex: evidence of subcortical specificity. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 19(3):283–292 doi:10.1176/appi.neuropsych.19.3.283
Pfefferbaum A, Adalsteinsson E, Rohlfing T, Sullivan EV (2008) Diffusion tensor imaging of deep gray matter brain structures: Effects of age and iron concentration. Neurobiol Aging (May 28, Epub ahead of print)
Pfefferbaum A, Sullivan EV, Hedehus M, Lim KO, Adalsteinsson E, Moseley M (2000) Age-related decline in brain white matter anisotropy measured with spatially corrected echo-planar diffusion tensor imaging. Magn Reson Med 44:259–268 doi:10.1002/1522-2594(200008)44:2<259::AID-MRM13>3.0.CO;2-6
Pfefferbaum A, Rosenbloom MJ, Adalsteinsson E, Sullivan EV (2007) Diffusion tensor imaging with quantitative fibre tracking in HIV infection and alcoholism comorbidity: synergistic white matter damage. Brain 130:48–64 doi:10.1093/brain/awl242
Pomara N, Crandall D, Choi S, Johnson G, Lim K (2001) White matter abnormalities in HIV-1 infection: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Psychiatry Res 106:15–24 doi:10.1016/S0925-4927(00)00082-2
Power C, Johnson RT (1995) HIV-1 associated dementia: clinical features and pathogenesis. Can J Neurol Sci 22:92–100
Radloff LL (1977) The CES-D scale: a self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Appl Psychol Meas 1:385–401 doi:10.1177/014662167700100306
Ragin AB, Wu Y, Storey P, Cohen BA, Edelman RR, Epstein LG (2005) Diffusion tensor imaging of subcortical brain injury in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. J Neurovirol 11:292–298 doi:10.1080/13550280590953799
Ragin AB, Wu Y, Storey P, Cohen BA, Edelman RR, Epstein LG (2006) Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 correlates with subcortical brain injury in HIV infection. Neurology 66:1255–1257 doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000208433.34723.65
Raz N, Rodrigue KM, Kennedy KM, Head D, Gunning-Dixon F, Acker JD (2003) Differential aging of the human striatum: longitudinal evidence. Am J Neuroradiol 24:1849–1856
Simes RJ (1986) An improved Bonferroni procedure for multiple tests of significance. Biometrika 73:751–754 doi:10.1093/biomet/73.3.751
Steiner J, Haughey N, Li W, Venkatesan A, Anderson C, Reid R et al (2006) Oxidative stress and therapeutic approaches in HIV dementia. Antioxid Redox Signal 8:2089–2100 doi:10.1089/ars.2006.8.2089
Sullivan E, Pfefferbaum A (2003) Diffusion tensor imaging in normal aging and neuropsychiatric disorders. Eur J Radiol 45:244–255 doi:10.1016/S0720-048X(02)00313-3
Thurnher MM, Castillo M, Stadler A, Rieger A, Schmid B, Sundgren PC (2005) Diffusion-tensor MR imaging of the brain in human immunodeficiency virus-positive patients. Am J Neuroradiol 26:2275–2281
Woods SP, Rippeth JD, Frol AB, Levy JK, Ryan E, Soukup VM et al (2004) Interrater reliability of clinical ratings and neurocognitive diagnoses in HIV. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 26:759–778
Wu Y, Storey P, Cohen BA, Epstein LG, Edelman RR, Ragin AB (2006) Diffusion alterations in corpus callosum of patients with HIV. Am J Neuroradiol 27:656–660
Acknowledgements
We thank our research participants and support by the NIH (2R01MH61427; K24-DA16170; K02-DA16991; 5P20-RR11091; G12-RR003061) and the Office of National Drug Control Policy (ONDCP). We also thank Kenneth Yue, PhD; Daniel Alicata, MD, PhD; Renat Yakupov, MS; Grace Crocket, BA; and Caroline Jiang, MS, for their assistance in data collection or analyses.
Disclosure
Dr. Miller is the author and distributor of the CalCAP program and has a financial interest in this software.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, L., Wong, V., Nakama, H. et al. Greater Than Age-Related Changes in Brain Diffusion of HIV Patients After 1 Year. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 3, 265–274 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-008-9120-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-008-9120-8