Summary
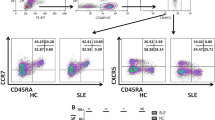
CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) and the expression of their molecular markers (GITR, Foxp3) in peripheral blood of the patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) were investigated in order to reveal the pathogenesis of SLE on the cellular and molecular levels. The level of Tregs in peripheral blood was detected by flow cytometry. The expression levels of GITR and Foxp3 mRNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were assayed by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). The level of IL-6 in the plasma was measured by ELISA. Comparisons were made among 3 groups: the active SLE group, the inactive SLE group, and normal control group. The level of Tregs in the active SLE group and the inactive SLE group was significantly lower than in the normal control group (P<0.01). The level of Tregs in the active group was lower than in the inactive group with the difference being not significant (P>0.05). The level of Tregs in SLE patients was significantly negatively correlated with the disease active index in SLE (SLEDAI) (r=−0.81, P<0.01). The expression levels of GITR mRNA in PBMCs of the active SLE group and the inactive SLE group were significantly higher than in the normal control group (P<0.05), and those of Foxp3 mRNA in SLE patients of both active and inactive SLE groups were significantly lower than in the normal control group (P<0.05). There was no significant difference in the expression of GITR and Foxp3 mRNA between the active SLE group and inactive SLE group (P>0.05). The plasma levels of IL-6 in both the inactive SLE group and active SLE group were significantly higher than in the normal control group (P<0.01). The plasma level of IL-6 in the active SLE group was significantly increased as compared with that in the inactive SLE group (P<0.05), and the plasma level of IL-6 in SLE was significantly positively correlated with SLEDAI scores (r=0.58, P<0.01) and significantly negatively correlated with the ratio of CD4+CD25+ cells/CD4+ cells (r=−0.389, P<0.05). It was concluded that the levels of Tregs and Foxp3 mRNA in peripheral blood of SLE patients were decreased and the levels of GITR mRNA and plasma IL-6 were increased. The Tregs and their molecular markers GITR, Foxp3 as well as the plasma IL-6 might play an important role in the pathogenesis of SLE.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crispin J C, Martinez A, Alcocer-Varela J. Quantification of regulatory T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Autoimmun, 2003,21(3):273–276
La Cava A, Fang C J, Singh R P et al. Manipulation of immune regulation in systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun Rev, 2005,4(8):515–519
Ye R G, Lu Z Y. Internal Medicine (Chinese). 6th ed. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2004,892.
Fehervari Z, Sakaguchi S. Development and function of CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells. Curr Opin Immunol, 2004,16(2):203–208
Gavin M, Rudensky A. Control of immune homeostasis by naturally arising regulatory CD4+ T cells. Curr Opin Immunol, 2003,15(6):690–696
Vasu C, Prabhakar B S, Holterman M J. Targeted CTLA-4 engagement induces CD4+CD25+ CTLA-4 high T regulatory cells with target (allo)antigen specificity. J Immunol, 2004,173(4):2866–2876
Shimizu J, Yamazaki S, Takahashi T et al. Stimulation of CD25(+)CD4(+) regulatory T cells through GITR breaks immunological self-tolerance. Nat Immunol, 2002,3(2):135–142
Nocentini G, Ronchetti S, Cuzzocrea S et al. GITR/GITRL: more than an effector T cell co-stimulatory system. Eur J Immunol, 2007,37(5):1165–1169
Esparza E M, Arch R H. Glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor functions as a costimulatory receptor that promotes survival in early phases of T cell activation. J Immunol, 2005,174(12):7869–7874
Fontenot J D, Rudensky A Y. A well adapted regulatory contrivance: regulatory T cell development and the fork-head family transcription factor Foxp3. Nat Immunol, 2005,6(4):331–337
Lee J, Wang L C, Lin Y T et al. Inverse correlation between CD4+ regulatory T-cell population and autoantibody levels in paediatric patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology, 2006,117(2):280–286
Doganci A, Sauer K, Karwot R et al. Pathological role of IL-6 in the experimental allergic bronchial asthma in mice. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol, 2005,28(3):257–270
Fehervari Z, Sakaguchi S. Control of Foxp3+CD25+CD4+ regulatory cell activation and function by dendritic cells. Int Immunol, 2004,16(12):1769–1780
Doganci A, Eigenbrod T, Krug N et al. The IL-6R alpha chain controls lung CD4+CD25+Treg development and function during allergic airway inflammation in vivo. J Clin Invest, 2005,115(2):313–325
Wan S, Xia C, Morel L et al. IL-6 produced by dendritic cells from lupus-prone mice inhibits CD4+CD25+ T cells regulatory functions. J Immunol, 2007,178(1): 271–279
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This project was supported by a grant from the Natural Sciences Foundation of Hubei, China (No. 2007ABA110).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, S., Xiao, W., Kong, F. et al. Regulatory T cells and their molecular markers in peripheral blood of the patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 28, 549–552 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-008-0513-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-008-0513-y