Summary
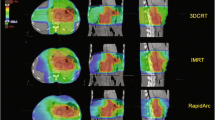
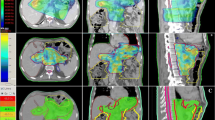
The purpose of this study was to compare the dose distribution of intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) in 7 and 5 fields as well as 3-D conformal radiotherapy (3D-CRT) plans for gastric cancer using dosimetric analysis. In 15 patients with gastric cancer after D1 resection, dosimetric parameters for IMRT (7 and 5 fields) and 3D-CRT were calculated with a total dose of 45 Gy (1.8 Gy/day). These parameters included the conformal index (CI), homogeneity index (HI), maximum dose spot for the planned target volume (PTV), dose-volume histogram (DVH) and dose distribution in the organs at risk (OAR), mean dose (Dmean), maximal dose (Dmax) in the spinal cord, percentage of the normal liver volume receiving more than 30 Gy (V30) and percentage of the normal kidney volume receiving more than 20 Gy (V20). IMRT (7 and 5 fields) and 3D-CRT achieved the PTV coverage. However, IMRT presented significantly higher CI and HI values and lower maximum dose spot distribution than 3D-CRT (P=0.001). For dose distribution of OAR, IMRT had a significantly lower Dmean and Dmax in spinal cord than 3D-CRT (P=0.009). There was no obvious difference in V30 of liver and V20 of kidney between IMRT and 3D-CRT, but 5-field IMRT showed lower Dmean in the normal liver than other two plans (P=0.001). IMRT revealed favorable tumor coverage as compared to 3D-CRT and IMRT plans. Specifically, 5-field IMRT plan was superior to 3D-CRT in protecting the spinal cord and liver, but this superiority was not observed in the kidney. Further studies are needed to compare differences among the three approaches.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sasako M, Sano T, Yamamoto S, et al. D2 lymphadenectomy alone or with para-aortic nodal dissection for gastric cancer. New Engl J Med, 2008,359(5):453–462
Maehara Y, Hasuda S, Koga T, et al. Postoperative outcome and sites of recurrence in patients following curative resection of gastric cancer. Br J Surg, 2000,87(3):353–357
Yoo C, Noh S, Shin D, et al. Recurrence following curative resection for gastric carcinoma. Br J Surg, 2000 87(2):236–242
De Manzoni G, Pedrazzani C, Pasini F, et al. Pattern of recurrence after surgery in adenocarcinoma of the gastrooesophageal junction. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2003,29(6):506–510
Van Cutsem E, Van de Velde C, Roth A, et al. Expert opinion on management of gastric and gastrooesophageal junction adenocarcinoma on behalf of the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC)-gastrointestinal cancer group. Eur J Cancer, 2008,44(2):182–194
Moehler M, Lyros O, Gockel I, et al. Multidisciplinary management of gastric and gastroesophageal cancers. World J Gastroenterol, 2008,14(24):3773
Macdonald JS, Smalley SR, Benedetti J, et al. Chemoradiotherapy after surgery compared with surgery alone for adenocarcinoma of the stomach or gastroesophageal junction. New Engl J Med, 2001,345(10):725–730
MacDonald J, Smalley S, Benedetti J, et al. SWOG; ECOG; RTOG; CALGB; NCCTG. Postoperative combined radiation and chemotherapy improves disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) in resected adenocarcinoma of the stomach and GE junction: update of the results of Intergroup Study INT-0116 (SWOG 9008). San Francisco, CA: ASCO, 2004
Kuo YC, Chiu YM, Shih WP, et al. Volumetric intensity-modulated Arc (RapidArc) therapy for primary hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison with intensity-modulated radiotherapy and 3-D conformal radiotherapy. Radiat Oncol, 2011,21(6):76
Hunt MA, Zelefsky MJ, Wolden S, et al. Treatment planning and delivery of intensity-modulated radiation therapy for primary nasopharynx cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2001,49(3):623–632
Chera BS, Rodriguez C, Morris CG, et al. Dosimetric comparison of three different involved nodal irradiation techniques for stage II Hodgkin’s lymphoma patients: conventional radiotherapy, intensity-modulated radiotherapy, and three-dimensional proton radiotherapy. Clin Occup Environ Med,2009,75(4):1173–1180
Hummel S, Simpson E, Hemingway P, et al. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy for the treatment of prostate cancer: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess, 2010,14(47):1–108
Egner JR. AJCC cancer staging manual. JAMA, 2010, 304(15):1726–1727
Matzinger O, Gerber E, Bernstein Z, et al. EORTC-ROG expert opinion: radiotherapy volume and treatment guidelines for neoadjuvant radiation of adenocarcinomas of the gastroesophageal junction and the stomach. Radiother Oncol, 2009,92(2):164–175
Cellini F, Valentini V, Pacelli F, et al. Preoperative radiotherapy in gastric cancer: CTV definition for conformal therapy according to tumor location. Rays, 2003,28(3):317
Knöös T, Kristensen I, Nilsson P. Volumetric and dosimetric evaluation of radiation treatment plans: radiation conformity index. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 1998, 42(5):1169–1176
Oh CE, Antes K, Darby M, et al. Comparison of 2D conventional, 3D conformal, and intensity-modulated treatment planning techniques for patients with prostate cancer with regard to target-dose homogeneity and dose to critical, uninvolved structures. Med Dosim, 1999,24(4):255–263
Bragg CM, Conway J, Robinson MH. The role of intensity-modulated radiotherapy in the treatment of parotid tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2002,52(3):729–738
Wu VW, Kwong DL, Sham JS. Target dose conformity in 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy and intensity modulated radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol, 2004,71(2):201–206
Dawson L. The evolving role of radiation therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer/Radiothérapie, 2008, 12(2):96–101
Baumann M, Budach V, Appold S. Radiation tolerance of the human spinal cord. Strahlenther Onkol, 1994,170(3):131–139
Emami B, Lyman J, Brown A, et al. Tolerance of normal tissue to therapeutic irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 1991,21(1):109–122
Jansen EP, Saunders MP, Boot H, et al. Prospective study on late renal toxicity following postoperative chemoradiotherapy in gastric cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2007,67(3):781–785
Lohr F, Dobler B, Mai S, et al. Optimization of dose distributions for adjuvant locoregional radiotherapy of gastric cancer by IMRT. Strahlenther Onkol, 2003,179(8):557–563
Minn AY, Hsu A, La T, et al. Comparison of intensity-modulated radiotherapy and 3-dimensional conformal radiotherapy as adjuvant therapy for gastric cancer. Cancer, 2010,116(16):3943–3952
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, H., Han, J., Zhang, T. et al. Comparison of dosiology between three dimensional conformal and intensity-modulated radiotherapies (5 and 7 fields) in gastric cancer post-surgery. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 33, 759–764 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-013-1193-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-013-1193-9