Abstract
Purpose
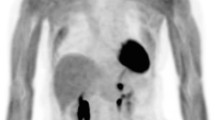
The aim of our study was to assess the feasibility and usefulness of 2-[18F]-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose positron emission tomography computed tomography ([18F]FDG-PET/CT) in patients affected by retroperitoneal fibrosis.
Materials and methods
We retrospectively evaluated 25 patients studied in two centers: 18 underwent [18F]FDG-PET/CT as initial evaluation, three during follow-up, three during steroid therapy, and one to re-evaluate the disease. Among the group who underwent initial evaluation, ten underwent a second [18F]FDG-PET/CT after steroid therapy.
Results
[18F]FDG-PET/CT was positive in 18 patients and negative in seven. Among the ten patients who underwent a second study after steroid therapy, six showed complete metabolic response, three partial response, and one no significant maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) reduction.
Conclusion
Our preliminary results show that [18F]FDG-PET/CT is feasible and suitable for evaluating retroperitoneal fibrosis and is useful in assessing therapy response. Larger studies are desirable to confirm these findings and to determine the appropriate position of [18F]FDG-PET/CT in the diagnostic flow chart for this disease.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van Bommel EFH. Retroperitoneal fibrosis. Neth J Med. 2002;60:231–42.
Vaglio A, Salvarani C, Buzio C. Retroperitoneal fibrosis. Lancet. 2006;367:241–51.
Van Bommel EFH, Jansen I, Hendriksz TR, Aarnoudse ALHJ. Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis: prospective evaluation of incidence and clinicoradiological presentation. Medicine. 2009;88:193–201.
Haug ES, Skomsvoll JF, Jacobsen G, Halvorsen TB, Saether OD, Myrhe HO. Inflammatory aortic aneurysm is associated with increased incidence of autoimmune disease. J Vasc Surg. 2003;38:492–7.
Vaglio A, Corradi D, Manenti L, Ferretti S, Garini G, Buzio C. Evidence of autoimmunity in chronic periaortitis: a prospective study. Am J Med. 2003;114:454–62.
Vega J, Goecke H, Tapia H, Labarca E, Santamarina M, Martinez G. Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis treatment with colchicines and steroids: a case series. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;53:628–37.
Swartz RD. Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis: a review of the pathogenesis and approaches to treatment. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;54:546–53.
Moroni G, Gallelli B, Banfi G, Sandri S, Messa P, Ponticelli C. Long-term outcome of idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis treated with surgical and/or medical approaches. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006;21:2485–90.
Marcolongo R, Tavolini IM, Lavender F, Busa M, Noventa F, Bassi P, et al. Immunosuppressive therapy for idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis: a retrospective analysis of 26 cases. Am J Med. 2004;116:194–7.
Warnatz K, Keskin AG, Uhl M, Scholz C, Katzenwadel A, Vaith P, et al. Immunosuppressive treatment of chronic periaortitis: a retrospective study of 20 patients with chronic periaortitis and a review of the literature. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64:828–33.
Maillart E, Laueriere L, Kassis S, Moulonquet-Doleris L, Prinseau, Baglin A, et al. Is there an evidencebased management of idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis? Rev Med Intern. 2006;27:854–7.
Kardar AH, Kattan S, Lindstedt E, Hanash K. Steroid therapy for idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis: dose and duration. J Urol. 2002;168:550–5.
Scheel PJ Jr, Piccini J, Rahman MH, Lawler L, Jarret T. Combined prednisone and mycophenolate mofetil treatment for retroperitoneal fibrosis. J Urol. 2007;178:140–3.
Van Bommel EF, Hendrisksz TR, Huiskes AW, Zeegers AG. Brief communication: tamoxifen therapy for nonmalignant retroperitoneal fibrosis. Ann Intern Med. 2006;144:101–6.
Di Chiro G, DeLaPaz RL, Brooks RA, Sokoloff L, Kornblith PL, Smith PH, et al. Glucose utilization of cerebral gliomas measured by 18FDG and PET. Neurology. 1982;32:1323–9.
Jabour BA, Choi Y, Hoh CK, Rege SD, Soong JC, Lufkin RB, et al. Extracranial head and neck: PET imaging with 18FDG and MR imaging correlation. Radiology. 1993;186:27–35.
Wilson CGJH. PET scanning in oncology. Eur J Cancer. 1992;28:508–10.
Strauss LG, Conti PS. The Application of PET in clinical oncology. J Nucl Med. 1991;32:623–48.
Kubota R, Yamada S, Kubota K, Ishiwata K, Tamahashi N, Ido T. Intratumoral distribution of FDG in vivo: high accumulation in macrophages and granulation tissue studied by microautoradiography. J Nucl Med. 1992;33:1972–80.
Ishimaru S, Tsujino I, Takei T, Tsukamoto E, Sakaue S, Kamigaki M, et al. Focal uptake on 18F-FDG PET images indicates cardiac involvement of sarcoidosis. Eur Heart J. 2005;26:1538–43.
El-Haddad G, Zhuang H, Gupta N, Alavi A. Evolving role of positron emission tomography in the management of patients with inflammatory and other benign disorders. Semin Nucl Med. 2004;34:313–29.
Bhargava P, Kumar R, Zhuang H, Charron M, Alavi A. Catheter-related focal FDG activity on whole body PET imaging. Clin Nucl Med. 2004;29:238–42.
Bertagna F, Giubbini R, Biasiotto G, Rosenbaum J, Alavi A. Incidental inflammatory findings in nerves and in patients with neoplastic diseases evaluated by 18F-FDG-PET/CT. Hell J Nucl Med. 2009;12:279–80.
Bertagna F, Bosio G, Caobelli F, Motta F, Biasiotto G, Giubbini R. Role of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography for therapy evaluation of patients with large-vessel vasculitis. Jpn J Radiol. 2010;28:199–204.
Bertagna F, Pizzocaro C, Biasiotto G, Giubbini R, Werner T, Alavi A. (18)F-FDG-PET/CT findings in patients affected by spondylodiscitis. Hell J Nucl Med. 2010;13:166–8.
Parums DV. The spectrum of chronic periaortitis. Histopathology. 1990;16:423–31.
Gilkeson GS, Allen NB. Retroperitoneal fibrosis: a true connective tissue disease. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1996;22:23–38.
Mitchinson MJ. Chronic periaortitis and periarteritis. Histopathology. 1984;8:589–600.
Vaglio A, Greco P, Versari A, Felica A, Cobelli R, Manenti L, et al. Post-treatment residual tissue in idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis: active residual disease or silent “scar”? A study using 18 F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography. Clin Exp Rheum. 2005;23:231–4.
Nakajo M, Jinnouchi S, Tanabe H, Tateno R, Nakajo M. 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography features of idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2007;31:539–43.
Vivas I, Nicolas AI, Velazquez P, Elduayen B, Fernandez-Villa T, Martinez-Cuesta A. Retroperitoneal fibrosis: typical and atypical manifestations. Br J Radiol. 2000;73:214–22.
Cronin CG, Lohan DG, Blake MA, Roche C, McCurty P, Murphy JM. Retroperitoneal fibrosis: a review of clinical features and imaging findings. Am J Roentgenol. 2008;191:423.
Ilie CP, Pemberton RJ, Tolley DA. Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis: the case for nonsurgical treatment. BJU Int. 2006;98:137–40.
Talati SJ, Abghari R, Kochkodan JJ, Helmer SR. Use of Ga-67 imaging in diagnosis and follow-up after steroid treatment of retroperitoneal fibrosis. Clin Nucl Med. 1995;20:995–7.
Tomita Y, Morishita H, Saitoh R. Successful treatment of idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis with steroid administration in a patient with a positive gallium scan. Clin Nucl Med. 1993;18:1042–4.
Leibowich S, Tumeh SS. Gallium-67 imaging and computed tomography in early retroperitoneal fibrosis. Clin Nucl Med. 1988;13:829–30.
Zhang W, Zhang Y. Tc-99 m MDP uptake in retroperitoneal fibrosis. Clin Nucl Med. 2009;34:189–90.
Drieskens O, Blockmans D, Van den Bruel A, Mortelmans L. Riedel’s thyroiditis and retroperitoneal fibrosis in multifocal fibrosclerosis: positron emission tomographic findings. Clin Nucl Med. 2002;27:413–5.
Nakajo M, Jinnouchi S, Noguchi M, Uozumi K, Tanabe H, Tateno R, et al. FDG PET and PET/CT monitoring of autoimmune pancreatitis associated with extrapancreatic autoimmune disease. Clin Nucl Med. 2007;32:282–5.
Agrawal A, Nair N, Baghel N. F-18 FDG PET in Ormond disease in a patient with renal cell carcinoma. Clin Nucl Med. 2007;32:320–2.
Takahashi M, Momose T, Kameyama M, Ohtomo K. Abnormal accumulation of [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose in the aortic wall related to inflammatory changes: three case reports. Ann Nucl Med. 2006;20:361–4.
Otsuka H, Morita N, Yamashita K, Nishitani H. FDG-PET/CT findings of autoimmune pancreatitis associated with idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis. Ann Nucl Med. 2007;21:593–6.
Nakajo M, Jinnouchi S, Fukukura Y, Tanabe H, Tateno R, Nakajo M. The efficacy of whole-body FDG-PET or PET/CT for autoimmune pancreatitis and associated extrapancreatic autoimmune lesions. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2007;34:2088–95.
Treglia G, Mattoli MV, Leccisotti L, Ferraccioli G, Giordano A. Usefulness of whole-body fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in patients with large-vessel vasculitis: a systematic review. Clin Rheumatol. 2011;30:1265–75.
Swartz R, Lake A, Roberts W, Faerber GJ, Wolf JS Jr. Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis: a role for mycophenolate mofetil. Clin Nephrol. 2008;65:260–8.
Dash R, Liu K, Sheafor D, Dodd L. Fine-needle aspiration findings in idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis. Diagn Cytopathol. 1999;21:22–6.
Jones J, Ross E, Matz L, Edwards D, Davies DR. Retroperitoneal fibrosis. Am J Med. 1970;48:203–8.
Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, Eishi Y, Koike M, Tsuruda K, et al. A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J Gastroenterol. 2003;38:982–4.
Corradi D, Maestri R, Palmisano A, Bosio S, Greco P, Manenti L, et al. Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis: clinicopathologic features and differential diagnosis. Kidney Int. 2007;72:742–53.
Nelid G, Rodriguez-Justo M, Wall C, Connolly J. Hyper-IgG4 disease: report and characterization of a new disease. BMC Med. 2006;4:23–35.
Saeki T, Nishi S, Ito T, Yamazaki H, Miyamura S, Emura I, et al. Renal lesions in IgG4-related systemic disease. Intern Med. 2007;46:1365–71.
Kamisawa T, Okamoto A, Wakabayashi T, Watanabe H, Sawabu N. Appropriate steroid therapy for autoimmune pancreatitis based on long-term outcome. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2008;43:609–13.
Jansen I, Hendriksz TR, Han SH, Huiskes AW, van Bommel EF. (18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose position emission tomography (FDG-PET) for monitoring disease activity and treatment response in idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis. Eur J Intern Med. 2010;21:216–21.
Piccoli GB, Consiglio V, Arena V, Pelosi E, Anastasios D, Ragni F, et al. Positron emission tomography as a tool for the ‘tailored’ management of retroperitoneal fibrosis: a nephro-urological experience. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010;25:2603–10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Bertagna, F., Treglia, G., Leccisotti, L. et al. [18F]FDG-PET/CT in patients affected by retroperitoneal fibrosis: a bicentric experience. Jpn J Radiol 30, 415–421 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-012-0066-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-012-0066-7