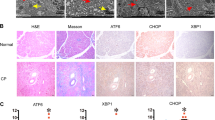
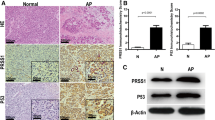
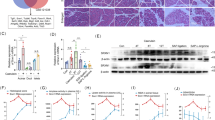
Abstract
Chronic endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in pancreatic acinar cells has emerged as a major contributor to the recovery of acute pancreatitis (AP). However, the molecular mechanisms linking AP and ER stress remain not fully understood. In this study, we employed caerulein to induce AP-like inflammation in the AR42J rat pancreatic acinar cells to mimic the AP-like acinar cell injury. Caerulein can activate ER stress in AR42J cells, but the molecular link between AP and ER stress remains to be identified. We here reported that translocating chain-associated membrane protein 1 (TRAM1), an ER-resident multispanning membrane protein, was involved in the onset of AP-like injury on AR42J cells. TRAM1 was significantly elevated in caerulein-treated AR42J cells. Furthermore, we showed that knockdown of TRAM1 led to hyperactivation of 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein precursor (GRP78) and C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) and the activation of downstream apoptosis pathway. Given the fact that the activation of ER stress played a protection role in AP, the pro-inflammatory mediators TNF-α and IL-6 and the marker of cell injury LDH were also analyzed. We found that depletion of TRAM1 markedly increased the secretion of TNF-α, IL-6, and LDH in the cells. Moreover, flow cytometry indicated that treatment with caerulein induced a significant decrease of apoptotic index and increase of necrosis index in TRAM1-siRNA cells, compared with control groups, as indicated by downregulated expression of cleaved caspase-3, caspase-8, and caspase-9 mRNA expression activity in TRAM1-siRNA cells. These data implicated that TRAM1 might protect AR42J cells against caerulein-induced AP in AR42J cells through alleviating ER stress.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feng N, Ma X, Wei X, Zhang J, Dong A, Jin M, Zhang H, Guo X (2014) Common variants in PERK, JNK, BIP and XBP1 genes are associated with the risk of prediabetes or diabetes-related phenotypes in a Chinese population. Chin Med J (Engl) 127:2438–2444
He S, Wang L, Miao L, Wang T, Du F, Zhao L, Wang X (2009) Receptor interacting protein kinase-3 determines cellular necrotic response to TNF-alpha. Cell 137:1100–1111
Hoque R, Farooq A, Ghani A, Gorelick F, Mehal WZ (2014) Lactate reduces liver and pancreatic injury in Toll-like receptor- and inflammasome-mediated inflammation via GPR81-mediated suppression of innate immunity. Gastroenterology 146:1763–1774
Kagan JC, Su T, Horng T, Chow A, Akira S, Medzhitov R (2008) TRAM couples endocytosis of Toll-like receptor 4 to the induction of interferon-beta. Nat Immunol 9:361–368
Kaufmann A, Rossler OG, Thiel G (2014) Expression of the transcription factor Egr-1 in pancreatic acinar cells following stimulation of cholecystokinin or Galphaq-coupled designer receptors. Cell Physiol Biochem Int J Exp Cell Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 33:1411–1425
Liu Y, Yang L, Chen KL, Zhou B, Yan H, Zhou ZG, Li Y (2014) Knockdown of GRP78 promotes apoptosis in pancreatic acinar cells and attenuates the severity of cerulein and LPS induced pancreatic inflammation. PLoS One 9:e92389
Mareninova OA, Hermann K, French SW, O’Konski MS, Pandol SJ, Webster P, Erickson AH, Katunuma N, Gorelick FS, Gukovsky I, Gukovskaya AS (2009) Impaired autophagic flux mediates acinar cell vacuole formation and trypsinogen activation in rodent models of acute pancreatitis. J Clin Invest 119:3340–3355
Mashima H, Ohnishi H (2014) The mechanism of the onset of acute pancreatitis. Jpn J Gastroenterol 111:1550–1560
Muili KA, Jin S, Orabi AI, Eisses JF, Javed TA, Le T, Bottino R, Jayaraman T, Husain SZ (2013) Pancreatic acinar cell nuclear factor kappaB activation because of bile acid exposure is dependent on calcineurin. J Biol Chem 288:21065–21073
Ng CL, Oresic K, Tortorella D (2010) TRAM1 is involved in disposal of ER membrane degradation substrates. Exp Cell Res 316:2113–2122
Noel P, Patel K, Durgampudi C, Trivedi RN, de Oliveira C, Crowell MD, Pannala R, Lee K, Brand R, Chennat J, Slivka A, Papachristou GI, Khalid A, Whitcomb DC, DeLany JP, Cline RA, Acharya C, Jaligama D, Murad FM, Yadav D, Navina S, Singh VP (2014) Peripancreatic fat necrosis worsens acute pancreatitis independent of pancreatic necrosis via unsaturated fatty acids increased in human pancreatic necrosis collections. Gut
Oresic K, Ng CL, Tortorella D (2009) TRAM1 participates in human cytomegalovirus US2- and US11-mediated dislocation of an endoplasmic reticulum membrane glycoprotein. J Biol Chem 284:5905–5914
Sah RP, Garg SK, Dixit AK, Dudeja V, Dawra RK, Saluja AK (2014) Endoplasmic reticulum stress is chronically activated in chronic pancreatitis. J Biol Chem 289:27551–27561
Schepers NJ, Besselink MG, van Santvoort HC, Bakker OJ, Bruno MJ, Dutch Pancreatitis Study, Group (2013) Early management of acute pancreatitis. Best Prac Res Clin Gastroenterol 27:727–743
Szmola R, Sahin-Toth M (2010) Pancreatitis-associated chymotrypsinogen C (CTRC) mutant elicits endoplasmic reticulum stress in pancreatic acinar cells. Gut 59:365–372
Tang Z, Zhang W, Wan C, Xu G, Nie X, Zhu X, Xia N, Zhao Y, Wang S, Cui S, Wang C (2015) TRAM1 protect HepG2 cells from palmitate induced insulin resistance through ER stress-JNK pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 457:578–584
Wang J, Chen G, Gong H, Huang W, Long D, Tang W (2012) Amelioration of experimental acute pancreatitis with Dachengqi Decoction via regulation of necrosis-apoptosis switch in the pancreatic acinar cell. PLoS One 7:e40160
Wang YZ, Zhang YC, Cheng JS, Ni Q, Li PW, Han W, Zhang YL (2014) Protective effects of BML-111 on cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis-associated lung injury via activation of Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. Inflammation 37:1120–1133
Wu L, Cai B, Liu X, Cai H (2014) Emodin attenuates calcium overload and endoplasmic reticulum stress in AR42J rat pancreatic acinar cells. Mol Med Rep 9:267–272
Wu L, Cai B, Zheng S, Liu X, Cai H, Li H (2013) Effect of emodin on endoplasmic reticulum stress in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Inflammation 36:1020–1029
Yinchu Z, Feng Z, Yinsheng S, Fengqing W, Xiaoyang Z, Jin L, Xiaofei G (2015) Potential effects of calcium binding protein S100A12 on severity evaluation and curative effect of severe acute pancreatitis. Inflammation 38:290–297
Zeng Y, Wang X, Zhang W, Wu K, Ma J (2012) Hypertriglyceridemia aggravates ER stress and pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis. Hepatogastroenterology 59:2318–2326
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, No. 2012CB822104), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31500647, 31170766, 81470806), the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (15KJA310003); the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20150408); the ‘Top Six Types of Talents’ Financial Assistance of Jiangsu Province Grant (2015-YY-009), and a project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editor: Tetsuji Okamoto
Yongxia Cai and Yanbo Shen contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, Y., Shen, Y., Xu, G. et al. TRAM1 protects AR42J cells from caerulein-induced acute pancreatitis through ER stress-apoptosis pathway. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 52, 530–536 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-016-0011-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-016-0011-7