Abstract
Summary
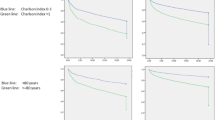
Despite orthogeriatric management, 12% of the elderly experienced PUs after hip fracture surgery. PUs were significantly associated with a low albumin level, history of atrial fibrillation coronary artery disease, and diabetes. The risk ratio of death at 6 months associated with pressure ulcer was 2.38 (95% CI 1.31–4.32%, p = 0.044).
Introduction
Pressure ulcers in hip fracture patients are frequent and associated with a poor outcome. An orthogeriatric management, recommended by international guidelines in hip fracture patients and including pressure ulcer prevention and treatment, could influence causes and consequences of pressure ulcer. However, remaining factors associated with pressure ulcer occurrence and prognostic value of pressure ulcer in hip fracture patients managed in an orthogeriatric care pathway remain unknown.
Methods
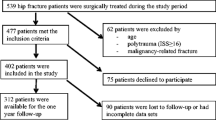
From June 2009 to April 2015, all consecutive patients with hip fracture admitted to a unit for Post-operative geriatric care were evaluated for eligibility. Patients were included if their primary presentation was due to hip fracture and if they were ≥ 70 years of age. Patients were excluded in the presence of pathological fracture or if they were already hospitalized at the time of the fracture. In our unit, orthogeriatric principles are implemented, including a multi-component intervention to improve pressure ulcer prevention and management. Patients were followed-up until 6 months after discharge.
Results
Five hundred sixty-seven patients were included, with an overall 14.4% 6-month mortality (95% CI 11.6–17.8%). Of these, 67 patients (12%) experienced at least one pressure ulcer. Despite orthogeriatric management, pressure ulcers were significantly associated with a low albumin level (RR 0.90, 95% CI 0.84–0.96; p = 0.003) and history of atrial fibrillation (RR 1.91, 95% CI 1.05–3.46; p = 0.033), coronary artery disease (RR 2.16, 95% CI 1.17–3.99; p = 0.014), and diabetes (RR 2.33, 95% CI 1.14–4.75; p = 0.02). A pressure ulcer was associated with 6-month mortality (RR 2.38, 95% CI 1.31–4.32, p = 0.044).
Conclusion
In elderly patients with hip fracture managed in an orthogeriatric care pathway, pressure ulcer remained associated with poorly modifiable risk factors and long-term mortality.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johnell O, Kanis JA (2006) An estimate of the worldwide prevalence and disability associated with osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporosis Int 17:1726–1733
Kanis JA, Oden A, McCloskey H et al (2012) A systematic review of hip fracture incidence and probability of fracture worldwide. Osteoporos Int 23:2239–2256
Karampampa K, Ahlbom A, Michaelsson K et al (2015) Declining incidence trends for hip fractures have not been accompanied by improvements in lifetime risk or post-fracture survival—a nationwide study of the Swedish population 60 years and older. Bone 78:55–61
Brauer CA, Coco-Perraillon M, Cutler DM et al (2009) Incidence and mortality of hip fractures in the United States. J Am Med Assoc 302:1573–1579
Le Manach Y, Collins G, Bhandari M et al (2015) Outcomes after hip fracture surgery compared with elective total hip replacement. JAMA 314(11):1159–1166
Penrod JD, Litke A, Hawkes WG et al (2008) The association of race, gender, and comorbidity with mortality and function after hip fracture. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 63(8):867–872
Ireland AW, Kelly PJ, Cumming RG (2015) Total hospital stay for hip fracture: measuring the variations due to pre-fracture residence, rehabilitation, complications and comorbidities. BMC Health Serv Res 15:17
Barrois B, Labalette C, Rousseau P et al (2008) A national prevalence study of pressure ulcers in French hospital inpatients. J Wound Care 17(9):373–378
Khor HM, Tan J, Saedon NI et al (2014) Determinants of mortality among older adults with pressure ulcers. Arch Gerontol Geriat 59(3):536–541
VanGilder C, Amlung S, Harrison P et al (2009) Results of the 2008–2009 international pressure ulcer prevalence survey and a 3 year, acute care, unit-specific analysis. Ostomy Wound Manage 55:39–45
Thompson D (2005) A critical review of the literature on pressure ulcer aetiology. J Wound Care 14:87–90
Baumgarten M, Margolis DJ, Orwig DL et al (2009) Pressure ulcers in elderly patients with hip fracture across the continuum of care. J Am Geriatr Soc 57(5):863–870
Ireland AW, Kelly PJ, Cumming RG (2015) Risk factor profiles for early and delayed mortality after hip fracture: analyses of linked Australian Department of Veterans. Affairs databases. Injury 46(6):1028–1035
Kammerlander C, Roth T, Friedman SM et al (2010) Ortho-geriatric service a literature review comparing different models. Osteoporos Int 21(suppl 4):S637–S646
Prestmo A, Hagen G, Sletvold O et al (2015) Comprehensive geriatric care for patients with hip fractures: a prospective, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet 385(9978):1623–1633
Tschannen D, Bates O, Talsma A et al (2012) Patient specific and surgical characteristics in the development of pressure ulcers. Am J Crit Care 21:116–125
Boddaert J, Cohen-Bittan J, Khiami F et al (2014) Postoperative admission to a dedicated geriatric unit decreases mortality in elderly patients with hip fracture. PLoS One 9(1):e83795
Langer G, Fink A (2014) Nutritional interventions for preventing and treating pressure ulcers. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 6:CD003216
Tian M, Gong X, Rath S et al (2016) Management of hip fractures in older people in Beijing: a retrospective audit and comparison with evidence-based guidelines and practice in the UK. Osteoporos Int 27(2):677–681
The National Hip Fracture Database (2012) National Report 2012. (online). Available at :www.nhfd.co.uk. Accessed 15 Sept 2015
Vidan M, Serra JA, Moreno C et al (2005) Efficacy of a comprehensive geriatric intervention in older patients hospitalized for hip fracture: a randomized, controlled trial. J Am Geriatr Soc 53:1476–1482
Moja L, Piatti A, Pecoraro V et al (2012) Timing matters in hip fracture surgery: patients operated within 48 hours have better outcomes. A meta-analysis and meta-regression of over 190 000 patients. PLoS One 7(10):e46175
Qaseem A, Mir TP, Starkey M et al (2015) Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Risk assessment and prevention of pressure ulcers: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med 162(5):359–369
Delmi M, Rapin CH, Bengoa JM et al (1990) Dietary supplementation in elderly patients with fractured neck of the femur. Lancet 335(8696):1013–1016
Uriz-Otano F, Uriz-Otano JI, Malafarina V (2016) Factors associated with short-term functional recovery in elderly people with a hip fracture. Influence of cognitive impairment. J Am Med Dir Assoc 16(3):215–220
Freeman C, Todd C, Camilleri-Ferrante C et al (2002) Quality improvement for patients with hip fracture: experience from a multi-site audit. Qual Saf Health Care 11(3):239–245
Lefaivre KA, Macadam SA, Davidson DJ et al (2009) Length of stay, mortality, morbidity and delay to surgery in hip fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br 91:922–927
Baumgarten M, Rich SE, Shardell MD et al (2012) Care-related risk factors for hospital- acquired pressure ulcers in elderly adults with hip fracture. J Am Geriatr Soc 60:277–283
Lindholm C, Sterner E, Romanelli M et al (2008) Hip fracture and pressure ulcers—the Pan-European pressure ulcer study—intrinsic and extrinsic risk factors. Int Wound J 5:315–328
Myers AH, Robinson EG, Van Natta ML et al (1991) Hip fracture among the elderly: factors associated with in-hospital mortality. Am J Epidemiol 134(10):1128–1137
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Magny, E., Vallet, H., Cohen-Bittan, J. et al. Pressure ulcers are associated with 6-month mortality in elderly patients with hip fracture managed in orthogeriatric care pathway. Arch Osteoporos 12, 77 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11657-017-0365-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11657-017-0365-9