Abstract
Objective
The purpose of this investigation was to determine whether there is an association between the putative reading disability (RD) susceptibility gene Doublecortin Domain Containing 2 (DCDC2), and gray matter (GM) distribution in the brain, in a sample of healthy control individuals.
Method
Fifty-six control subjects were genotyped for an RD-associated deletion in intron 2 of DCDC2. Voxel based morphometry (VBM) was used to examine structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans to assess GM differences between the two groups.
Results
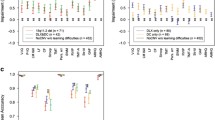
Individuals heterozygous for the deletion exhibited significantly higher GM volumes in reading/language and symbol-decoding related brain regions including superior, medial and inferior temporal, fusiform, hippocampal/parahippocampal, inferior occipito-parietal, inferior and middle frontal gyri, especially in the left hemisphere. GM values correlated with published data on regional DCDC2 expression in a lateralized manner.
Conclusions
These data suggest a role for DCDC2 in GM distribution in language-related brain regions in healthy individuals.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aylward, E. H., Richards, T. L., Berninger, V. W., Nagy, W. E., Field, K. M., Grimme, A. C., et al. (2003). Instructional treatment associated with changes in brain activation in children with dyslexia. Neurology, 61(2), 212–219.
Brambati, S. M., Termine, C., Ruffino, M., Danna, M., Lanzi, G., Stella, G., et al. (2006). Neuropsychological deficits and neural dysfunction in familial dyslexia. Brain Research, 1113(1), 174–185.
Brambati, S. M., Termine, C., Ruffino, M., Stella, G., Fazio, F., Cappa, S. F., et al. (2004). Regional reductions of gray matter volume in familial dyslexia. Neurology, 63(4), 742–745.
Brown, W. E., Eliez, S., Menon, V., Rumsey, J. M., White, C. D., & Reiss, A. L. (2001). Preliminary evidence of widespread morphological variations of the brain in dyslexia. Neurology, 56(6), 781–783.
Cao, F., Bitan, T., Chou, T. L., Burman, D. D., & Booth, J. R. (2006). Deficient orthographic and phonological representations in children with dyslexia revealed by brain activation patterns. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 47(10), 1041–1050.
Casanova, M. F., Christensen, J. D., Giedd, J., Rumsey, J. M., Garver, D. L., & Postel, G. C. (2005). Magnetic resonance imaging study of brain asymmetries in dyslexic patients. Journal of Child Neurology, 20(10), 842–847.
DeFries, J. C., Fulker, D. W., & LaBuda, M. C. (1987). Evidence for a genetic aetiology in reading disability of twins. Nature, 329(6139), 537–539.
Eckert, M. A., Leonard, C. M., Richards, T. L., Aylward, E. H., Thomson, J., & Berninger, V. W. (2003). Anatomical correlates of dyslexia: Frontal and cerebellar findings. Brain, 126(2), 482–494.
Eliez, S., Rumsey, J. M., Giedd, J. N., Schmitt, J. E., Patwardhan, A. J., & Reiss, A. L. (2000). Morphological alteration of temporal lobe gray matter in dyslexia: An MRI study. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 41(5), 637–644.
Good, C. D., Johnsrude, I. S., Ashburner, J., Henson, R. N., Friston, K. J., & Frackowiak, R. S. (2001). A voxel-based morphometric study of ageing in 465 normal adult human brains. Neuroimage, 14(1 Pt 1), 21–36.
Harold, D., Paracchini, S., Scerri, T., Dennis, M., Cope, N., Hill, G., et al. (2006). Further evidence that the KIAA0319 gene confers susceptibility to developmental dyslexia. Molecular Psychiatry, 11, 1085–1091 1061.
Hayasaka, S., Phan, K. L., Liberzon, I., Worsley, K. J., & Nichols, T. E. (2004). Nonstationary cluster-size inference with random field and permutation methods. Neuroimage, 22, 676–687.
Holland, S. K., Plante, E., Weber Byars, A., Strawsburg, R. H., Schmithorst, V. J., & Ball Jr., W. S. (2001). Normal fMRI brain activation patterns in children performing a verb generation task. Neuroimage, 14(4), 837–843.
Kronbichler, M., Wimmer, H., Staffen, W., Hutzler, F., Mair, A., & Ladurner, G. (2007). Developmental dyslexia: Gray matter abnormalities in the occipitotemporal cortex. Human Brain Mapping.
Meng, H., Smith, S. D., Hager, K., Held, M., Liu, J., Olson, R. K., et al. (2005). DCDC2 is associated with reading disability and modulates neuronal development in the brain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(47), 17053–17058.
Paracchini, S., Scerri, T., & Monaco, A. P. (2007). The genetic lexicon of dyslexia. Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics, 8(1), 57.
Raskind, W. H., Hsu, L., Berninger, V. W., Thomson, J. B., & Wijsman, E. M. (2000). Familial aggregation of dyslexia phenotypes. Behavior Genetics, 30(5), 385–396.
Ruff, S., Marie, N., Celsis, P., Cardebat, D., & Demonet, J. F. (2003). Neural substrates of impaired categorical perception of phonemes in adult dyslexics: An fMRI study. Brain and Cognition, 53(2), 331–334.
Rumsey, J. M., Horwitz, B., Donohue, B. C., Nace, K. L., Maisog, J. M., & Andreason, P. (1999). A functional lesion in developmental dyslexia: Left angular gyral blood flow predicts severity. Brain and Language, 70(2), 187–204.
Salgado-Pineda, P., Baeza, I., Perez-Gomez, M., Vendrell, P., Junque, C., Bargallo, N., et al. (2003). Sustained attention impairment correlates to gray matter decreases in first episode neuroleptic-naive schizophrenic patients. Neuroimage, 19(2 Pt 1), 365–375.
Schumacher, J., Anthoni, H., Dahdouh, F., Konig, I. R., Hillmer, A. M., Kluck, N., et al. (2006). Strong genetic evidence of DCDC2 as a susceptibility gene for dyslexia. American Journal of Human Genetics, 78(1), 52–62.
Silani, G., Frith, U., Demonet, J. F., Fazio, F., Perani, D., Price, C., et al. (2005). Brain abnormalities underlying altered activation in dyslexia: A voxel based morphometry study. Brain, 128(Pt 10), 2453–2461.
Thompson, P. M., Cannon, T. D., Narr, K. L., van Erp, T., Poutanen, V. P., Huttunen, M., et al. (2001). Genetic influences on brain structure. Nature Neuroscience, 4(12), 1253–1258.
Vinckenbosch, E., Robichon, F., & Eliez, S. (2005). Gray matter alteration in dyslexia: Converging evidence from volumetric and voxel-by-voxel MRI analyses. Neuropsychologia, 43(3), 324–331.
Wilke, M., & Lidzba, K. (2007). LI-tool: A new toolbox to assess lateralization in functional MR-data. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 163(1), 128–36.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Ann Marie Lacobelle and Greg Kay for technical assistance. This research was supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health, under RO1 grants MH60504, MH43775, MH52886 and an NIMH MERIT award (to GP) 1 R01 EB 000840 and 1 R01 EB 005846, R01 DA12690, R01 DA12849, K24 DA15105; 1 R01 NS43530 to JRG; the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (the VA Connecticut–Massachusetts Mental Illness Research, Education and Clinical Center [MIRECC]) to JG; a Hartford Hospital Open Grant Award, and a National Association for Research in Schizophrenia and Affective Disorders Young Investigator Award to VC.
Support for HM is from a General Grant Award of the International Dyslexia Association.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Presented at The Joint Annual Meeting International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine—European Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine and Biology 2007, Berlin, Germany.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meda, S.A., Gelernter, J., Gruen, J.R. et al. Polymorphism of DCDC2 Reveals Differences in Cortical Morphology of Healthy Individuals—A Preliminary Voxel Based Morphometry Study. Brain Imaging and Behavior 2, 21–26 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-007-9012-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-007-9012-1