Abstract
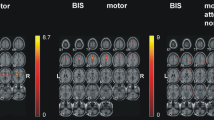
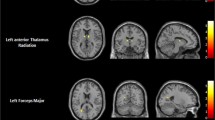
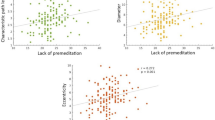
According to bottom-up/top-down models, impulsivity facets are represented across the cerebral cortex and subcortex. Hypothesized gray matter correlates of motor, attentional and non-planning impulsivity were examined in groups of 35 psychiatric patients characterized by self-control problems and 18 healthy volunteers. Among patients, a positive correlation was found between motor impulsivity and the right cerebellum, and a negative correlation emerged between attentional impulsivity and the left lateral orbitofrontal cortex (OFC). Among controls, attentional and motor impulsivity correlated negatively with the left superior temporal gyrus, while non-planning impulsivity correlated positively with the left OFC and lateral frontopolar cortex. Follow-up analyses revealed convergence in correlation patterns from patients to controls, but not vice versa. That pattern suggested broader neural representation of the trait in the healthy controls, who were less impulsive than the psychiatric patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aron, A. R. (2007). The neural basis of inhibition in cognitive control. The Neuroscientist, 13, 214–228.
Aron, A. R., Robbins, T. W., & Poldrack, R. A. (2004). Inhibition and the right inferior frontal cortex. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 8, 170–177.
Asahi, S., Okamoto, Y., Okada, G., Yamawaki, S., & Yokota, N. (2004). Negative correlation between right prefrontal activity during response inhibition and impulsiveness: a fMRI study. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 254, 245–251.
Ashburner, J., & Friston, K. J. (2005). Unified segmentation. NeuroImage, 26, 839–851.
Barkley, R. A. (1998). A theory of ADHD: Inhibition, executive functions, & time. In Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Handbook for Diagnosis and Treatment, 2nd Edn (pp. 225–260). New York: Guilford.
Bechara, A. (2005). Decision making, impulse control and loss of willpower to resist drugs: a neurocognitive perspective. Nature Neuroscience, 8, 1458–1463.
Bechara, A., Damasio, H., & Damasio, A. R. (2000). Emotion, decision making, and the orbitofrontal cortex. Cerebral Cortex, 10, 295–307.
Berlin, H. A., Rolls, E. T., & Kischka, U. (2004). Impulsivity, time perception, emotion and reinforcement sensitivity in patients with orbitofrontal cortex lesions. Brain, 127, 1108–1126.
Bjork, J. M., Momenan, R., & Hommer, D. W. (2009). Delay discounting correlates with proportional lateral frontal cortex volumes. Biological Psychiatry, 65, 710–713.
Boes, A. D., Bechara, A., Tranel, D., Anderson, S. W., Richman, L., & Nopoulos, P. (2009). Right ventromedial prefrontal cortex: a neuroanatomical correlate of impulse control in boys. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 4, 1–9.
Botvinick, M., Nystrom, L. E., Fissell, K., Carter, C. S., & Cohen, J. D. (1999). Conflict monitoring versus selection-for-action in anterior cingulate cortex. Nature, 402, 179–181.
Botvinick, M. M., Cohen, J. D., & Carter, C. S. (2004). Conflict monitoring and anterior cingulate cortex: an update. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 8, 539–546.
Brown, S. M., Manuck, S. B., Flory, J. D., & Hariri, A. R. (2006). Neural basis of individual differences in impulsivity: contributions of corticolimbic circuits for behavioral arousal and control. Emotion, 6, 239–245.
Burgess, P. W., Gilbert, S. J., & Dumontheil, I. (2007). Function and localization within rostral prefrontal cortex (area 10). Philosophical Transaction of the Royal Society B, 362, 887–899.
Clark, L., Bechara, A., Damasio, H., Aitken, M. R. F., Sahakian, B. J., & Robbins, T. W. (2008). Differential effects of insular and ventromedial prefrontal cortex lesions on risky decision-making. Brain, 131, 1311–1322.
DeYoung, C. G., Hirsch, J. B., Shane, M. S., Papademetris, X., Rajeevan, & Gray, J. R. (2010). Testing predictions from personality neuroscience: brain structure and the big five. Psychological Science, 21, 820–828.
Dickman, S. J. (1990). Functional and dysfunctional impulsivity: personality and cognitive correlates. Journal of Personality and Social Personality, 58, 95–102.
Dickstein, S. G., Bannon, K., Castellanos, F. X., & Milham, M. P. (2006). The neural correlates of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: an ALE meta-analysis. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 47, 11051–1063.
Durston, S., Davidson, M. C., Mulder, M. J., Spicer, J. A., Galvan, A., Tottenham, N., et al. (2007). Neural and behavioral correlates of expectancy violations in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 48, 881–889.
Duvernoy, H. (1991). The human brain surface, blood supply, and three-dimensional sectional anatomy (2nd ed.). New York: Springer-Verlag/Wien.
Emerton, B. C., Jerram, M., Fulwiler, C., & Gansler, D. A. (2008). A VBM based exploration of MRI acquisition protocol variance. Poster presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Clinical Neuropsychology, Boston, MA.
Fuster, J. M. (2008). The prefrontal cortex (4th ed.). Boston: Academic.
Gall, F. J. (1819). Anatomie et physiologie du système nerveux en général et anatomie du cerveau en particulier, vol. 4.
Gansler, D. A., McLaughlin, N. C. R., Iguchi, L., Jerram, M., Moore, D. W., Bhadelia, R., et al. (2009). A multivariate approach to aggression and the orbital frontal cortex in psychiatric patients. Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging, 171, 145–154.
Gaser, C. (2009) VBM5 version 1.19 [Computer software] Retrieved June 2009, from http://dbm.neuro.uni-jena.de/vbm/download/.
Good, C. D., Johnsrude, I. S., Ashburner, J., Henson, R. N., Friston, K. J., & Frackowiak, R. S. (2001). A voxel-based morphometric study of ageing in 465 normal adult human brains. Neuroimage, 14, 21–36.
Hariri, A. R., Brown, S. M., Williamson, D. E., Flory, J. D., de Wit, H., & Manuck, S. B. (2006). Preference for immediate over delayed rewards is associated with magnitide of ventral striatal activity. The Journal of Neuroscience, 26, 13213–13217.
Hayasaka, S., Phan, K. L., Liberzon, I., Worsley, K. J., & Nichols, T. E. (2004). Nonstationary cluster-size inference with random field and permutation methods. NeuroImage, 22, 676–687. 36.
Hopfinger, J. B., Buonocore, M. H., & Mangun, G. R. (2000). The neural mechanisms of top-down attentional control. Nature Neuroscience, 3, 284–291.
Karnath, H. O. (2001). New insights into the functions of the superior temporal cortex. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2, 568–576.
Koechlin, E., & Hyafil, A. (2007). Anterior prefrontal function and the limits of human decision-making. Science, 318, 594–598.
Koenigsberg, H. W., Fan, J., Ochsner, K. N., Liu, X., Guise, K. G., Pizzarello, S., et al. (2009). Neural correlates of the use of psychological distancing to regulate responses to negative social cues: a study of patients with borderline personality disorder. Biological Psychiatry, 66, 854–863.
Krueger, R. F., Markon, E. M., Patrick, C. J., & Iacono, W. G. (2005). Externalizing psychopathology in adulthood: a dimensional-spectrum conceptualization and its implications for DSM-V. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 114, 537–550.
Mallory-Diniz, L., Fuentes, D., Leite, W. B., Correa, H., & Bechara, A. (2007). Impulsive behavior in adults with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: characterization of attentional, motor and cognitive impulsiveness. Journal of International Neuropsychological Society, 13, 693–698.
Malykhin, N. V., Carter, R., Seres, P., & Coupland, N. J. (2010). Structural changes in the hippocampus in major depressive disorder: contributions of disease and treatment. Journal of Psychiatry and Neuroscience, 35, 337–343.
Matsuo, K., Nicoletti, M., Nemoto, K., Hatch, J. P., Peluso, M. A. M., Nery, F. G., et al. (2009). A voxel-based morphometry study of frontal gray matter correlates of impulsivity. Human Brain Mapping, 30, 1188–1195.
McClure, S. M., Laibson, D. I., Loewenstein, G., & Cohen, J. D. (2004). Separate neural systems value immediate and delayed monetary rewards. Science, 306, 503–507.
Moeller, F. G., Barratt, E. S., Dougherty, D. M., Schmitz, J. M., & Swann, A. C. (2001). Psychiatric aspects of impulsivity. American Journal of Psychiatry, 158, 1783–1793.
Monahan, J., Steadman, H. J., Appelbaum, P. S., Robbins, P. C., Mulvey, E. P., Silver, E., et al. (2000). Developing a clinically useful actuarial tool for assessing violence risk. British Journal of Psychiatry, 176, 312–319.
Moncrieff, J., & Leo, J. (2010). A systematic review of the effects of antipsychotic drugs on brain volume. Psychological Medicine, 40, 1409–1422.
Müller, N. G., & Knight, R. T. (2006). The functional neuroanatomy of working memory: contributions of human brain lesion studies. Neuroscience, 139, 51–58.
O’Reilly, J. X., Mesulam, M. M., & Nobre, A. C. (2008). The cerebellum predicts the timing of perceptual events. The Journal of Neuroscience, 28, 2252–2260.
Patton, J. H., Stanford, M. S., & Barratt, E. S. (1995). Factor structure of the Barratt Impulsiveness Scale. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 51, 768–774.
Petrides, M., Alivisatos, B., & Frey, S. (2002). Differential activation of the human orbital, mid-ventrolateral, and mid-dorsolateral prefrontal cortex during the processing of visual stimuli. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 99, 5649–5654.
Semendeferi, K., Armstrong, E., Schleicher, A., Zilles, K., & Van Hoesen, G. W. (2001). Prefrontal cortex in humans and apes: a comparative study of area 10. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 114, 224–241.
Soloff, P., Nutche, J., Goradia, D., & Diwadkar, V. (2008). Structural brain abnormalities in borderline personality disorder: a voxel-based morphometry study. Psychiatry Research, 164, 223–236.
Stanford, M. S., Mathias, C. W., Dougherty, D. M., Lake, S. L., Anderson, N. E., & Patton, J. H. (2009). Fifty years of the Barratt Impulsiveness Scale: an update and review. Personality and Individual Difference, 47, 385–395.
Stahl, S. M. (2008). Stahl’s essential psychopharmacology: Neuroscientific basis and practical applications (3rd ed.). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Swann, A. C., Steinberg, J. L., Lijffijt, M., & Moeller, F. G. (2008). Impulsivity: differential relationship to depression and mania in bipolar disorder. Journal of Affective Disorders, 106, 241–248.
Tebartz, V. E. L., Trimble, M. R., & Ebert, D. (2001). Dual brain pathology in patients with affective aggressive episodes. Archives of General Psychiatry, 58, 1187–1188.
Vanderhasselt, M., De Raedt, D., & Baeken, C. (2009). Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and Stroop performance: tackling the lateralization. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 16(3), 609–612.
Völlm, B. A., Zhao, L., Richardson, P., Clark, L., Deakin, J. F. W., Williams, S., et al. (2009). A voxel-based morphometric MRI study in men with borderline personality disorder: preliminary findings. Criminal Behavior and Mental Health, 19, 64–72.
Worsley, K. J., Andermann, M., Koulis, T., MacDonald, D., & Evans, A. C. (1999). Detecting changes in nonisotropic images. Human Brain Mapping, 8, 98–101.
Acknowledgment
This research was internally supported by the College of Arts and Sciences at Suffolk University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, A.K.W., Jerram, M., Fulwiler, C. et al. Neural correlates of impulsivity factors in psychiatric patients and healthy volunteers: a voxel-based morphometry study. Brain Imaging and Behavior 5, 52–64 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-010-9112-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-010-9112-1