Abstract
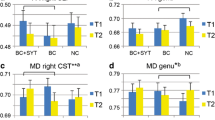
Adjuvant chemotherapy (CT) for breast cancer (BC) is associated with very late side-effects on brain function and structure. However, little is known about neurotoxicity of specific treatment regimens. To compare neurotoxicity profiles after different treatment strategies, we used neurocognitive testing and multimodality MRI in BC survivors randomized to high-dose (HI), conventional-dose (CON-) CT or radiotherapy (RT) only and a healthy control (HC) group. BC survivors who received CON-CT (n = 20) and HC (n = 20) were assessed using a neurocognitive test battery and multimodality MRI including 3D-T1, Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) and 1H-MR spectroscopy (1H-MRS) to measure various aspects of cerebral white (WM) and gray matter (GM). Data were compared to previously assessed groups of BC survivors who received HI-CT (n = 17) and RT-only (n = 15). Testing took place on average 11.5 years post-CT. 3D-T1 showed focal GM volume reductions both for HI-CT and CON-CT compared to RT-only (p < .004). DTI-derived mean diffusivity and 1H-MRS derived N-acetyl aspartate showed WM injury specific to HI-CT but not CON-CT (p < .05). Residual effects were revealed in the RT-only group compared to HC on MRI and neurocognitive measurements (p < .05). Ten years after adjuvant CT for BC lower cerebral GM volume was found in HI as well as CON-CT BC survivors whereas injury to WM is restricted to HI-CT. This might indicate that WM brain changes after BC treatment may show more pronounced (partial) recovery than GM. Furthermore, our results suggest residual neurotoxicity in the RT-only group, which warrants further investigation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaronson, N. K., Ahmedzai, S., Bergman, B., Bullinger, M., Cull, A., Duez, N. J., & de Haes, J. C. (1993). The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-C30: a quality-of-life instrument for use in international clinical trials in oncology. J Natl Cancer Inst, 85(5), 365–76.
Biglia, N., Bounous, V. E., Malabaila, A., Palmisano, D., Torta, D. M. E., D’Alonzo, M., & Torta, R. (2012). Objective and self-reported cognitive dysfunction in breast cancer women treated with chemotherapy: a prospective study. Euro j of cancer care, 21(4), 485–92. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2354.2011.01320.x.
Brown, M. S., Stemmer, S. M., Simon, J. H., Stears, J. C., Jones, R. B., Cagnoni, P. J., & Sheeder, J. L. (1998). White matter disease induced by high-dose chemotherapy: longitudinal study with MR imaging and proton spectroscopy. AJNR American journal of neuroradiology, 19(2), 217–21.
Collado-Hidalgo, A., Bower, J. E., Ganz, P. A., Cole, S. W., & Irwin, M. R. (2006). Inflammatory biomarkers for persistent fatigue in breast cancer survivors. Clinical cancer research. j of the American Association for Cancer Research, 12(9), 2759–66. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2398.
Conroy, S. K., McDonald, B. C., Smith, D. J., Moser, L. R., West, J. D., Kamendulis, L. M., & Saykin, A. J. (2013). Alterations in brain structure and function in breast cancer survivors: effect of post-chemotherapy interval and relation to oxidative DNA damage. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 137(2), 493–502. doi:10.1007/s10549-012-2385-x.
De Ruiter, M. B., & Schagen, S. B. (2013). Functional MRI studies in non-CNS cancers. Brain imaging and behavior. doi:10.1007/s11682-013-9249-9.
De Ruiter, M. B., Reneman, L., Boogerd, W., Veltman, D. J., van Dam, F. S., Schagen, S. B., & Nederveen, A. J. (2011). Cerebral hyporesponsiveness and cognitive impairment 10 years after chemotherapy for breast cancer. Hum Brain Mapp, 32(8), 1206–19. doi:10.1002/hbm.21102.
De Ruiter, M. B., Reneman, L., Boogerd, W., Veltman, D. J., Caan, M., Douaud, G., & Schagen, S. B. (2012). Late effects of high-dose adjuvant chemotherapy on white and gray matter in breast cancer survivors: converging results from multimodal magnetic resonance imaging. Hum Brain Mapp, 33(12), 2971–83. doi:10.1002/hbm.21422.
DeCarlo, L. T. (1997). On the meaning and use of kurtosis. Psychol Methods, 2(3), 292–307. doi:10.1037//1082-989X.2.3.292.
Deprez, S., Amant, F., Yigit, R., Porke, K., Verhoeven, J., Van den Stock, J., & Sunaert, S. (2011). Chemotherapy-induced structural changes in cerebral white matter and its correlation with impaired cognitive functioning in breast cancer patients. Hum Brain Mapp, 32(3), 480–93. doi:10.1002/hbm.21033.
Deprez, S., Billiet, T., Sunaert, S., & Leemans, A. (2013). Diffusion tensor MRI of chemotherapy-induced cognitive impairment in non-CNS cancer patients: a review. Brain imaging and behavior. doi:10.1007/s11682-012-9220-1.
Dietrich, J., Monje, M., Wefel, J., & Meyers, C. (2008). Clinical patterns and biological correlates of cognitive dysfunction associated with cancer therapy. Oncologist, 13(12), 1285–95. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2008-0130.
Eberling, J. L., Wu, C., Tong-Turnbeaugh, R., & Jagust, W. J. (2004). Estrogen- and tamoxifen-associated effects on brain structure and function. NeuroImage, 21(1), 364–371. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2003.08.037.
Hesbacher, P. T., Rickels, K., Morris, R. J., Newman, H., & Rosenfeld, H. (1980). Psychiatric illness in family practice. The J of clinical psychiatry, 41(1), 6–10.
Husain, K., Whitworth, C., Hazelrigg, S., & Rybak, L. (2003). Carboplatin-Induced Oxidative Injury in Rat Inferior Colliculus. Int J Toxicol, 22(5), 335–342. doi:10.1177/109158180302200502.
Jenkinson, M., Beckmann, C. F., Behrens, T. E. J., Woolrich, M. W., & Smith, S. M. (2012). FSL NeuroImage, 62(2), 782–90. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.09.015.
Jim, H. S. L., Donovan, K. A., Small, B. J., Andrykowski, M. A., Munster, P. N., & Jacobsen, P. B. (2009). Cognitive functioning in breast cancer survivors: a controlled comparison. Cancer, 115(8), 1776–83. doi:10.1002/cncr.24192.
Koppelmans, V., Breteler, M. M. B., Boogerd, W., Seynaeve, C., Gundy, C., & Schagen, S. B. (2012a). Neuropsychological performance in survivors of breast cancer more than 20 years after adjuvant chemotherapy. Journal of clinical oncology official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, 30(10), 1080–6. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.37.0189.
Koppelmans, V., de Ruiter, M. B., van der Lijn, F., Boogerd, W., Seynaeve, C., van der Lugt, A., & Schagen, S. B. (2012b). Global and focal brain volume in long-term breast cancer survivors exposed to adjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 132(3), 1099–106. doi:10.1007/s10549-011-1888-1.
Koppelmans, V., de Groot, M., de Ruiter, M. B., Boogerd, W., Seynaeve, C., Vernooij, M. W., & Breteler, M. M. B. (2014). Global and focal white matter integrity in breast cancer survivors 20 years after adjuvant chemotherapy. Hum Brain Mapp, 35(3), 889–99. doi:10.1002/hbm.22221.
Mangin, J.-F., Poupon, C., Clark, C., Le Bihan, D., & Bloch, I. (2002). Distortion correction and robust tensor estimation for MR diffusion imaging. Med Image Anal, 6(3), 191–8.
Nichols, T. E., & Holmes, A. P. (2002). Nonparametric permutation tests for functional neuroimaging: a primer with examples. Hum Brain Mapp, 15(1), 1–25.
Phillips, K. M., Jim, H. S., Small, B. J., Laronga, C., Andrykowski, M. A., & Jacobsen, P. B. (2012). Cognitive functioning after cancer treatment: a 3-year longitudinal comparison of breast cancer survivors treated with chemotherapy or radiation and noncancer controls. Cancer, 118(7), 1925–32. doi:10.1002/cncr.26432.
Pomykala, K. L., de Ruiter, M. B., Deprez, S., McDonald, B. C., & Silverman, D. H. S. (2013). Integrating imaging findings in evaluating the post-chemotherapy brain. Brain imaging and behavior. doi:10.1007/s11682-013-9239-y.
Provencher, S. W. (1993). Estimation of metabolite concentrations from localized in vivo proton NMR spectra Magnetic resonance in medicine. official journal of the Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine/Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 30(6), 672–9.
Pullens, M. J. J., De Vries, J., & Roukema, J. A. (2010). Subjective cognitive dysfunction in breast cancer patients: a systematic review. Psycho-Oncology, 19(11), 1127–38. doi:10.1002/pon.1673.
Rodenhuis, S., Bontenbal, M., Beex, L. V. A. M., Wagstaff, J., Richel, D. J., Nooij, M. A., & de Vries, E. G. E. (2003). High-dose chemotherapy with hematopoietic stem-cell rescue for high-risk breast cancer. N Engl J Med, 349(1), 7–16. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa022794.
Schagen, S. B., Muller, M. J., Boogerd, W., Mellenbergh, G. J., & van Dam, F. S. A. M. (2006). Change in cognitive function after chemotherapy: a prospective longitudinal study in breast cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst, 98(23), 1742–5. doi:10.1093/jnci/djj470.
Schilder, C. M., Eggens, P. C., Seynaeve, C., Linn, S. C., Boogerd, W., Gundy, C. M., & Schagen, S. B. (2009). Neuropsychological functioning in postmenopausal breast cancer patients treated with tamoxifen or exemestane after AC-chemotherapy: cross-sectional findings from the neuropsychological TEAM-side study. Acta Oncol, 48(1), 76–85. doi:10.1080/02841860802314738.
Schilder, C. M., Seynaeve, C., Beex, L. V., Boogerd, W., Linn, S. C., Gundy, C. M., & Schagen, S. B. (2010). Effects of tamoxifen and exemestane on cognitive functioning of postmenopausal patients with breast cancer: results from the neuropsychological side study of the tamoxifen and exemestane adjuvant multinational trial. J of clinical oncology official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, 28(8), 1294–300. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.21.3553.
Schmahmann, J. D., Smith, E. E., Eichler, F. S., & Filley, C. M. (2008). Cerebral white matter: neuroanatomy, clinical neurology, and neurobehavioral correlates. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 1142, 266–309. doi:10.1196/annals.1444.017.
Shilling, V., & Jenkins, V. (2007). Self-reported cognitive problems in women receiving adjuvant therapy for breast cancer. Euro j of oncology nursing the official j of Euro Oncology Nursing Society, 11(1), 6–15. doi:10.1016/j.ejon.2006.02.005.
Smith, S. M. (2002). Fast robust automated brain extraction. Hum Brain Mapp, 17(3), 143–55. doi:10.1002/hbm.10062.
Strick, P. L., Dum, R. P., & Fiez, J. A. (2009). Cerebellum and nonmotor function. Annu Rev Neurosci, 32, 413–34. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.31.060407.125606.
Tang, C. Y., Friedman, J., Shungu, D., Chang, L., Ernst, T., Stewart, D., & Gorman, J. M. (2007). Correlations between Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) and Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (1H MRS) in schizophrenic patients and normal controls. BMC psychiatry. doi:10.1186/1471-244X-7-25.
Wefel, J. S., & Schagen, S. B. (2012). Chemotherapy-related cognitive dysfunction. Current neurology and neuroscience reports, 12(3), 267–75. doi:10.1007/s11910-012-0264-9.
Wefel, J. S., Vardy, J., Ahles, T., & Schagen, S. B. (2011). International Cognition and Cancer Task Force recommendations to harmonise studies of cognitive function in patients with cancer. The lancet oncology, 12(7), 703–8. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70294-1.
Zhang, Y., Brady, M., & Smith, S. (2001). Segmentation of brain MR images through a hidden Markov random field model and the expectation-maximization algorithm. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 20(1), 45–57. doi:10.1109/42.906424.
Acknowledgments
We thank all the participants and colleagues who contributed to our studies.
Funding
This is a non-industry-sponsored study. This research was supported by the AMC Medical Research, grant 09.25.229 I 09.03.270.
Conflicts of Interest
Myrle M. Stouten-Kemperman, Michiel B. de Ruiter, Vincent Koppelmans, Willem Boogerd, Liesbeth Reneman, and Sanne B. Schagen report no conflicts of interest.
Informed consent statement
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, and the applicable revisions at the time of the investigation. Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stouten-Kemperman, M.M., de Ruiter, M.B., Koppelmans, V. et al. Neurotoxicity in breast cancer survivors ≥10 years post-treatment is dependent on treatment type. Brain Imaging and Behavior 9, 275–284 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-014-9305-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-014-9305-0