Abstract
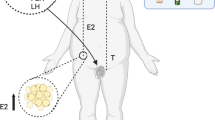
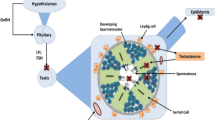
There are possible hazardous health effects of exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic radiations emitted from mobile phone on the human reproductive pattern. It is more effective while keeping mobile phones in pocket or near testicular organs. Present review examines the possible concern on radio frequency radiation interaction and biological effects such as enzyme induction, and toxicological effects, including genotoxicity and carcinogenicity, testicular cancer, and reproductive outcomes. Testicular infertility or testicular cancer due to mobile phone or microwave radiations suggests an increased level of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Though generation of ROS in testis has been responsible for possible toxic effects on physiology of reproduction, the reviews of last few decades have well established that these radiations are very harmful and cause mutagenic changes in reproductive pattern and leads to infertility. The debate will be focused on bio-interaction mechanism between mobile phone and testicular cancer due to ROS formation. This causes the biological damage and leads to several changes like decreased sperm count, enzymatic and hormonal changes, DNA damage, and apoptosis formation. In the present review, physics of mobile phone including future research on various aspects has been discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Markov, M. S. (2000). Dosimetry of magnetic fields in the radio frequency range. In B. J. Klauenberg & D. Miklavcic (Eds.), Radio frequency radiation dosimetry (pp. 239–245). New York: Kluwer Academic Press.
Kesari, K. K., & Behari, J. (2010). Effect of microwave at 2.45 GHz radiations on reproductive system of male rats. Toxicological and Environmental Chemistry, 92, 1135–1147.
Kesari, K. K., Kumar, S., & Behari, J. (2010). Mobile phone usage and male infertility in Wistar rats. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology, 48(10), 987–992.
Kesari, K. K., Kumar, S., & Behari, J. (2011). Effects of radiofrequency electromagnetic waves exposure from cellular phone on reproductive pattern in male Wistar rats. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 164, 546–559.
Desai, N. R., Kesari, K. K., & Agarwal, A. (2009). Pathophysiology of cell phone radiation: Oxidative stress and carcinogenesis with focus on male reproductive system. Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology, 7, 114.
Moller, P., Wallin, H., & Knudsen, L. E. (1996). Oxidative stress associated with exercise, psychological stress and life-style factors. Chemical Biological Interaction, 102, 17–36.
Kumar, S., Kesari, K. K., & Behari, J. (2011). Influence of microwave exposure on fertility of male rats. Fertility Sterility, 95(4), 1500–1502.
Kesari, K. K., & Behari, J. (2009). Fifty-gigahertz microwave exposure effect of radiations on rat brain. Applied Biochemistry Biotechnology, 158, 126–139.
Kesari, K. K., Behari, J., & Kumar, S. (2010). Mutagenic response of 2.45 GHz radiation exposure on rat brain. International Journal of Radiation Biology, 86(4), 334–343.
Kesari, K. K., Kumar, S., & Behari, J. (2011). 900-MHz microwave radiation promotes oxidation in rat brain. Electromagnetic Biology and Medicine, 30(4), 219–234.
Kesari, K. K., & Behari, J. (2010). Microwave exposure affecting reproductive system in male rats. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 162, 416–428.
Fejes, I., Závaczki, Z., Szöllosi, J., et al. (2005). Is there a relationship between cell phone use and semen quality? Archive of Andrology, 51(5), 385–393.
Aitken, R. J., Bennetts, L. E., & Sawyer, D. (2005). Impact of radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation on DNA integrity in the male germline. International Journal of Andrology, 28(3), 171–179.
Erogul, O., Oztas, F., Yildirim, I., et al. (2006). Effects of electromagnetic radiation from a cellular phone on human sperm motility: an in vitro study. Archive of Medical Research, 37(7), 840–843.
Yan, J. G., Agresti, M., Bruce, T., et al. (2007). Effects of cellular phone emissions on sperm motility in rats. Fertility Sterility, 88(4), 957–964.
Agarwal, A., Desai, N. R., Makker, K., et al. (2009). Effects of radiofrequency electromagnetic waves (RF-EMW) from cellular phones on human ejaculated semen: An in vitro pilot study. Fertility Sterility, 92(4), 1318–1325.
Agarwal, A., Deepinder, F., Sharma, R. K., et al. (2008). Effect of cell phone usage on semen analysis in men attending infertility clinic: An observational study. Fertility Sterility, 89(1), 124–128.
Falzone, N., Huyser, C., Fourie, F., et al. (2008). In vitro effect of pulsed 900 MHz GSM radiation on mitochondrial membrane potential and motility of human spermatozoa. Bioelectromagnetics, 29(4), 268–276.
Deepinder, F., Makker, K., & Agarwal, A. (2007). Cell phones and male infertility: Dissecting the relationship. Reproductive Biomedicine Online, 15(3), 266–270.
Wdowiak, A., Wdowiak, L., & Wiktor, H. (2007). Evaluation of the effect of using mobile phones on male fertility. Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine, 14(1), 169–172.
Mailankot, M., Kunnath, A. P., Jayalekshmi, H., et al. (2009). Radio frequency electromagnetic radiation (RF-EMR) from GSM (0.9/1.8 GHz) mobile phones induces oxidative stress and reduces sperm motility in rats. Clinics (Sao Paulo), 64(6), 561–565.
Pacini, S., Ruggiero, M., Sardi, I., et al. (2002). Exposure to global system for mobile communication (GSM) cellular phone radiofrequency alters gene expression, proliferation, and morphology of human skin fibroblasts. Oncology Research, 13, 19–24.
Mashevich, M., Folkman, D., Kesar, A., et al. (2003). Exposure of human peripheral blood lymphocytes to electromagnetic fields associated with cellular phones leads to chromosomal instability. Bioelectromagnetics, 24, 82–90.
Sykes, P. J., McCallum, B. D., Bangay, M. J., et al. (2001). Effect of exposure to 900 MHz radiofrequency radiation on intrachromosomal recombination in pKZ1 mice. Radiation Research, 156, 495–502.
Kunjilwar, K. K., & Behari, J. (1993). Effect of amplitude-modulated radio frequency radiation on cholinergic system of developing rats. Brain Research, 601, 321–324.
Burch, J. B., Reif, J. S., Noonan, C. W., et al. (2002). Melatonin metabolite excretion among cellular telephone users. International Journal of Radiation Biology, 78, 1029–1036.
Kumar, S., Kesari, K. K., & Behari, J. (2010). Evaluation of genotoxic effects in male Wistar rats following microwave exposure. Indian Journal of Experimental Biology, 48, 586–592.
Hu, P. Y., Chu, X. L., Li, J. Y., et al. (1985). Effect of microwave contraception on human serum testosterone and luteinizing hormone. Shengzhi Yu Biyun, 5, 32–34.
Steinberger, E. (1971). Hormonal control of mammalian spermatogenesis. Physiological Review, 51(1), 1–22.
Dasdag, S., Ketani, M. A., Akdag, Z., et al. (1999). Whole-body microwave exposure emitted by cellular phones and testicular function of rats. Urological Research, 27, 219–223.
Ozguner, M., Koyu, A., Cesur, G., et al. (2005). Biological and morphological effects on the reproductive organs of rats after exposure to electromagnetic field. Soudi Medical Journal, 26(3), 405–410.
Carl, A. B., Ashwood, E. R., & Bruns, D. E. (2006). Tietz text book of clinical chemistry and molecular diagnostics (pp. 191–218). St. Louis, MO: Elsevier/Sanders.
Hackney, A. C., Moore, A. W., & Brownlee, K. K. (2005). Testosterone and endurance “exercise hypogonadal male condition”. Acta Physiological Hungarica, 92, 121–137.
Meo, S. A., Al-Drees, A. M., & Husain, S. (2010). Effect of mobile phone on serum testosterone in Wistar Albino rats. Saudi Medical Journal, 31(8), 869–873.
Sarookhani, M. R., Rezaei, M. A., Safari, A., et al. (2011). The influence of 950 MHz magnetic field (mobile phone radiation) on sex organ and adrenal functions of male rabbits. African Journal of Biochemistry Research, 5(2), 65–68.
Kumar, S., Kesari, K. K., & Behari, J. (2011). Synergistic effect of 2.45 GHz and pulsed magnetic field on reproductive pattern of male Wistar rats. Clinics, 66(7), 1237–1245.
Mailankot, M., Kunnath, A. P., Jayalekshmi, H., et al. (2009). Radio frequency electromagnetic radiation (RF-EMR) from GSM (0.9/1.8 GHz) mobile phone induces oxidative stress and reduces sperm motility in rats. Clinics (Sao Paulo), 64, 561–565.
Desai, N., Sharma, R., Makker, K., et al. (2009). Physiologic and pathologic levels of reactive oxygen species in neat semen of infertile men. Fertility and Sterility, 92(5), 1626–1631.
D’Autreaux, B., & Toledano, M. B. (2007). ROS as signalling molecules: Mechanisms that generate specificity in ROS homeostasis. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 8, 813–824.
Bandyopadhyay, U., Das, D., & Banerjee, R. K. (1999). Reactive oxygen species: Oxidative damage and pathogenesis. Current Science, 77(5), 658–666.
De Iuliis, G. N., Newey, R. J., King, B. V., et al. (2009). Mobile phone radiation induces reactive oxygen species production and DNA damage in human spermatozoa in vitro. PLoS ONE, 4(7), e6446.
Agarwal, A., Singh, A., Hamada, A., et al. (2011). Cell phones and male infertility: A review of recent innovations in technology and consequences. International Brazilian Journal of Urology, 37(4), 432–454.
Halliwell, B., & Gutteridge, J. M. C. (1999). Free radicals in biology and medicine (2nd ed.). Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-19850-044-0.
Vassalle, C., Petrozzi, L., Botto, N., et al. (2004). Oxidative stress and its association with coronary artery disease and different atherogenic risk factors. Journal of International Medicine, 256(4), 308–315.
Araujo, F. B., Barbosa, D. S., Hsin, C. Y., et al. (1995). Evaluation of oxidative stress in patients with Hyperlipidemia. Atherosclerosis, 117(1), 61–71.
Reilly, M. P., Pratico, D., Delanty, N., et al. (1998). Increased formation of distinct F2 isoprostanes in Hypercholesterolemia. Circulation, 98(25), 2822–2828.
Stojiljkovic, M. P., Lopes, H. F., Zhang, D., et al. (2002). Increasing plasma fatty acids elevates F2-isoprostanes in humans: Implications for the cardiovascular risk factor cluster. Journal of Hypertension, 20(6), 1215–1221.
Mecocci, P., MacGarvey, U., Kaufman, A. E., et al. (1994). Oxidative damage to mitochondrial DNA is increased in Alzheimer’s disease. Annals Neurology, 36(5), 747–751.
Milton, N. G. (2004). Role of hydrogen peroxide in the aetiology of Alzheimer’s disease: Implications for treatment. Drugs and Aging, 21(2), 81–100.
Nishioka, N., & Arnold, S. E. (2004). Evidence for oxidative DNA damage in the hippocampus of elderly patients with chronic schizophrenia. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 12(2), 167–175.
Paredi, P., Kharitonov, S. A., Hanazawa, T., et al. (2001). Local vasodilator response to mobile phones. Laryngoscope, 111(1), 159–162.
Yariktas, M., Doner, F., Ozguner, F., et al. (2005). Nitric oxide level in the nasal and sinus mucosa after exposure to electromagnetic field. Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery, 132, 713–716.
Blokhina, O., Virolainen, E., & Fagerstedt, K. V. (2003). Antioxidants, oxidative damage and oxygen deprivation stress: A review. Annals of Botony (London), 91, 179–194.
McNamee, J. P., McLean, J. R. N., Ferrarotto, C. L., et al. (2000). Comet assay: Rapid processing of multiple samples. Mutation Research, 466, 63–69.
Singh, N. P., McCoy, M. T., Tice, R. R., et al. (2003). A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Experimental Cell Research, 175(1), 184–191.
Lai, H., & Singh, N. P. (1995). Acute low-intensity microwave exposure increases DNA single-strand breaks in rat brain cells. Bioelectromagnetics, 16, 207–210.
Sakuma, N., Komatsubara, Y., Takeda, H., et al. (2006). DNA strand breaks are not induced in human cells exposed to 2.1425 GHz band CW and W-CDMA modulated radiofrequency fields allocated to mobile radio base stations. Bioelectromagnetics, 27, 51–57.
Agarwal, A., Deepinder, F., & Sharma, R. K. (2007). Effect of cell phone usage on semen analysis in men attending infertility clinic: An observational study. Fertility and Sterility,. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2007.01.166.
Lai, H., & Singh, N. P. (1997). Acute exposure to a 60-Hz magnetic field increases DNA strand breaks in rat brain cells. Bioelectromagnetics, 18, 156–165.
Behari, J., & Kesari, K. K. (2006). Effects of microwave radiations on reproductive system of male rats. Embryo Talk, 1, 81–85.
Vijayalaxmi, & Obe, G. (2004). Controversial cytogenetic observations in mammalian somatic cells exposed to radiofrequency radiation. Radiation Research, 162, 481–496.
Ivancsits, S., Diem, E., Pilger, A., et al. (2002). Induction of DNA strand breaks by intermittent exposure to extremely-low-frequency electromagnetic fields in human diploid fibroblasts. Mutation Research, 519, 1–13.
Ivancsits, S., Diem, E., Jahn, O., et al. (2003). Intermittent extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields cause DNA damage in a dose-dependent way. International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health, 76, 431–436.
Ivancsits, S., Diem, E., Jahn, O., et al. (2003). Age-related effects on induction of DNA strand breaks by intermittent exposure to electromagnetic fields. Mechanism of Ageing and Development, 124, 847–850.
Guchelaar, H. J., Vermes, A., Vermes, I., et al. (1997). Apoptosis: Molecular mechanisms and implications for cancer chemotherapy. Pharmacology World Sciences, 19, 119–125.
Sherr, C. J. (1996). Cancer cell cycles. Science, 274, 1672–1677.
Aitken, R. J., Bennetts, L. E., Sawyer, D., et al. (2005). Impact of radio frequency electromagnetic radiation on DNA integrity in the male germline. International Journal of Andrology, 28, 171–179.
Koshland, D., & Strunnikov, A. (1996). Mitotic chromosome condensation. Annals Review Cell Biology, 12, 305–333.
Manjhi, J., Mathur, R., & Behari, J. (2009). Effect of low level capacitive-coupled pulsed electric field stimulation on mineral profile of weight-bearing bones in ovariectomized rats. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials, 92(1), 189–195.
Prakash, D., & Behari, J. (2009). Synergistic role of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles and pulsed electromagnetic field therapy to prevent bone loss in rats following exposure to simulated microgravity. International Journal of Nanomedicine, 4, 1–12.
Holmberg, B. (1995). Magnetic fields and cancer: Animal and cellular evidence—An overview. Environmental Health Perspectives, 103(2), 63–67.
Loscher, W., & Mevissen, M. (1994). Animal studies on the role of 50/60-Hertz magnetic fields in carcinogenesis. Life Science, 54, 1531–1543.
Ahlbom, A., Day, N., Feychting, M., et al. (2000). A pooled analysis of magnetic fields and childhood leukaemia. Brazilian Journal of Cancer, 83, 692–698.
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kesari, K.K., Kumar, S., Nirala, J. et al. Biophysical Evaluation of Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Field Effects on Male Reproductive Pattern. Cell Biochem Biophys 65, 85–96 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-012-9414-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-012-9414-6