Abstract
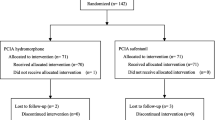
The objective is to study the effects of flurbiprofen axetil (FA) with fentanyl together in postoperative controlled intravenous analgesia (PCIA) on pain intensity, cytokine levels in peripheral blood and adverse reactions of thoracotomy patients. Fifty thoracotomy patients were divided into a FA and a control group, each with 25 cases. Postoperative analgesia was administered in the two groups using PCIA. The pressing times of analgesia pump, the visual analog scale (VAS) scores during resting and coughing at 2, 6, 24, 48, 72 h after surgery and the incidence of adverse drug reactions were recorded. Levels of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-2, and TNF-α in peripheral blood were determined before the administration of FA (T0), and at 24 h (T1), 48 h (T2), 72 h (T3) after surgery. The analgesia pump pressing times in the FA group was less than that of the control group. The VAS scores during resting and coughing at 2, 6, 24, 48, 72 h after surgery, were statistically less than those of control group. The incidence rate of nausea and vomiting was insignificantly different between the two groups. Administration of FA together with PCIA in thoracotomy patients can improve postoperative analgesia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Watkins, L. R., & Maier, S. F. (1995). Immune activation: the role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in inflammation, illness responses and pathological pain states. Pain, 63, 289–302.
Yan, H. Q., Banos, M. A., Herregodts, P., et al. (1992). Expression of interleukin (IL)-1 beta, IL-6 and their respective receptors in the normal rat brain and after injury. European Journal of Immunology, 22, 2963–2971.
Woolf, C. J., Allchorne, A., Safieh-Garabedian, B., et al. (1997). Cytokines, nerve growth factor and inflammatory hyperalgesia: The contribution of tumour necrosis factor alpha. British Journal of Pharmacology, 121, 417–424.
Aoki, H., Satomoto, M., Yamada, S., et al. (2002). The effectiveness of perioperative intravenous flurbiprefen in minor ear, neck and nose surgery. Masui, 5l, 857–861.
Yamashita, K., Fukusaki, M., Ando, Y., et al. (2006). Preoperative administration of intravenous flurbiprofen axetil reduces postoperative pain for spinal fusion surgery. Anesthesia, 20, 92–95.
Xu, G., Li, X., Duan, L., et al. (2004). Phase II clinical trials for the treatment of mild postoperative pain with flurbiprofen acetate injection. Chinese Journal of New Drugs, 13, 846–848.
Beilin, B., Shavit, Y., Trabekin, E., et al. (2003). The effects of postoperative pain management on immune response to surgery. Anesthesia and Analgesia, 97, 822–827.
Jiang, C. L., Xu, D., Lu, C. L., et al. (2000). Interleukin-2: Structural and biological relatedness to opioid peptides. NeuroImmunoModulation, 8, 20–24.
Wolf, G., Livshits, D., Beilin, B., et al. (2008). Interleukin-1 signaling is required for induction and maintenance of postoperative incisional pain: Genetic and pharmacological studies in mice. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, 22, 1072–1077.
Chueng-He, L., Pei-Chieh, C., et al. (2004). Preincisional intravenous pentoxifylline attenuating perioperative cytokine response, reducing morphine consumption, and improving recovery of bowel function in patients undergoing colorectal cancer surgery. Anesthesia and Analgesia, 99, 1465–1471.
Ching-Tang, W., Shu-Wen, J., et al. (2004). The effect of epidural clonidine on perioperative cytokine response, postoperative pain, and bowel function in patients undergoing colorectal surgery. Anesthesia and Analgesia, 99, 502–509.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, M., Li, B. & Kong, M. Effects of Flurbiprofen Axetil on Postoperative Analgesia and Cytokines in Peripheral Blood of Thoracotomy Patients. Cell Biochem Biophys 72, 429–432 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0482-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0482-7