Abstract
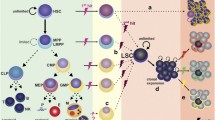
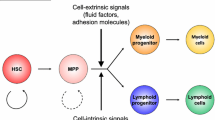
The replenishment of all blood cell lineages is hierarchically organized by the process of hematopoiesis, which is based on the differentiation pathways of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs). Due to the ability to balance between self-renewal and differentiation, hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) can generate the appropriate cell type that is required by the immune system and peripheral blood in response to physiological or pathological conditions. Numerous studies have shown that some proinflammatory cytokines contribute to the regulation of the various hematopoietic compartments. Of these, IFN-γ is a type II interferon primarily produced by T cells and natural killer cells, and plays a major role in the defense against invading pathogens and transformed cancer cells; moreover, a growing amount of research indicates that it exerts negative or positive regulatory effect on hematopoiesis. Although IFN-γ is a widely regarded negative regulator of HSC proliferation, it also participates in some chronic infections or hematological malignancies that induce bone marrow failure. Recent studies have demonstrated unexpected effects of IFN-γ, including the promotion of HSC formation and the stimulation of myelopoiesis. Here, we review the direct and indirect effects of IFN-γ on hematopoiesis, as well as the underlying signaling mechanisms of how IFN-γ modulates the self-renewal, cell cycle entry, and proliferation of HSCs. Next, we describe how IFN-γ affects different stages of the lineage differentiation from HSCs. Finally, we discuss the relationship between IFN-γ and compensatory extramedullary hematopoiesis, as well as some related clinical diseases.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Costa, G., Kouskoff, V., & Lacaud, G. (2012). Origin of blood cells and HSC production in the embryo. Trends in Immunology, 33(5), 215–223.
Ciriza, J., Thompson, H., Petrosian, R., Manilay, J. O., & Garcia-Ojeda, M. E. (2013). The migration of hematopoietic progenitors from the fetal liver to the fetal bone marrow: lessons learned and possible clinical applications. Experimental Hematology, 41(5), 411–423.
Nagai, Y., Garrett, K. P., Ohta, S., Bahrun, U., Kouro, T., Akira, S., et al. (2006). Toll-like receptors on hematopoietic progenitor cells stimulate innate immune system replenishment. Immunity, 24(6), 801–812.
Essers, M. A., Offner, S., Blanco-Bose, W. E., Waibler, Z., Kalinke, U., Duchosal, M. A., et al. (2009). IFNalpha activates dormant haematopoietic stem cells in vivo. Nature, 458(7240), 904–908.
Selleri, C., Sato, T., Anderson, S., Young, N. S., & Maciejewski, J. P. (1995). Interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha suppress both early and late stages of hematopoiesis and induce programmed cell death. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 165(3), 538–546.
Rezzoug, F., Huang, Y., Tanner, M. K., Wysoczynski, M., Schanie, C. L., Chilton, P. M., et al. (2008). TNF-alpha is critical to facilitate hemopoietic stem cell engraftment and function. Journal of Immunology, 180(1), 49–57.
Richards, M. K., Liu, F., Iwasaki, H., Akashi, K., & Link, D. C. (2003). Pivotal role of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in the development of progenitors in the common myeloid pathway. Blood, 102(10), 3562–3568.
Grassinger, J., Williams, B., Olsen, G. H., Haylock, D. N., & Nilsson, S. K. (2012). Granulocyte colony stimulating factor expands hematopoietic stem cells within the central but not endosteal bone marrow region. Cytokine, 58(2), 218–225.
Liu, J., & Cao, X. (2016). Cellular and molecular regulation of innate inflammatory responses. Cellular & Molecular Immunology, 13(6), 711–721.
Klimpel, G. R., Fleischmann, W. R., & Klimpel, K. D. Jr (1982). Gamma interferon (IFN gamma) and IFN alpha/beta suppress murine myeloid colony formation (CFU-C)N: magnitude of suppression is dependent upon level of colony-stimulating factor (CSF). Journal of Immunology, 129(1), 76–80.
Broxmeyer, H. E., Lu, L., Platzer, E., Feit, C., Juliano, L., & Rubin, B. Y. (1983). Comparative analysis of the influences of human gamma, alpha and beta interferons on human multipotential (CFU-GEMM), erythroid (BFU-E) and granulocyte-macrophage (CFU-GM) progenitor cells. Journal of Immunology, 131(3), 1300–1305.
de Bruin, A. M., Demirel, O., Hooibrink, B., Brandts, C. H., & Nolte, M. A. (2013). Interferon-gamma impairs proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells in mice. Blood, 121(18), 3578–3585.
Schurch, C. M., Riether, C., & Ochsenbein, A. F. (2014). Cytotoxic CD8 + T cells stimulate hematopoietic progenitors by promoting cytokine release from bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells. Cell Stem Cell, 14(4), 460–472.
McCabe, A., Zhang, Y., Thai, V., Jones, M., Jordan, M. B., & MacNamara, K. C. (2015). Macrophage-lineage cells negatively regulate the hematopoietic stem cell pool in response to interferon gamma at steady state and during infection. Stem Cells, 33(7), 2294–2305.
Belyaev, N. N., Biro, J., Langhorne, J., & Potocnik, A. J. (2013). Extramedullary myelopoiesis in malaria depends on mobilization of myeloid-restricted progenitors by IFN-gamma induced chemokines. PLoS Pathogens, 9(6), e1003406.
Frame, J. M., McGrath, K. E., & Palis, J. (2013). Erythro-myeloid progenitors: “definitive” hematopoiesis in the conceptus prior to the emergence of hematopoietic stem cells. Blood Cells, Molecules, and Diseases, 51(4), 220–225.
Yokota, T., Huang, J., Tavian, M., Nagai, Y., Hirose, J., Zuniga-Pflucker, J. C., et al. (2006). Tracing the first waves of lymphopoiesis in mice. Development, 133(10), 2041–2051.
Liu, C. P., & Auerbach, R. (1991). In vitro development of murine T cells from prethymic and preliver embryonic yolk sac hematopoietic stem cells. Development, 113(4), 1315–1323.
Bertrand, J. Y., Jalil, A., Klaine, M., Jung, S., Cumano, A., & Godin, I. (2005). Three pathways to mature macrophages in the early mouse yolk sac. Blood, 106(9), 3004–3011.
Orelio, C., Haak, E., Peeters, M., & Dzierzak, E. (2008). Interleukin-1-mediated hematopoietic cell regulation in the aorta-gonad-mesonephros region of the mouse embryo. Blood, 112(13), 4895–4904.
Li, Y., Esain, V., Teng, L., Xu, J., Kwan, W., Frost, I. M., et al. (2014). Inflammatory signaling regulates embryonic hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell production. Genes & Development, 28(23), 2597–2612.
Sawamiphak, S., Kontarakis, Z., & Stainier, D. Y. (2014). Interferon gamma signaling positively regulates hematopoietic stem cell emergence. Developmental Cell, 31(5), 640–653.
Bigas, A., Guiu, J., & Gama-Norton, L. (2013). Notch and Wnt signaling in the emergence of hematopoietic stem cells. Blood Cells, Molecules, and Diseases, 51(5), 264–270.
Baldridge, M. T., King, K. Y., Boles, N. C., Weksberg, D. C., & Goodell, M. A. (2010). Quiescent haematopoietic stem cells are activated by IFN-gamma in response to chronic infection. Nature, 465(7299), 793–797.
MacNamara, K. C., Jones, M., Martin, O., & Winslow, G. M. (2011). Transient activation of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells by IFNgamma during acute bacterial infection. PLoS One, 6(12), e28669.
Yu, J. M., Emmons, R. V., Hanazono, Y., Sellers, S., Young, N. S., & Dunbar, C. E. (1999). Expression of interferon-gamma by stromal cells inhibits murine long-term repopulating hematopoietic stem cell activity. Experimental Hematology, 27(5), 895–903.
Snoeck, H. W., Van Bockstaele, D. R., Nys, G., Lenjou, M., Lardon, F., Haenen, L., et al. (1994). Interferon gamma selectively inhibits very primitive CD34+CD38- and not more mature CD34+CD38+ human hematopoietic progenitor cells. The Journal of Experimental Medicine, 180(3), 1177–1182.
Selleri, C., Maciejewski, J. P., Sato, T., & Young, N. S. (1996). Interferon-gamma constitutively expressed in the stromal microenvironment of human marrow cultures mediates potent hematopoietic inhibition. Blood, 87(10), 4149–4157.
Yang, L., Dybedal, I., Bryder, D., Nilsson, L., Sitnicka, E., Sasaki, Y., et al. (2005). IFN-gamma negatively modulates self-renewal of repopulating human hemopoietic stem cells. Journal of Immunology, 174(2), 752–757.
Matatall, K. A., Shen, C. C., Challen, G. A., & King, K. Y. (2014). Type II interferon promotes differentiation of myeloid-biased hematopoietic stem cells. Stem Cells, 32(11), 3023–3030.
Matatall, K. A., Jeong, M., Chen, S., Sun, D., Chen, F., Mo, Q., et al. (2016). Chronic infection depletes hematopoietic stem cells through stress-induced terminal differentiation. Cell Report, 17(10), 2584–2595.
Ishihara, J., Umemoto, T., Yamato, M., Shiratsuchi, Y., Takaki, S., Petrich, B. G., et al. (2014). Nov/CCN3 regulates long-term repopulating activity of murine hematopoietic stem cells via integrin alphavbeta3. International Journal of Hematology, 99(4), 393–406.
Joshi, S., Sharma, B., Kaur, S., Majchrzak, B., Ueda, T., Fukunaga, R., et al. (2011). Essential role for Mnk kinases in type II interferon (IFNgamma) signaling and its suppressive effects on normal hematopoiesis. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 286(8), 6017–6026.
Sharma, B., Altman, J. K., Goussetis, D. J., Verma, A. K., & Platanias, L. C. (2011). Protein kinase R as mediator of the effects of interferon (IFN) gamma and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) alpha on normal and dysplastic hematopoiesis. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 286(31), 27506–27514.
Zhao, X., Ren, G., Liang, L., Ai, P., Zheng, B., Tischfield, J. A., et al. (2010). Brief report: interferon-gamma induces expansion of Lin(-)Sca-1(+)C-Kit(+) Cells. Stem Cells, 28(1), 122–126.
Malek, T. R., Danis, K. M., & Codias, E. K. (1989). Tumor necrosis factor synergistically acts with IFN-gamma to regulate Ly-6A/E expression in T lymphocytes, thymocytes and bone marrow cells. Journal of Immunology, 142(6), 1929–1936.
Snapper, C. M., Yamaguchi, H., Urban, J. F. Jr., & Finkelman, F. D. (1991). Induction of Ly-6A/E expression by murine lymphocytes after in vivo immunization is strictly dependent upon the action of IFN-alpha/beta and/or IFN-gamma. International Immunology, 3(9), 845–852.
Chen, J., Feng, X., Desierto, M. J., Keyvanfar, K., & Young, N. S. (2015). IFN-gamma-mediated hematopoietic cell destruction in murine models of immune-mediated bone marrow failure. Blood, 126(24), 2621–2631.
Tsoncheva, V. L., Todorova, K. A., & Maximova, V. A. (2008). Decreased DNA repair capacity of UV-irradiated cells following interferon treatment. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung Section C, 63(7–8), 605–611.
Tasdogan, A., Kumar, S., Allies, G., Bausinger, J., Beckel, F., Hofemeister, H., et al. (2016). DNA damage-induced HSPC malfunction depends on ROS accumulation downstream of IFN-1 signaling and bid mobilization. Cell Stem Cell, 19(6), 752–767.
Belyaev, N. N., Brown, D. E., Diaz, A. I., Rae, A., Jarra, W., Thompson, J., et al. (2010). Induction of an IL7-R(+)c-Kit(hi) myelolymphoid progenitor critically dependent on IFN-gamma signaling during acute malaria. Nature Immunology, 11(6), 477–485.
MacNamara, K. C., Oduro, K., Martin, O., Jones, D. D., McLaughlin, M., Choi, K., et al. (2011). Infection-induced myelopoiesis during intracellular bacterial infection is critically dependent upon IFN-γ signaling. Journal of Immunology, 186(2), 1032–1043.
Lin, F. C., Karwan, M., Saleh, B., Hodge, D. L., Chan, T., Boelte, K. C., et al. (2014). IFN-gamma causes aplastic anemia by altering hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell composition and disrupting lineage differentiation. Blood, 124(25), 3699–3708.
Lee, F. T., Mountain, A. J., Kelly, M. P., Hall, C., Rigopoulos, A., Johns, T. G., et al. (2005). Enhanced efficacy of radioimmunotherapy with 90Y-CHX-A’’-DTPA-hu3S193 by inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling with EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor AG1478. Clinical Cancer Research, 11(19 Pt 2), 7080s-7086s.
Maltby, S., Hansbro, N. G., Tay, H. L., Stewart, J., Plank, M., Donges, B., et al. (2014). Production and differentiation of myeloid cells driven by proinflammatory cytokines in response to acute pneumovirus infection in mice. Journal of Immunology, 193(8), 4072–4082.
de Bruin, A. M., Libregts, S. F., Valkhof, M., Boon, L., Touw, I. P., & Nolte, M. A. (2012). IFNγ induces monopoiesis and inhibits neutrophil development during inflammation. Blood, 119(6), 1543–1554.
de Bruin, A. M., Buitenhuis, M., van der Sluijs, K. F., van Gisbergen, K. P., Boon, L., & Nolte, M. A. (2010). Eosinophil differentiation in the bone marrow is inhibited by T cell-derived IFN-gamma. Blood, 116(14), 2559–2569.
Taddio, A., Tommasini, A., Valencic, E., Biagi, E., Decorti, G., De Iudicibus, S., et al. (2015). Failure of interferon-γ pre-treated mesenchymal stem cell treatment in a patient with Crohn’s disease. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 21(14), 4379–4384.
Liu, G. Y., Liu, Y., Lu, Y., Qin, Y. R., Di, G. H., Lei, Y. H., et al. (2016). Short-term memory of danger signals or environmental stimuli in mesenchymal stem cells: implications for therapeutic potential. Cellular & Molecular Immunology, 13(3), 369–378.
Baratono, S. R., Chu, N., Richman, L. P., & Behrens, E. M. (2015). Toll-like receptor 9 and interferon-γ receptor signaling suppress the B-cell fate of uncommitted progenitors in mice. European Journal of Immunology, 45(5), 1313–1325.
Yamada, G., Ogawa, M., Akagi, K., Miyamoto, H., Nakano, N., Itoh, S., et al. (1991). Specific depletion of the B-cell population induced by aberrant expression of human interferon regulatory factor 1 gene in transgenic mice. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 88(2), 532–536.
Young, H. A., Klinman, D. M., Reynolds, D. A., Grzegorzewski, K. J., Nii, A., Ward, J. M., et al. (1997). Bone marrow and thymus expression of interferon-gamma results in severe B-cell lineage reduction, T-cell lineage alterations, and hematopoietic progenitor deficiencies. Blood, 89(2), 583–595.
Garvy, B. A., & Riley, R. L. (1994). IFN-gamma abrogates IL-7-dependent proliferation in pre-B cells, coinciding with onset of apoptosis. Immunology, 81(3), 381–388.
Corfe, S. A., Rottapel, R., & Paige, C. J. (2011). Modulation of IL-7 thresholds by SOCS proteins in developing B lineage cells. Journal of Immunology, 187(7), 3499–3510.
Bradley, L. M., Dalton, D. K., & Croft, M. (1996). A direct role for IFN-gamma in regulation of Th1 cell development. Journal of Immunology, 157(4), 1350–1358.
Maldonado, R. A., Soriano, M. A., Perdomo, L. C., Sigrist, K., Irvine, D. J., Decker, T., et al. (2009). Control of T helper cell differentiation through cytokine receptor inclusion in the immunological synapse. The Journal of Experimental Medicine, 206(4), 877–892.
Shimozato, O., Ortaldo, J. R., Komschlies, K. L., & Young, H. A. (2002). Impaired NK cell development in an IFN-gamma transgenic mouse: aberrantly expressed IFN-gamma enhances hematopoietic stem cell apoptosis and affects NK cell differentiation. Journal of Immunology, 168(4), 1746–1752.
Wu, X., Chen, Y., Sun, R., Wei, H., & Tian, Z. (2012). Impairment of hepatic NK cell development in IFN-gamma deficient mice. Cytokine, 60(3), 616–625.
Urban, B. C., Hien, T. T., Day, N. P., Phu, N. H., Roberts, R., Pongponratn, E., et al. (2005). Fatal plasmodium falciparum malaria causes specific patterns of splenic architectural disorganization. Infection and Immunity, 73(4), 1986–1994.
Achtman, A. H., Khan, M., MacLennan, I. C., & Langhorne, J. (2003). Plasmodium chabaudi chabaudi infection in mice induces strong B cell responses and striking but temporary changes in splenic cell distribution. Journal of Immunology, 171(1), 317–324.
Furusawa, J., Mizoguchi, I., Chiba, ,Y., Hisada, M., Kobayashi, F., Yoshida, H., et al. (2016). Promotion of expansion and differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells by interleukin-27 into myeloid progenitors to control infection in emergency myelopoiesis. PLoS Pathogens, 12(3), e1005507.
Schurch, C., Riether, C., Amrein, M. A., & Ochsenbein, A. F. (2013). Cytotoxic T cells induce proliferation of chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells by secreting interferon-γ. The Journal of Experimental Medicine, 210(3), 605–621.
Rottman, M., Soudais, C., Vogt, G., Renia, L., Emile, J. F., Decaluwe, H., et al. (2008). IFN-gamma mediates the rejection of haematopoietic stem cells in IFN-gammaR1-deficient hosts. PLoS Medicine, 5(1), e26.
Cheng, Q., Ma, S., Lin, D., Mei, Y., Gong, H., Lei, L., et al. (2015). The S1P1 receptor-selective agonist CYM-5442 reduces the severity of acute GVHD by inhibiting macrophage recruitment. Cellular & Molecular Immunology, 12(6), 681–691.
Cai, Y., Ma, S., Liu, Y., Gong, H., Cheng, Q., Hu, B., et al. (2016). Adoptively transferred donor IL-17-producing CD4+ T cells augment, but IL-17 alleviates, acute graft-versus-host disease. Cellular & Molecular Immunology. doi:10.1038/cmi.2016.37.
Shlomchik, W. D. (2007). Graft-versus-host disease. Nature Reviews in Immunology, 7(5), 340–352.
Wang, H., & Yang, Y. G. (2014). The complex and central role of interferon-γ in graft-versus-host disease and graft-versus-tumor activity. Immunological Reviews, 258(1), 30–44.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National 973 Basic Research Program of China (# 2013CB944901) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (# 91442114, # 81472646 and # 81771686).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, Y., Zhang, C. The Regulatory Role of IFN-γ on the Proliferation and Differentiation of Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells. Stem Cell Rev and Rep 13, 705–712 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-017-9761-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-017-9761-1