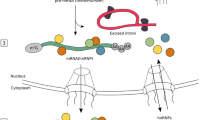
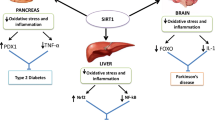
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are single-stranded noncoding regions of approximately 21 nucleotides that regulate protein synthesis by targeting mRNAs for translational repression or degradation at the post-transcriptional level. These classes of RNAs are highly conserved across species and are known to regulate several protein-coding genes in humans. Therefore, their dysregulation is synonymous with inflammation, autoimmunity, neurodegeneration, viral infections, heart diseases, and cancer, among other conditions. Recent years have witnessed considerable amount of research interest in studies on miRNA-mediated modulation of gene function during neuroinflammation. This review is a meticulous compilation of information on biogenesis of miRNAs and their role in neuroinflammatory diseases. Further, their potential as markers of inflammatory diseases or novel therapeutic agents against neuroinflammation has also been discussed in detail.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heimberg AM, Sempere LF, Moy VN, Donoghue PC, Peterson KJ (2008) MicroRNAs and the advent of vertebrate morphological complexity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(8):2946–2950
Sonkoly E, Pivarcsi A (2009) microRNAs in inflammation. Int Rev Immunol 28(6):535–561
Pasquinelli AE, Reinhart BJ, Slack F, Martindale MQ, Kuroda MI, Maller B, Hayward DC, Ball EE, Degnan B, Muller P, Spring J, Srinivasan A, Fishman M, Finnerty J, Corbo J, Levine M, Leahy P, Davidson E, Ruvkun G (2000) Conservation of the sequence and temporal expression of let-7 heterochronic regulatory RNA. Nature 408(6808):86–89
Pillai RS (2005) MicroRNA function: multiple mechanisms for a tiny RNA? RNA 11(12):1753–1761
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116(2):281–297
Tufekci KU, Oner MG, Genc S, Genc K (2011) MicroRNAs and multiple sclerosis. Autoimmune Dis 2011:807426
Griffiths-Jones S (2010) miRBase: microRNA sequences and annotation. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics Chapter 12 Unit 12 9:1–10
Kanwar JR, Mahidhara G, Kanwar RK (2010) MicroRNA in human cancer and chronic inflammatory diseases. Front Biosci (Schol Ed) 2:1113–1126
Sonntag KC (2010) MicroRNAs and deregulated gene expression networks in neurodegeneration. Brain Res 1338:48–57
Bushati N, Cohen SM (2008) MicroRNAs in neurodegeneration. Curr Opin Neurobiol 18(3):292–296
Nelson PT, Wang WX, Rajeev BW (2008) MicroRNAs (miRNAs) in neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Pathol 18(1):130–138
Lee Y, Kim M, Han J, Yeom KH, Lee S, Baek SH, Kim VN (2004) MicroRNA genes are transcribed by RNA polymerase II. EMBO J 23(20):4051–4060
Davis BN, Hata A (2009) Regulation of MicroRNA biogenesis: a miRiad of mechanisms. Cell Commun Signal 718
Davis-Dusenbery BN, Hata A (2010) Mechanisms of control of microRNA biogenesis. J Biochem 148(4):381–392
Han J, Lee Y, Yeom KH, Kim YK, Jin H, Kim VN (2004) The Drosha–DGCR8 complex in primary microRNA processing. Genes Dev 18(24):3016–3027
Carthew RW, Sontheimer EJ (2009) Origins and mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell 136(4):642–655
Rodriguez A, Vigorito E, Clare S, Warren MV, Couttet P, Soond DR, van Dongen S, Grocock RJ, Das PP, Miska EA, Vetrie D, Okkenhaug K, Enright AJ, Dougan G, Turner M, Bradley A (2007) Requirement of bic/microRNA-155 for normal immune function. Science 316(5824):608–611
Zhang Z, Qin YW, Brewer G, Jing Q (2012) MicroRNA degradation and turnover: regulating the regulators. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 3(4):593–600
Sethi P, Lukiw WJ (2009) Micro-RNA abundance and stability in human brain: specific alterations in Alzheimer's disease temporal lobe neocortex. Neurosci Lett 459(2):100–104
Zhou JY, Ma WL, Liang S, Zeng Y, Shi R, Yu HL, Xiao WW, Zheng WL (2009) Analysis of microRNA expression profiles during the cell cycle in synchronized HeLa cells. BMB Rep 42(9):593–598
Zhang Z, Zou J, Wang GK, Zhang JT, Huang S, Qin YW, Jing Q (2011) Uracils at nucleotide position 9-11 are required for the rapid turnover of miR-29 family. Nucleic Acids Res 39(10):4387–4395
Krol J, Busskamp V, Markiewicz I, Stadler MB, Ribi S, Richter J, Duebel J, Bicker S, Fehling HJ, Schubeler D, Oertner TG, Schratt G, Bibel M, Roska B, Filipowicz W (2010) Characterizing light-regulated retinal microRNAs reveals rapid turnover as a common property of neuronal microRNAs. Cell 141(4):618–631
Ruegger S, Grosshans H (2012) MicroRNA turnover: when, how, and why. Trends Biochem Sci 37(10):436–446
Chatterjee S, Fasler M, Bussing I, Grosshans H (2011) Target-mediated protection of endogenous microRNAs in C. elegans. Dev Cell 20(3):388–396
Chen PS, Su JL, Cha ST, Tarn WY, Wang MY, Hsu HC, Lin MT, Chu CY, Hua KT, Chen CN, Kuo TC, Chang KJ, Hsiao M, Chang YW, Chen JS, Yang PC, Kuo ML (2011) miR-107 promotes tumor progression by targeting the let-7 microRNA in mice and humans. J Clin Invest 121(9):3442–3455
Tsitsiou E, Lindsay MA (2009) microRNAs and the immune response. Curr Opin Pharmacol 9(4):514–520
Nahid MA, Satoh M, Chan EK (2011) MicroRNA in TLR signaling and endotoxin tolerance. Cell Mol Immunol 8(5):388–403
Quinn SR, O'Neill LA (2011) A trio of microRNAs that control Toll-like receptor signalling. Int Immunol 23(7):421–425
O'Neill LA, Sheedy FJ, McCoy CE (2011) MicroRNAs: the fine-tuners of Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 11(3):163–175
Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang KJ, Baltimore D (2006) NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(33):12481–12486
Tili E, Michaille JJ, Cimino A, Costinean S, Dumitru CD, Adair B, Fabbri M, Alder H, Liu CG, Calin GA, Croce CM (2007) Modulation of miR-155 and miR-125b levels following lipopolysaccharide/TNF-alpha stimulation and their possible roles in regulating the response to endotoxin shock. J Immunol 179(8):5082–5089
O'Connell RM, Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Cheng G, Baltimore D (2007) MicroRNA-155 is induced during the macrophage inflammatory response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(5):1604–1609
Sheedy FJ, Palsson-McDermott E, Hennessy EJ, Martin C, O'Leary JJ, Ruan Q, Johnson DS, Chen Y, O'Neill LA (2009) Negative regulation of TLR4 via targeting of the proinflammatory tumor suppressor PDCD4 by the microRNA miR-21. Nat Immunol 11(2):141–147
Streit WJ (2006) Microglial senescence: does the brain's immune system have an expiration date? Trends Neurosci 29(9):506–510
Streit WJ, Sammons NW, Kuhns AJ, Sparks DL (2004) Dystrophic microglia in the aging human brain. Glia 45(2):208–212
Ponomarev ED, Shriver LP, Maresz K, Dittel BN (2005) Microglial cell activation and proliferation precedes the onset of CNS autoimmunity. J Neurosci Res 81(3):374–389
Lynch MA (2009) The multifaceted profile of activated microglia. Mol Neurobiol 40(2):139–156
Kaushik DK, Gupta M, Das S, Basu A (2010) Kruppel-like factor 4, a novel transcription factor regulates microglial activation and subsequent neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation 768
Veremeyko T, Starossom SC, Weiner HL, Ponomarev ED (2012) Detection of microRNAs in microglia by real-time PCR in normal CNS and during neuroinflammation. J Vis Exp (65)
Ponomarev ED, Veremeyko T, Barteneva N, Krichevsky AM, Weiner HL (2010) MicroRNA-124 promotes microglia quiescence and suppresses EAE by deactivating macrophages via the C/EBP-alpha-PU.1 pathway. Nat Med 17(1):64–70
Ponomarev ED, Veremeyko T, Barteneva N, Krichevsky AM, Weiner HL (2011) MicroRNA-124 promotes microglia quiescence and suppresses EAE by deactivating macrophages via the C/EBP-alpha-PU.1 pathway. Nat Med 17(1):64–70
Celada A, Borras FE, Soler C, Lloberas J, Klemsz M, van Beveren C, McKercher S, Maki RA (1996) The transcription factor PU.1 is involved in macrophage proliferation. J Exp Med 184(1):61–69
Zhang L, Dong LY, Li YJ, Hong Z, Wei WS (2012) miR-21 represses FasL in microglia and protects against microglia-mediated neuronal cell death following hypoxia/ischemia. Glia
Tarassishin L, Loudig O, Bauman A, Shafit-Zagardo B, Suh HS, Lee SC (2011) Interferon regulatory factor 3 inhibits astrocyte inflammatory gene expression through suppression of the proinflammatory miR-155 and miR-155*. Glia 59(12):1911–1922
Noorbakhsh F, Ramachandran R, Barsby N, Ellestad KK, LeBlanc A, Dickie P, Baker G, Hollenberg MD, Cohen EA, Power C (2010) MicroRNA profiling reveals new aspects of HIV neurodegeneration: caspase-6 regulates astrocyte survival. FASEB J 24(6):1799–1812
Iyer A, Zurolo E, Prabowo A, Fluiter K, Spliet WG, van Rijen PC, Gorter JA, Aronica E (2012) MicroRNA-146a: a key regulator of astrocyte-mediated inflammatory response. PLoS One 7(9):e44789
Fineberg SK, Kosik KS, Davidson BL (2009) MicroRNAs potentiate neural development. Neuron 64(3):303–309
Vo NK, Cambronne XA, Goodman RH (2010) MicroRNA pathways in neural development and plasticity. Curr Opin Neurobiol 20(4):457–465
Johnson R, Zuccato C, Belyaev ND, Guest DJ, Cattaneo E, Buckley NJ (2008) A microRNA-based gene dysregulation pathway in Huntington's disease. Neurobiol Dis 29(3):438–445
Packer AN, Xing Y, Harper SQ, Jones L, Davidson BL (2008) The bifunctional microRNA miR-9/miR-9* regulates REST and CoREST and is downregulated in Huntington's disease. J Neurosci 28(53):14341–14346
Bravo JA, Dinan TG (2011) MicroRNAs: a novel therapeutic target for schizophrenia. Curr Pharm Des 17(2):176–188
Mouradian MM (2012) MicroRNAs in Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Dis 46(2):279–284
Hebert SS, De Strooper B (2007) Molecular biology. miRNAs in neurodegeneration. Science 317(5842):1179–1180
Ertekin-Taner N (2007) Genetics of Alzheimer's disease: a centennial review. Neurol Clin 25(3):611–667
Wilson RS, Scherr PA, Schneider JA, Tang Y, Bennett DA (2007) Relation of cognitive activity to risk of developing Alzheimer disease. Neurology 69(20):1911–1920
Bernardi L, Tomaino C, Anfossi M, Gallo M, Geracitano S, Puccio G, Colao R, Frangipane F, Mirabelli M, Smirne N, Maletta RG, Bruni AC (2008) Late onset familial Alzheimer's disease: novel presenilin 2 mutation and PS1 E318G polymorphism. J Neurol 255(4):604–606
Neve RL (2008) Alzheimer's disease sends the wrong signals—a perspective. Amyloid 15(1):1–4
Cheung KH, Shineman D, Muller M, Cardenas C, Mei L, Yang J, Tomita T, Iwatsubo T, Lee VM, Foskett JK (2008) Mechanism of Ca2+ disruption in Alzheimer's disease by presenilin regulation of InsP3 receptor channel gating. Neuron 58(6):871–883
Checler F, Sunyach C, Pardossi-Piquard R, Sevalle J, Vincent B, Kawarai T, Girardot N, St George-Hyslop P, da Costa CA (2007) The gamma/epsilon-secretase-derived APP intracellular domain fragments regulate p53. Curr Alzheimer Res 4(4):423–426
McLoughlin DM, Miller CC (2008) The FE65 proteins and Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci Res 86(4):744–754
Hebert SS, Horre K, Nicolai L, Bergmans B, Papadopoulou AS, Delacourte A, De Strooper B (2009) MicroRNA regulation of Alzheimer's amyloid precursor protein expression. Neurobiol Dis 33(3):422–428
Rovelet-Lecrux A, Hannequin D, Raux G, Le Meur N, Laquerriere A, Vital A, Dumanchin C, Feuillette S, Brice A, Vercelletto M, Dubas F, Frebourg T, Campion D (2006) APP locus duplication causes autosomal dominant early-onset Alzheimer disease with cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Nat Genet 38(1):24–26
Lukiw WJ (2007) Micro-RNA speciation in fetal, adult and Alzheimer's disease hippocampus. Neuroreport 18(3):297–300
Chen Y, Huang X, Zhang YW, Rockenstein E, Bu G, Golde TE, Masliah E, Xu H (2012) Alzheimer's beta-secretase (BACE1) regulates the cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway independently of beta-amyloid. J Neurosci 32(33):11390–11395
Sun X, Bromley-Brits K, Song W (2012) Regulation of beta-site APP-cleaving enzyme 1 gene expression and its role in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem 120(Suppl):162–170
Wang WX, Rajeev BW, Stromberg AJ, Ren N, Tang G, Huang Q, Rigoutsos I, Nelson PT (2008) The expression of microRNA miR-107 decreases early in Alzheimer's disease and may accelerate disease progression through regulation of beta-site amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme 1. J Neurosci 28(5):1213–1223
Colangelo V, Schurr J, Ball MJ, Pelaez RP, Bazan NG, Lukiw WJ (2002) Gene expression profiling of 12633 genes in Alzheimer hippocampal CA1: transcription and neurotrophic factor down-regulation and up-regulation of apoptotic and pro-inflammatory signaling. J Neurosci Res 70(3):462–473
Lukiw WJ, Zhao Y, Cui JG (2008) An NF-kappaB-sensitive micro RNA-146a-mediated inflammatory circuit in Alzheimer disease and in stressed human brain cells. J Biol Chem 283(46):31315–31322
Otaegui D, Baranzini SE, Armananzas R, Calvo B, Munoz-Culla M, Khankhanian P, Inza I, Lozano JA, Castillo-Trivino T, Asensio A, Olaskoaga J, Lopez de Munain A (2009) Differential micro RNA expression in PBMC from multiple sclerosis patients. PLoS One 4(7):e6309
Keller A, Leidinger P, Lange J, Borries A, Schroers H, Scheffler M, Lenhof HP, Ruprecht K, Meese E (2009) Multiple sclerosis: microRNA expression profiles accurately differentiate patients with relapsing-remitting disease from healthy controls. PLoS One 4(10):e7440
Du C, Liu C, Kang J, Zhao G, Ye Z, Huang S, Li Z, Wu Z, Pei G (2009) MicroRNA miR-326 regulates TH-17 differentiation and is associated with the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Nat Immunol 10(12):1252–1259
Junker A, Krumbholz M, Eisele S, Mohan H, Augstein F, Bittner R, Lassmann H, Wekerle H, Hohlfeld R, Meinl E (2009) MicroRNA profiling of multiple sclerosis lesions identifies modulators of the regulatory protein CD47. Brain 132(Pt 12):3342–3352
Lindberg RL, Hoffmann F, Mehling M, Kuhle J, Kappos L (2010) Altered expression of miR-17-5p in CD4+ lymphocytes of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis patients. Eur J Immunol 40(3):888–898
Cox MB, Cairns MJ, Gandhi KS, Carroll AP, Moscovis S, Stewart GJ, Broadley S, Scott RJ, Booth DR, Lechner-Scott J (2010) MicroRNAs miR-17 and miR-20a inhibit T cell activation genes and are under-expressed in MS whole blood. PLoS One 5(8):e12132
Murugaiyan G, Beynon V, Mittal A, Joller N, Weiner HL (2011) Silencing microRNA-155 ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 187(5):2213–2221
Lescher J, Paap F, Schultz V, Redenbach L, Scheidt U, Rosewich H, Nessler S, Fuchs E, Gartner J, Bruck W, Junker A (2012) MicroRNA regulation in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice and marmosets resembles regulation in human multiple sclerosis lesions. J Neuroimmunol 246(1–2):27–33
Cullen BR (2010) Five questions about viruses and microRNAs. PLoS Pathog 6(2):e1000787
Toma HS, Murina AT, Areaux RG Jr, Neumann DM, Bhattacharjee PS, Foster TP, Kaufman HE, Hill JM (2008) Ocular HSV-1 latency, reactivation and recurrent disease. Semin Ophthalmol 23(4):249–273
Lehtinen M, Koivisto V, Lahtinen P, Lehtinen T, Aaran RK, Leinikki P (1988) Phospholipase A2 activity is copurified together with herpes simplex virus-specified Fc receptor proteins. Intervirology 29(1):50–56
Bazan NG, Colangelo V, Lukiw WJ (2002) Prostaglandins and other lipid mediators in Alzheimer's disease. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 68–69:197–210
Hill JM, Zhao Y, Clement C, Neumann DM, Lukiw WJ (2009) HSV-1 infection of human brain cells induces miRNA-146a and Alzheimer-type inflammatory signaling. Neuroreport 20(16):1500–1505
Heaton RK, Clifford DB, Franklin DR Jr, Woods SP, Ake C, Vaida F, Ellis RJ, Letendre SL, Marcotte TD, Atkinson JH, Rivera-Mindt M, Vigil OR, Taylor MJ, Collier AC, Marra CM, Gelman BB, McArthur JC, Morgello S, Simpson DM, McCutchan JA, Abramson I, Gamst A, Fennema-Notestine C, Jernigan TL, Wong J, Grant I (2010) HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders persist in the era of potent antiretroviral therapy: CHARTER Study. Neurology 75(23):2087–2096
Gray F, Adle-Biassette H, Chretien F, Lorin de la Grandmaison G, Force G, Keohane C (2001) Neuropathology and neurodegeneration in human immunodeficiency virus infection. Pathogenesis of HIV-induced lesions of the brain, correlations with HIV-associated disorders and modifications according to treatments. Clin Neuropathol 20(4):146–155
Del Valle L, Pina-Oviedo S (2006) HIV disorders of the brain: pathology and pathogenesis. Front Biosci 11:718–732
Rom S, Rom I, Passiatore G, Pacifici M, Radhakrishnan S, Del Valle L, Pina-Oviedo S, Khalili K, Eletto D, Peruzzi F (2010) CCL8/MCP-2 is a target for mir-146a in HIV-1-infected human microglial cells. FASEB J 24(7):2292–2300
Li W, Li G, Steiner J, Nath A (2009) Role of Tat protein in HIV neuropathogenesis. Neurotox Res 16(3):205–220
Mishra R, Chhatbar C, Singh SK (2012) HIV-1 Tat C-mediated regulation of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor-3 by microRNA 32 in human microglia. J Neuroinflammation 9:131
Vaidya SA, Cheng G (2003) Toll-like receptors and innate antiviral responses. Curr Opin Immunol 15(4):402–407
O'Connell RM, Rao DS, Chaudhuri AA, Baltimore D (2010) Physiological and pathological roles for microRNAs in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 10(2):111–122
Xiao C, Rajewsky K (2009) MicroRNA control in the immune system: basic principles. Cell 136(1):26–36
Takeuchi O, Akira S (2008) MDA5/RIG-I and virus recognition. Curr Opin Immunol 20(1):17–22
Nazmi A, Dutta K, Basu A (2011) RIG-I mediates innate immune response in mouse neurons following Japanese encephalitis virus infection. PLoS One 6(6):e21761
Hou J, Wang P, Lin L, Liu X, Ma F, An H, Wang Z, Cao X (2009) MicroRNA-146a feedback inhibits RIG-I-dependent Type I IFN production in macrophages by targeting TRAF6, IRAK1, and IRAK2. J Immunol 183(3):2150–2158
Wang P, Hou J, Lin L, Wang C, Liu X, Li D, Ma F, Wang Z, Cao X (2010) Inducible microRNA-155 feedback promotes type I IFN signaling in antiviral innate immunity by targeting suppressor of cytokine signaling 1. J Immunol 185(10):6226–6233
Pan KM, Baldwin M, Nguyen J, Gasset M, Serban A, Groth D, Mehlhorn I, Huang Z, Fletterick RJ, Cohen FE et al (1993) Conversion of alpha-helices into beta-sheets features in the formation of the scrapie prion proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90(23):10962–10966
Frost B, Diamond MI (2010) Prion-like mechanisms in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev Neurosci 11(3):155–159
Saba R, Goodman CD, Huzarewich RL, Robertson C, Booth SA (2008) A miRNA signature of prion induced neurodegeneration. PLoS One 3(11):e3652
Montag J, Hitt R, Opitz L, Schulz-Schaeffer WJ, Hunsmann G, Motzkus D (2009) Upregulation of miRNA hsa-miR-342-3p in experimental and idiopathic prion disease. Mol Neurodegener 436
Saba R, Gushue S, Huzarewich RL, Manguiat K, Medina S, Robertson C, Booth SA (2012) MicroRNA 146a (miR-146a) is over-expressed during prion disease and modulates the innate immune response and the microglial activation state. PLoS One 7(2):e30832
Hu Z, Yu D, Almeida-Suhett C, Tu K, Marini AM, Eiden L, Braga MF, Zhu J, Li Z (2012) Expression of miRNAs and their cooperative regulation of the pathophysiology in traumatic brain injury. PLoS One 7(6):e39357
Cederberg D, Siesjo P (2010) What has inflammation to do with traumatic brain injury? Childs Nerv Syst 26(2):221–226
Hausmann EH, Berman NE, Wang YY, Meara JB, Wood GW, Klein RM (1998) Selective chemokine mRNA expression following brain injury. Brain Res 788(1–2):49–59
Saugstad JA (2010) MicroRNAs as effectors of brain function with roles in ischemia and injury, neuroprotection, and neurodegeneration. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30(9):1564–1576
Redell JB, Liu Y, Dash PK (2009) Traumatic brain injury alters expression of hippocampal microRNAs: potential regulators of multiple pathophysiological processes. J Neurosci Res 87(6):1435–1448
Sahni V, Mukhopadhyay A, Tysseling V, Hebert A, Birch D, McGuire TL, Stupp SI, Kessler JA (2010) BMPR1a and BMPR1b signaling exert opposing effects on gliosis after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci 30(5):1839–1855
Madathil SK, Nelson PT, Saatman KE, Wilfred BR (2011) MicroRNAs in CNS injury: potential roles and therapeutic implications. Bioessays 33(1):21–26
Lei P, Li Y, Chen X, Yang S, Zhang J (2009) Microarray based analysis of microRNA expression in rat cerebral cortex after traumatic brain injury. Brain Res 1284:191–201
Truettner JS, Alonso OF, Bramlett HM, Dietrich WD (2011) Therapeutic hypothermia alters microRNA responses to traumatic brain injury in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31(9):1897–1907
Morrissey DV, Lockridge JA, Shaw L, Blanchard K, Jensen K, Breen W, Hartsough K, Machemer L, Radka S, Jadhav V, Vaish N, Zinnen S, Vargeese C, Bowman K, Shaffer CS, Jeffs LB, Judge A, MacLachlan I, Polisky B (2005) Potent and persistent in vivo anti-HBV activity of chemically modified siRNAs. Nat Biotechnol 23(8):1002–1007
William CSC (2011) MicroRNAs in cancer translational research (Edited by William C. S. C.), Vol. 13, p. 557. Springer
van Rooij E, Marshall WS, Olson EN (2008) Toward microRNA-based therapeutics for heart disease: the sense in antisense. Circ Res 103(9):919–928
Allegra A, Alonci A, Campo S, Penna G, Petrungaro A, Gerace D, Musolino C (2012) Circulating microRNAs: new biomarkers in diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of cancer (Review). Int J Oncol 41(6):1897–1912
Ajit SK (2012) Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers, therapeutic targets, and signaling molecules. Sensors (Basel) 12(3):3359–3369
Lukiw WJ, Pogue AI (2007) Induction of specific micro RNA (miRNA) species by ROS-generating metal sulfates in primary human brain cells. J Inorg Biochem 101(9):1265–1269
Cogswell JP, Ward J, Taylor IA, Waters M, Shi Y, Cannon B, Kelnar K, Kemppainen J, Brown D, Chen C, Prinjha RK, Richardson JC, Saunders AM, Roses AD, Richards CA (2008) Identification of miRNA changes in Alzheimer's disease brain and CSF yields putative biomarkers and insights into disease pathways. J Alzheimers Dis 14(1):27–41
Boissonneault V, Plante I, Rivest S, Provost P (2009) MicroRNA-298 and microRNA-328 regulate expression of mouse beta-amyloid precursor protein-converting enzyme 1. J Biol Chem 284(4):1971–1981
De Santis G, Ferracin M, Biondani A, Caniatti L, Rosaria Tola M, Castellazzi M, Zagatti B, Battistini L, Borsellino G, Fainardi E, Gavioli R, Negrini M, Furlan R, Granieri E (2010) Altered miRNA expression in T regulatory cells in course of multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 226(1–2):165–171
Kim J, Inoue K, Ishii J, Vanti WB, Voronov SV, Murchison E, Hannon G, Abeliovich A (2007) A MicroRNA feedback circuit in midbrain dopamine neurons. Science 317(5842):1220–1224
Gillardon F, Mack M, Rist W, Schnack C, Lenter M, Hildebrandt T, Hengerer B (2008) MicroRNA and proteome expression profiling in early-symptomatic alpha-synuclein(A30P)-transgenic mice. Proteomics Clin Appl 2(5):697–705
Perkins DO, Jeffries CD, Jarskog LF, Thomson JM, Woods K, Newman MA, Parker JS, Jin J, Hammond SM (2007) microRNA expression in the prefrontal cortex of individuals with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Genome Biol 8(2):R27
Beveridge NJ, Tooney PA, Carroll AP, Gardiner E, Bowden N, Scott RJ, Tran N, Dedova I, Cairns MJ (2008) Dysregulation of miRNA 181b in the temporal cortex in schizophrenia. Hum Mol Genet 17(8):1156–1168
Acknowledgments
The work in the author's laboratory is funded by grants from the Department of Biotechnology(Award #s BT/PR/5799/MED/14/698/2005 and BT/PR8682/Med/14/1273/2007), Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (27(0173)/07/EMR-II), and Life Science Research Board, Defense Research & Developmental Organization (DLS/81/48222/LSRB-213/EPB2010), Government of India. A.B. is a recipient of the National Bioscience Award for Career Development from DBT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thounaojam, M.C., Kaushik, D.K. & Basu, A. MicroRNAs in the Brain: It's Regulatory Role in Neuroinflammation. Mol Neurobiol 47, 1034–1044 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8400-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8400-3