Abstract
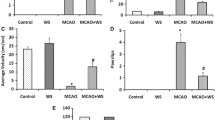
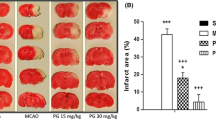
Withania somnifera (WS), popularly known as “Ashwagandha” has been used for centuries as a nerve tonic. Its protective effect has been elucidated in many neurodegenerative pathologies, although there is a paucity of data regarding its effects in ischemic stroke. We examined the neuroprotective properties of an aqueous extract of WS in both pre- and poststroke treatment regimens in a mouse model of permanent distal middle cerebral artery occlusion (pMCAO). WS (200 mg/kg) improved functional recovery and significantly reduced the infarct volume in mice, when compared to those treated with vehicle, in both paradigms. We investigated the protective mechanism/s induced by WS using brain cortices by testing its ability to modulate the expression of key proteins in the ischemic-apoptotic cascade. The Western blots and immunofluorescence analyses of mice cortices revealed that WS upregulated the expression of hemeoxygenase 1 (HO1) and attenuated the expression of the proapoptotic protein poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP1) via the PARP1-AIF pathway, thus preventing the nuclear translocation of apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF), and subsequent apoptosis. Semaphorin-3A (Sema3A) expression was reduced in WS-treated group, whereas Wnt, pGSK3β, and pCRMP2 expression levels were virtually unaltered. These results indicate the interplay of antioxidant-antiapoptic pathways and the possible involvement of angiogenesis in the protective mechanism of WS while emphasizing the noninvolvement of one of the prime pathways of neurogenesis. Our results suggest that WS could be a potential prophylactic as well as a therapeutic agent aiding stroke repair, and that part of its mechanism could be attributed to its antiapoptotic and antioxidant properties.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roger VL, Go AS, Lloyd-Jones DM, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Borden WB, Bravata DM, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Fullerton HJ, Gillespie C, Hailpern SM, Heit JA, Howard VJ, Kissela BM, Kittner SJ, Lackland DT, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Makuc DM, Marcus GM, Marelli A, Matchar DB, Moy CS, Mozaffarian D, Mussolino ME, Nichol G, Paynter NP, Soliman EZ, Sorlie PD, Sotoodehnia N, Turan TN, Virani SS, Wong ND, Woo D, Turner MB (2012) Heart disease and stroke statistics–2012 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 125:e2–e220
Zivin JA (2009) Acute stroke therapy with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) since it was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Ann Neurol 66:6–10
Barreto G, White RE, Ouyang Y, Xu L, Giffard RG (2011) Astrocytes: targets for neuroprotection in stroke. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem 11:164–173
Wermuth CG (2004) Multitargeted drugs: the end of the “one-target-one-disease” philosophy? Drug Discov Today 9:826–827
Adams JD Jr, Yang J, Mishra LC, Singh BB (2002) Effects of ashwagandha in a rat model of stroke. Altern Ther Health Med 8:18–19
Rathore P, Dohare P, Varma S, Ray A, Sharma U, Jagannathan NR, Ray M (2008) Curcuma oil: reduces early accumulation of oxidative product and is anti-apoptogenic in transient focal ischemia in rat brain. Neurochem Res 33:1672–1682
Shah ZA, Nada SE, Dore S (2011) Heme oxygenase 1, beneficial role in permanent ischemic stroke and in Gingko biloba (EGb 761) neuroprotection. Neuroscience 180:248–255
Zhu J, Jiang Y, Wu L, Lu T, Xu G, Liu X (2012) Suppression of local inflammation contributes to the neuroprotective effect of ginsenoside Rb1 in rats with cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience 202:342–351
Kulkarni SK, Dhir A (2008) Withania somnifera: an Indian ginseng. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32:1093–1105
Kumar S, Seal CJ, Howes MJ, Kite GC, Okello EJ (2010) In vitro protective effects of Withania somnifera (L.) dunal root extract against hydrogen peroxide and beta-amyloid(1-42)-induced cytotoxicity in differentiated PC12 cells. Phytother Res 24:1567–1574
Russo A, Izzo AA, Cardile V, Borrelli F, Vanella A (2001) Indian medicinal plants as antiradicals and DNA cleavage protectors. Phytomedicine 8:125–132
Kumar S, Harris RJ, Seal CJ, Okello EJ (2012) An aqueous extract of Withania somnifera root inhibits amyloid beta fibril formation in vitro. Phytother Res 26:113–117
Choudhary MI, Nawaz SA, Ul-Haq Z, Lodhi MA, Ghayur MN, Jalil S, Riaz N, Yousuf S, Malik A, Gilani AH, Ur-Rahman A (2005) Withanolides, a new class of natural cholinesterase inhibitors with calcium antagonistic properties. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 334:276–287
Ahmad M, Saleem S, Ahmad AS, Ansari MA, Yousuf S, Hoda MN, Islam F (2005) Neuroprotective effects of Withania somnifera on 6-hydroxydopamine induced Parkinsonism in rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 24:137–147
Sankar SR, Manivasagam T, Krishnamurti A, Ramanathan M (2007) The neuroprotective effect of Withania somnifera root extract in MPTP-intoxicated mice: an analysis of behavioral and biochemical variables. Cell Mol Biol Lett 12:473–481
Kumar P, Kumar A (2009) Possible neuroprotective effect of Withania somnifera root extract against 3-nitropropionic acid-induced behavioral, biochemical, and mitochondrial dysfunction in an animal model of Huntington’s disease. J Med Food 12:591–600
Naidu PS, Singh A, Kulkarni SK (2006) Effect of Withania somnifera root extract on reserpine-induced orofacial dyskinesia and cognitive dysfunction. Phytother Res 20:140–146
Tohda C, Joyashiki E (2009) Sominone enhances neurite outgrowth and spatial memory mediated by the neurotrophic factor receptor, RET. Br J Pharmacol 157:1427–1440
Mohanty IR, Arya DS, Gupta SK (2008) Withania somnifera provides cardioprotection and attenuates ischemia-reperfusion induced apoptosis. Clin Nutr 27:635–642
Chaudhary G, Sharma U, Jagannathan NR, Gupta YK (2003) Evaluation of Withania somnifera in a middle cerebral artery occlusion model of stroke in rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 30:399–404
Kataria H, Wadhwa R, Kaul SC, Kaur G (2012) Water extract from the leaves of Withania somnifera protect RA differentiated C6 and IMR-32 cells against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. PLoS One 7:e37080
Margaill I, Plotkine M, Lerouet D (2005) Antioxidant strategies in the treatment of stroke. Free Radic Biol Med 39:429–443
Aztatzi-Santillan E, Nares-Lopez FE, Marquez-Valadez B, Aguilera P, Chanez-Cardenas ME (2010) The protective role of heme oxygenase-1 in cerebral ischemia. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem 10:310–316
Li X, Klaus JA, Zhang J, Xu Z, Kibler KK, Andrabi SA, Rao K, Yang ZJ, Dawson TM, Dawson VL, Koehler RC (2010) Contributions of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 and -2 to nuclear translocation of apoptosis-inducing factor and injury from focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurochem 113:1012–1022
Kim YT, Hur EM, Snider WD, Zhou FQ (2011) Role of GSK3 signaling in neuronal morphogenesis. Front Mol Neurosci 4:48
Wu D, Pan W (2010) GSK3: a multifaceted kinase in Wnt signaling. Trends Biochem Sci 35:161–168
Joyal JS, Sitaras N, Binet F, Rivera JC, Stahl A, Zaniolo K, Shao Z, Polosa A, Zhu T, Hamel D, Djavari M, Kunik D, Honore JC, Picard E, Zabeida A, Varma DR, Hickson G, Mancini J, Klagsbrun M, Costantino S, Beausejour C, Lachapelle P, Smith LE, Chemtob S, Sapieha P (2011) Ischemic neurons prevent vascular regeneration of neural tissue by secreting semaphorin 3A. Blood 117:6024–6035
Bacigaluppi M, Comi G, Hermann DM (2010) Animal models of ischemic stroke. Part two: modeling cerebral ischemia. Open Neurol J 4:34–38
Freireich EJ, Gehan EA, Rall DP, Schmidt LH, Skipper HE (1966) Quantitative comparison of toxicity of anticancer agents in mouse, rat, hamster, dog, monkey, and man. Cancer Chemother Rep Part 1(50):219–244
Jennions MD, Moller AP (2003) A survey of the statistical power of research in behavioral ecology and animal behavior. Behav Ecol 14:438–445
Parihar MS, Chaudhary M, Shetty R, Hemnani T (2004) Susceptibility of hippocampus and cerebral cortex to oxidative damage in streptozotocin treated mice: prevention by extracts of Withania somnifera and Aloe vera. J Clin Neurosci: Off J Neurosurg Soc Australas 11:397–402
Love S (1999) Oxidative stress in brain ischemia. Brain Pathol 9:119–131
Dore S (2002) Decreased activity of the antioxidant heme oxygenase enzyme: implications in ischemia and in Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic Biol Med 32:1276–1282
Dulak J, Deshane J, Jozkowicz A, Agarwal A (2008) Heme oxygenase-1 and carbon monoxide in vascular pathobiology: focus on angiogenesis. Circulation 117:231–241
Al-Owais MM, Scragg JL, Dallas ML, Boycott HE, Warburton P, Chakrabarty A, Boyle JP, Peers C (2012) Carbon monoxide mediates the anti-apoptotic effects of heme oxygenase-1 in medulloblastoma DAOY cells via K + channel inhibition. J Biol Chem 287:24754–24764
Otterbein LE, Bach FH, Alam J, Soares M, Tao Lu H, Wysk M, Davis RJ, Flavell RA, Choi AM (2000) Carbon monoxide has anti-inflammatory effects involving the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Nat Med 6:422–428
Nakka VP, Gusain A, Mehta SL, Raghubir R (2008) Molecular mechanisms of apoptosis in cerebral ischemia: multiple neuroprotective opportunities. Mol Neurobiol 37:7–38
Broughton BR, Reutens DC, Sobey CG (2009) Apoptotic mechanisms after cerebral ischemia. Stroke 40:e331–e339
Broker LE, Kruyt FA, Giaccone G (2005) Cell death independent of caspases: a review. Clin Cancer Res 11:3155–3162
Cande C, Cohen I, Daugas E, Ravagnan L, Larochette N, Zamzami N, Kroemer G (2002) Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF): a novel caspase-independent death effector released from mitochondria. Biochimie 84:215–222
Cregan SP, Fortin A, MacLaurin JG, Callaghan SM, Cecconi F, Yu SW, Dawson TM, Dawson VL, Park DS, Kroemer G, Slack RS (2002) Apoptosis-inducing factor is involved in the regulation of caspase-independent neuronal cell death. J Cell Biol 158:507–517
Shih CM, Wu JS, Ko WC, Wang LF, Wei YH, Liang HF, Chen YC, Chen CT (2003) Mitochondria-mediated caspase-independent apoptosis induced by cadmium in normal human lung cells. J Cell Biochem 89:335–347
Plesnila N, Zhu C, Culmsee C, Groger M, Moskowitz MA, Blomgren K (2004) Nuclear translocation of apoptosis-inducing factor after focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 24:458–466
Zhu C, Qiu L, Wang X, Hallin U, Cande C, Kroemer G, Hagberg H, Blomgren K (2003) Involvement of apoptosis-inducing factor in neuronal death after hypoxia-ischemia in the neonatal rat brain. J Neurochem 86:306–317
Chaitanya GV, Babu PP (2008) Multiple apoptogenic proteins are involved in the nuclear translocation of apoptosis inducing factor during transient focal cerebral ischemia in rat. Brain Res 1246:178–190
Cao G, Xing J, Xiao X, Liou AK, Gao Y, Yin XM, Clark RS, Graham SH, Chen J (2007) Critical role of calpain I in mitochondrial release of apoptosis-inducing factor in ischemic neuronal injury. J Neurosci 27:9278–9293
Abd Elmageed ZY, Naura AS, Errami Y, Zerfaoui M (2012) The poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs): new roles in intracellular transport. Cell Signal 24:1–8
Yu SW, Wang H, Poitras MF, Coombs C, Bowers WJ, Federoff HJ, Poirier GG, Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2002) Mediation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1-dependent cell death by apoptosis-inducing factor. Science 297:259–263
Chiarugi A (2002) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase: killer or conspirator? The ‘suicide hypothesis’ revisited. Trends Pharmacol Sci 23:122–129
Carmichael ST (2008) Themes and strategies for studying the biology of stroke recovery in the poststroke epoch. Stroke 39:1380–1388
Font MA, Arboix A, Krupinski J (2010) Angiogenesis, neurogenesis and neuroplasticity in ischemic stroke. Curr Cardiol Rev 6:238–244
Gangaraju S, Sultan K, Whitehead SN, Nilchi L, Slinn J, Li X, Hou ST (2013) Cerebral endothelial expression of Robo1 affects brain infiltration of polymorphonuclear neutrophils during mouse stroke recovery. Neurobiol Dis 54:24–31
Hou ST, Keklikian A, Slinn J, O’Hare M, Jiang SX, Aylsworth A (2008) Sustained up-regulation of semaphorin 3A, neuropilin1, and doublecortin expression in ischemic mouse brain during long-term recovery. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 367:109–115
Soleman S, Filippov MA, Dityatev A, Fawcett JW (2013) Targeting the neural extracellular matrix in neurological disorders. Neuroscience 253:194–213
Kolodkin AL, Matthes DJ, Goodman CS (1993) The semaphorin genes encode a family of transmembrane and secreted growth cone guidance molecules. Cell 75:1389–1399
Luo Y, Raible D, Raper JA (1993) Collapsin: a protein in brain that induces the collapse and paralysis of neuronal growth cones. Cell 75:217–227
Pekcec A, Yigitkanli K, Jung JE, Pallast S, Xing C, Antipenko A, Minchenko M, Nikolov DB, Holman TR, Lo EH, van Leyen K (2013) Following experimental stroke, the recovering brain is vulnerable to lipoxygenase-dependent semaphorin signaling. FASEB J 27:437–445
Acevedo LM, Barillas S, Weis SM, Gothert JR, Cheresh DA (2008) Semaphorin 3A suppresses VEGF-mediated angiogenesis yet acts as a vascular permeability factor. Blood 111:2674–2680
Nada SE, Tulsulkar J, Shah ZA (2013) Heme oxygenase 1-mediated neurogenesis is enhanced by ginkgo biloba (EGb 761(R)) after permanent ischemic stroke in mice. Mol Neurobiol 49(2):945–56
Song H, Ming G, He Z, Lehmann M, McKerracher L, Tessier-Lavigne M, Poo M (1998) Conversion of neuronal growth cone responses from repulsion to attraction by cyclic nucleotides. Science 281:1515–1518
Suchting S, Bicknell R, Eichmann A (2006) Neuronal clues to vascular guidance. Exp Cell Res 312:668–675
Ohab JJ, Fleming S, Blesch A, Carmichael ST (2006) A neurovascular niche for neurogenesis after stroke. J Neurosci 26:13007–13016
Shruster A, Ben-Zur T, Melamed E, Offen D (2012) Wnt signaling enhances neurogenesis and improves neurological function after focal ischemic injury. PLoS One 7:e40843
Hirabayashi Y, Itoh Y, Tabata H, Nakajima K, Akiyama T, Masuyama N, Gotoh Y (2004) The Wnt/beta-catenin pathway directs neuronal differentiation of cortical neural precursor cells. Development 131:2791–2801
Ho KS, Scott MP (2002) Sonic hedgehog in the nervous system: functions, modifications and mechanisms. Curr Opin Neurobiol 12:57–63
Galvez-Contreras AY, Gonzalez-Castaneda RE, Luquin S, Gonzalez-Perez O (2012) Role of fibroblast growth factor receptors in astrocytic stem cells. Curr Signal Transduct Ther 7:81–86
Shimojo H, Ohtsuka T, Kageyama R (2011) Dynamic expression of notch signaling genes in neural stem/progenitor cells. Front Neurosci 5:78
Rosso SB, Inestrosa NC (2013) WNT signaling in neuronal maturation and synaptogenesis. Front Cell Neurosci 7:103
Oliva CA, Vargas JY, Inestrosa NC (2013) Wnts in adult brain: from synaptic plasticity to cognitive deficiencies. Front Cell Neurosci 7:224
Toledo EM, Colombres M, Inestrosa NC (2008) Wnt signaling in neuroprotection and stem cell differentiation. Prog Neurobiol 86:281–296
Varela-Nallar L, Inestrosa NC (2013) Wnt signaling in the regulation of adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Front Cell Neurosci 7:100
Xing Y, Zhang X, Zhao K, Cui L, Wang L, Dong L, Li Y, Liu Z, Wang C, Zhang X, Zhu C, Qiao H, Ji Y, Cao X (2012) Beneficial effects of sulindac in focal cerebral ischemia: a positive role in Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Brain Res 1482:71–80
Hur EM, Zhou FQ (2010) GSK3 signalling in neural development. Nat Rev Neurosci 11:539–551
Veeman MT, Axelrod JD, Moon RT (2003) A second canon. Functions and mechanisms of beta-catenin-independent Wnt signaling. Dev Cell 5:367–377
Grumolato L, Liu G, Mong P, Mudbhary R, Biswas R, Arroyave R, Vijayakumar S, Economides AN, Aaronson SA (2010) Canonical and noncanonical Wnts use a common mechanism to activate completely unrelated coreceptors. Genes Dev 24:2517–2530
Lu Q, Harris VA, Sun X, Hou Y, Black SM (2013) Ca(2)(+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II contributes to hypoxic ischemic cell death in neonatal hippocampal slice cultures. PLoS One 8:e70750
Repici M, Centeno C, Tomasi S, Forloni G, Bonny C, Vercelli A, Borsello T (2007) Time-course of c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation after cerebral ischemia and effect of D-JNKI1 on c-Jun and caspase-3 activation. Neuroscience 150:40–49
Schlessinger K, Hall A, Tolwinski N (2009) Wnt signaling pathways meet Rho GTPases. Genes Dev 23:265–277
Arimura N, Menager C, Kawano Y, Yoshimura T, Kawabata S, Hattori A, Fukata Y, Amano M, Goshima Y, Inagaki M, Morone N, Usukura J, Kaibuchi K (2005) Phosphorylation by Rho kinase regulates CRMP-2 activity in growth cones. Mol Cell Biol 25:9973–9984
Hou ST, Jiang SX, Aylsworth A, Ferguson G, Slinn J, Hu H, Leung T, Kappler J, Kaibuchi K (2009) CaMKII phosphorylates collapsin response mediator protein 2 and modulates axonal damage during glutamate excitotoxicity. J Neurochem 111:870–881
Acknowledgments
This work was supported partly by a grant from the National Institutes of Health—(R00AT004197) and start-up funds from the University of Toledo to ZAS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raghavan, A., Shah, Z.A. Withania somnifera Improves Ischemic Stroke Outcomes by Attenuating PARP1-AIF-Mediated Caspase-Independent Apoptosis. Mol Neurobiol 52, 1093–1105 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8907-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8907-2