Abstract
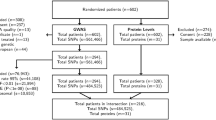
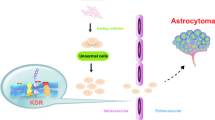
A glioma is the most common type of brain tumor that accounts for nearly 80 % of brain cancers. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptor, the kinase insert domain receptor (KDR), are involved in the angiogenesis of cancers. In this study, we investigate whether the polymorphisms of VEGF and KDR are associated with a glioma risk. Blood samples were collected from 477 glioma patients and 477 healthy controls. Five tag-single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of KDR were obtained from the HapMap database, and eight tag-SNPs of VEGF were selected based on previous studies. After extraction of genomic DNAs by a Qiagen DNA blood kit, the SNPs of VEGF and KDR were genotyped with a Sequenom MassArray iPLEX platform and further analyzed with matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry. The odds ratios and their 95 % confidence interval (95 % CI) were used to assess the association between VEGF, KDR polymorphisms, and glioma risks with the aid of SPSS 13.0 software. The haplotype analysis demonstrated that two SNPs of VEGF [rs3025039 (C>T), rs2010963 (G>C)] could elevate the susceptibility to a glioma in the homozygous model [odds ratio (OR) = 3.13 (95 % confidence interval (CI) 1.30–7.49, P = 0.007) and OR = 1.58 (95 % CI 1.07–2.34, P = 0.022), respectively], dominant model [OR = 1.38 (95 % CI 1.04–1.84, P = 0.025) and OR = 1.32 (95 % CI 1.01–1.72, P = 0.043), respectively], and allelic model [OR = 1.43 (95 % CI 1.11–1.84, P = 0.005) and OR = 1.24 (95 % CI 1.04–1.50, P = 0.019), respectively]. Furthermore, three SNPs of KDR [rs7667298 (A>G), rs2305948 (C>T), rs1870377 (T>A)] were also assumed to be associated with an increased risk of a glioma in the homozygous [OR = 1.93 (95 % CI 1.30–2.86, P = 0.001), OR = 2.56 (95 % CI 1.28–5.11, P = 0.006), and OR = 1.52 (95 % CI 1.00–2.31, P = 0.049), respectively], dominant [OR = 1.52 (95 % CI 1.16–1.98, P = 0.002), OR = 1.41 (95 % CI 1.05–1.87, P = 0.020), and OR = 1.48 (95 % CI 1.13–1.93, P = 0.004), respectively], and allele models [OR = 1.39 (95 % CI 1.15–1.67, P = 0.001), OR = 1.47 (95 % CI 1.14–1.89, P = 0.002), and OR = 1.27 (95 % CI 1.05–1.52, P = 0.013), respectively]. The genetic polymorphisms of VEGF [rs3025039 (C>T), rs2010963 (G>C)] and KDR [rs7667298 (A>G), rs2305948 (C>T), rs1870377 (T>A)] increased glioma susceptibility in a Chinese population, suggesting the possibility of VEGF and KDR as genetic markers for glioma. Additional functional and association studies with different ethnic groups included are needed to further confirm our results.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schwartzbaum JA, Fisher JL, Aldape KD, Wrensch M (2006) Epidemiology and molecular pathology of glioma. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 2:494–503, quiz 1 p following 16
Armstrong GT, Stovall M, Robison LL (2010) Long-term effects of radiation exposure among adult survivors of childhood cancer: results from the childhood cancer survivor study. Radiat Res 174:840–850
Louis DN, von Deimling A (1995) Hereditary tumor syndromes of the nervous system: overview and rare syndromes. Brain Pathol 5:145–151
Melean G, Sestini R, Ammannati F, Papi L (2004) Genetic insights into familial tumors of the nervous system. Am J Med Genet C: Semin Med Genet 129C:74–84
Shete S, Hosking FJ, Robertson LB, Dobbins SE, Sanson M, Malmer B et al (2009) Genome-wide association study identifies five susceptibility loci for glioma. Nat Genet 41:899–904
Wrensch M, Jenkins RB, Chang JS, Yeh RF, Xiao Y, Decker PA et al (2009) Variants in the CDKN2B and RTEL1 regions are associated with high-grade glioma susceptibility. Nat Genet 41:905–908
Sanson M, Hosking FJ, Shete S, Zelenika D, Dobbins SE, Ma Y et al (2011) Chromosome 7p11.2 (EGFR) variation influences glioma risk. Hum Mol Genet 20:2897–2904
Andersson U, Schwartzbaum J, Wiklund F, Sjostrom S, Liu Y, Tsavachidis S et al (2010) A comprehensive study of the association between the EGFR and ERBB2 genes and glioma risk. Acta Oncol 49:767–775
Villegas G, Lange-Sperandio B, Tufro A (2005) Autocrine and paracrine functions of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in renal tubular epithelial cells. Kidney Int 67:449–457
Cebe-Suarez S, Zehnder-Fjallman A, Ballmer-Hofer K (2006) The role of VEGF receptors in angiogenesis; complex partnerships. Cell Mol Life Sci : CMLS 63:601–615
Shibuya M, Claesson-Welsh L (2006) Signal transduction by VEGF receptors in regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Exp Cell Res 312:549–560
Nagy JA, Benjamin L, Zeng H, Dvorak AM, Dvorak HF (2008) Vascular permeability, vascular hyperpermeability and angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 11:109–119
Zhou YH, Tan F, Hess KR, Yung WK (2003) The expression of PAX6, PTEN, vascular endothelial growth factor, and epidermal growth factor receptor in gliomas: relationship to tumor grade and survival. Clin Cancer Res : Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res 9:3369–3375
Knizetova P, Ehrmann J, Hlobilkova A, Vancova I, Kalita O, Kolar Z et al (2008) Autocrine regulation of glioblastoma cell cycle progression, viability and radioresistance through the VEGF-VEGFR2 (KDR) interplay. Cell Cycle 7:2553–2561
Renner W, Kotschan S, Hoffmann C, Obermayer-Pietsch B, Pilger E (2000) A common 936 C/T mutation in the gene for vascular endothelial growth factor is associated with vascular endothelial growth factor plasma levels. J Vasc Res 37:443–448
Watson CJ, Webb NJ, Bottomley MJ, Brenchley PE (2000) Identification of polymorphisms within the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) gene: correlation with variation in VEGF protein production. Cytokine 12:1232–1235
Lee SJ, Lee SY, Jeon HS, Park SH, Jang JS, Lee GY et al (2005) Vascular endothelial growth factor gene polymorphisms and risk of primary lung cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev : Publ Am Assoc Cancer Res Am Soc Prev Oncol 14:571–575
Slattery ML, Lundgreen A, Wolff RK (2014) VEGFA, FLT1, KDR and colorectal cancer: assessment of disease risk, tumor molecular phenotype, and survival. Mol Carcinog 53(Suppl 1):E140–E150
Beeghly-Fadiel A, Shu XO, Lu W, Long J, Cai Q, Xiang YB et al (2011) Genetic variation in VEGF family genes and breast cancer risk: a report from the Shanghai Breast Cancer Genetics Study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev : Publ Am Assoc Cancer Res Am Soc Prev Oncol 20:33–41
Rinck-Junior JA, Oliveira C, Lourenco GJ, Sagarra RA, Derchain SF, Segalla JG, et al (2014) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) polymorphism and increased risk of epithelial ovarian cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol
Guan X, Zhao H, Niu J, Tang D, Ajani JA, Wei Q (2009) The VEGF -634G>C promoter polymorphism is associated with risk of gastric cancer. BMC Gastroenterol 9:77
Garcia-Closas M, Malats N, Real FX, Yeager M, Welch R, Silverman D et al (2007) Large-scale evaluation of candidate genes identifies associations between VEGF polymorphisms and bladder cancer risk. PLoS Genet 3, e29
Wang Y, Zheng Y, Zhang W, Yu H, Lou K, Zhang Y et al (2007) Polymorphisms of KDR gene are associated with coronary heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 50:760–767
Zhang W, Sun K, Zhen Y, Wang D, Wang Y, Chen J et al (2009) VEGF receptor-2 variants are associated with susceptibility to stroke and recurrence. Stroke J Cereb Circ 40:2720–2726
Galan A, Ferlin A, Caretti L, Buson G, Sato G, Frigo AC et al (2010) Association of age-related macular degeneration with polymorphisms in vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor. Ophthalmology 117:1769–1774
Churchill AJ, Carter JG, Lovell HC, Ramsden C, Turner SJ, Yeung A et al (2006) VEGF polymorphisms are associated with neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Hum Mol Genet 15:2955–2961
Novosel EC, Kleinhans C, Kluger PJ (2011) Vascularization is the key challenge in tissue engineering. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 63:300–311
Tokunaga T, Oshika Y, Abe Y, Ozeki Y, Sadahiro S, Kijima H et al (1998) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) mRNA isoform expression pattern is correlated with liver metastasis and poor prognosis in colon cancer. Br J Cancer 77:998
Li Y-H, Hu C-F, Shao Q, Huang M-Y, Hou J-H, Xie D et al (2008) Elevated expressions of survivin and VEGF protein are strong independent predictors of survival in advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Transl Med 6:1
Han H, Silverman JF, Santucci TS, Macherey RS, Tung MY, Weyant RJ et al (2001) Vascular endothelial growth factor expression in stage I non-small cell lung cancer correlates with neoangiogenesis and a poor prognosis. Ann Surg Oncol 8:72–79
Yao JC, Wang L, Wei D, Gong W, Hassan M, Wu T-T et al (2004) Association between expression of transcription factor Sp1 and increased vascular endothelial growth factor expression, advanced stage, and poor survival in patients with resected gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10:4109–4117
Hansen TF, Jakobsen A (2011) Clinical implications of genetic variations in the VEGF system in relation to colorectal cancer. Pharmacogenomics 12:1681–1693
Ke Q, Liang J, Wang LN, Hu ZB, Jin GF, Zhou Y et al (2008) Potentially functional polymorphisms of the vascular endothelial growth factor gene and risk of gastric cancer. Mol Carcinog 47:647–651
Bae SJ, Kim JW, Kang H, Hwang SG, Oh D, Kim NK (2008) Gender-specific association between polymorphism of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF 936 C>T) gene and colon cancer in Korea. Anticancer Res 28:1271–1276
Jacobs EJ, Feigelson HS, Bain EB, Brady KA, Rodriguez C, Stevens VL et al (2006) Polymorphisms in the vascular endothelial growth factor gene and breast cancer in the cancer prevention study II cohort. Breast Cancer Res : BCR 8:R22
Seetharam L, Gotoh N, Maru Y, Neufeld G, Yamaguchi S, Shibuya M (1995) A unique signal transduction from FLT tyrosine kinase, a receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor VEGF. Oncogene 10:135–147
Kim DH, Xu W, Kamel-Reid S, Liu X, Jung CW, Kim S et al (2010) Clinical relevance of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGFA) and VEGF receptor (VEGFR2) gene polymorphism on the treatment outcome following imatinib therapy. Ann Oncol : Off J Eur Soc Med Oncol / ESMO 21:1179–1188
Dong G, Guo X, Fu X, Wan S, Zhou F, Myers RE et al (2012) Potentially functional genetic variants in KDR gene as prognostic markers in patients with resected colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci 103:561–568
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Nature Science Foundation (81372705), the Shanghai Science and Technology Development Fund (10JC1409802), and the Wu Jieping Medical Foundation (320.6750.11092).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Jiannan Zhang, Jian Yang, and Yuqing Chen equally contributed to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Yang, J., Chen, Y. et al. Genetic Variants of VEGF (rs201963 and rs3025039) and KDR (rs7667298, rs2305948, and rs1870377) Are Associated with Glioma Risk in a Han Chinese Population: a Case-Control Study. Mol Neurobiol 53, 2610–2618 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9240-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9240-0