Abstract
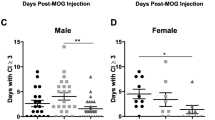
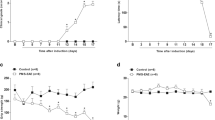
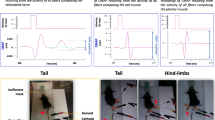
Pain is one of the main symptoms of multiple sclerosis, a demyelinating disease of the central nervous system that affects millions of people worldwide. The experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) is considered an experimental model of multiple sclerosis, and besides motor weakness, hypernociception is one of the clinical signs of animals with EAE. In this study, we investigated the influence of some cytokines in the generation of the hypernociceptive response in a mouse model of EAE using MOG35–55. We measured some cytokines in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG), an important anatomical structure involved in pain. We found increased levels of the cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, and Kc in DRGs of animals with EAE. We used the antibody IL-1ra to antagonize the effects of IL-1β, and animals presented a decrease in the hypernociceptive response. Thus, our results suggest that hypernociception in this experimental model of EAE may be a consequence of the increase in some cytokines in DRGs, especially IL-1β.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
McFarland HF, Martin R (2007) Multiple sclerosis: a complicated picture of autoimmunity. Nat Immunol 8(9):913–919
Siniscalchi A, Gallelli L, De Sarro G (2007) Drugs treatment of pain in multiple sclerosis. Curr Clin Pharmacol 2(3):227–233
Beard S, Hunn A, Wight J (2003) Treatments for spasticity and pain in multiple sclerosis: a systematic review. Health Technol Assess 7:1–124
Foley PL, Vesterinen HM, Laird BJ, Sena ES, Colvin LA, Chandran S, MacLeod MR, Fallon MT (2013) Prevalence and natural history of pain in adults with multiple sclerosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain 154(5):632–642
O’Connor AB et al (2008) Pain associated with multiple sclerosis: systematic review and proposed classification. Pain 137:96–111
Gold R, Linington C, Lassmann H (2006) Understanding pathogenesis and therapy of multiple sclerosis via animal models: 70 years of merits and culprits in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis research. Brain 129:1953–1971
Bettelli E, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK (2007) T(H)-17 cells in the circle of immunity and autoimmunity. Nat Immunol 8:345–350
Dos Santos AC, Roffê E, Arantes RM, Juliano L, Pesquero JL, Pesquero JB, Bader M, Teixeira MM et al (2008) Kinin B2 receptor regulates chemokines CCL2 and CCL5 expression and modulates leukocyte recruitment and pathology in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) in mice. J Neuroinflammation 5:49
Grace PM, Hutchinson MR, Maier SF, Watkins LR (2014) Pathological pain and the neuroimmune interface. Nat Rev Immunol 14(4):217–231
Sean Riminton D, Körner H, Strickland DH, Lemckert FA, Pollard JD, Sedgwick JD (1998) Challenging cytokine redundancy: inflammatory cell movement and clinical course of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis are normal in lymphotoxin-deficient, but not tumor necrosis factor-deficient, mice. J Exp Med 187(9):1517–1528
Schiffenbauer J, Streit WJ, Butfiloski E, LaBow M, Edwards C 3rd, Moldawer LL (2000) The induction of EAE is only partially dependent on TNF receptor signaling but requires the IL-1 type I receptor. Clin Immunol 95(2):117–123
Cunha TM, Verri WA Jr, Valério DA, Guerrero AT, Nogueira LG, Vieira SM, Souza DG, Teixeira MM et al (2008) Role of cytokines in mediating mechanical hypernociception in a model of delayed-type hypersensitivity in mice. Eur J Pain 12(8):1059–1068
Begum F, Zhu W, Cortes C, MacNeil B, Namaka M (2013) Elevation of tumor necrosis factor α in dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord is associated with neuroimmune modulation of pain in an animal model of multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 8(3):677–690
Thibault K, Calvino B, Pezet S (2011) Characterisation of sensory abnormalities observed in an animal model of multiple sclerosis: a behavioural and pharmacological study. Eur J Pain 15(3):231.e1-16
Rodrigues DH, Sachs D, Teixeira AL (2009) Mechanical hypernociception in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 67(1):78–81
Olechowski CJ, Truong JJ, Kerr BJ (2009) Neuropathic pain behaviours in a chronic-relapsing model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). Pain 141(1–2):156–164
Aicher SA, Silverman MB, Winkler CW, Bebo BF Jr (2004) Hyperalgesia in an animal model of multiple sclerosis. Pain 110(3):560–570
Weaver A, Silva AG, Nuttall RK et al (2005) An elevated matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) in an animal model of multiple sclerosis is protective by affecting Th1/Th2 polarization. FASEB J 19:1668–1670
Brundula V, Rewcastle NB, Metz LM, Bernard CC, Yong VW (2002) Targeting leukocyte MMPs and transmigration: minocycline as a potential therapy for multiple sclerosis. Brain 125:1297–1308
Coelho FM, Pinho V, Amaral FA et al (2008) The chemokine receptors CXCR1/2 modulate antigen-induced arthritis by regulating adhesion of neutrophils to the synovial microvasculature. Arthritis Rheum 58:2329–2337
Dos Santos AC, Roffê E, Arantes RM, Juliano L, Pesquero JL, Pesquero JB, Bader M, Teixeira MM et al (2008) Kinin B2 receptor regulates chemokines CCL2 and CCL5 expression and modulates leukocyte recruitment and pathology in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) in mice. J Neuroinflammation 5:5–49
Rodrigues DH, Vilela MC, Barcelos LS, Pinho V, Teixeira MM, Teixeira AL (2010) Absence of PI3Kgamma leads to increased leukocyte apoptosis and diminished severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol 222(1–2):90–94
Galic MA, Riazi K, Pittman QJ (2012) Cytokines and brain excitability. Front Neuroendocrinol 33(1):116–125
Wang J, Yu J, Ding CP, Han SP, Zeng XY, Wang JY (2015) Transforming growth factor-beta in the red nucleus plays antinociceptive effect under physiological and pathological pain conditions. Neuroscience 291:37–45
Sloane E, Ledeboer A, Seibert W, Coats B, van Strien M, Maier SF, Johnson KW, Chavez R et al (2009) Anti-inflammatory cytokine gene therapy decreases sensory and motor dysfunction in experimental multiple sclerosis: MOG-EAE behavioral and anatomical symptom treatment with cytokine gene therapy. Brain Behav Immun 23(1):92–100
Lisi L, Navarra P, Cirocchi R, Sharp A, Stigliano E, Feinstein DL, Dello Russo C (2012) Rapamycin reduces clinical signs and neuropathic pain in a chronic model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol 243(1–2):43–51
Melanson M, Miao P, Eisenstat D, Gong Y, Gu X, Au K, Zhu W, Begum F et al (2009) Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis-induced upregulation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the dorsal root ganglia. Mult Scler 15(10):1135–1145
Matsuki T, Nakae S, Sudo K, Horai R, Iwakura Y (2006) Abnormal T cell activation caused by the imbalance of the IL-1/IL-1R antagonist system is responsible for the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Int Immunol 18(2):399–407
Sim YB, Park SH, Kang YJ, Jung JS, Ryu OH, Choi MG, Suh HW (2012) Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) increases pain behavior and the blood glucose level: possible involvement of sympathetic nervous system. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 102(1):170–176
Binshtok AM, Wang H, Zimmermann K, Amaya F, Vardeh D, Shi L, Brenner GJ, Ji RR et al (2008) Nociceptors are interleukin-1beta sensors. J Neurosci 28:14062–14073
Caterina MJ, Leffler A, Malmberg AB, Martin WJ, Trafton J, Petersen-Zeitz KR, Koltzenburg M, Basbaum AI et al (2000) Impaired nociception and pain sensation in mice lacking the capsaicin receptor. Science 14 288(5464):306–313
Cummins TR, Sheets PL, Waxman SG (2007) The roles of sodium channels in nociception: implications for mechanisms of pain. Pain 131(3):243–257
Hwang SW, Cho H, Kwak J, Lee SY, Kang CJ, Jung J, Cho S, Min KH et al (2000) Direct activation of capsaicin receptors by products of lipoxygenases: endogenous capsaicin-like substances. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97(11):6155–6160
Ji RR, Samad TA, Jin SX, Schmoll R, Woolf CJ (2002) p38 MAPK activation by NGF in primary sensory neurons after inflammation increases TRPV1 levels and maintains heat hyperalgesia. Neuron 36(1):57–68
Jarvis MF, Honore P, Shieh CC et al (2007) A-803467, a potent and selective Nav1.8 sodium channel blocker, attenuates neuropathic and inflammatory pain in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(20):8520–8525
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was funded by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG) and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodrigues, D.H., Leles, B.P., Costa, V.V. et al. IL-1β Is Involved with the Generation of Pain in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Mol Neurobiol 53, 6540–6547 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9552-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9552-0