Abstract
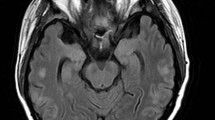
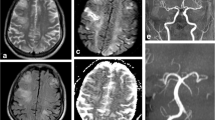
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) is a rare neurological disease. Recently, an increase in the number of transplantations has led to more cases being associated with PRES than what was previously reported. Calcineurin inhibitors (CNIs) are major risk factors for PRES in posttransplantation patients. The mechanisms of the development of PRES remain to be unclear. The typical clinical symptoms of PRES include seizures, acute encephalopathy syndrome, and visual symptoms. The hyperintense signal on fluid-attenuated inversion recovery image is the characteristic of the imaging appearance in these patients. In addition, other abnormal signals distributed in multiple locations are also reported in some atypical cases. Unfortunately, PRES is often not recognized or diagnosed too late due to complicated differential diagnoses, such as ischemic stroke, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, and neurodegenerative diseases. Thus, this review emphasizes the importance of considering the possibility of PRES when neurological disturbances appear after solid organ transplantation or hematopoietic cell transplantation. Moreover, this review demonstrates the molecular mechanisms of PRES associated with CNIs after transplantation, which aims to help clinicians further understand PRES in the transplantation era.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACEI:
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors
- ADC:
-
Apparent diffusion coefficient
- CNIs:
-
Calcineurin inhibitors
- CsA:
-
Cyclosporine A
- CSF:
-
Cerebrospinal fluid
- DNA:
-
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- DWI:
-
Diffusion weighted MRI
- EBV:
-
Epstein–Barr virus
- FLAIR:
-
Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery
- HSCT:
-
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- ODS:
-
Osmotic demyelination syndrome
- PAI-1:
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1
- PKA:
-
Protein kinase A
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase C
- PRES:
-
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome
- PTLD:
-
Posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorder
- T1WI:
-
T1-weighted image
- T2WI:
-
T2-weighted image
- TAC:
-
Tacrolimus
- SOT:
-
Solid organ transplantation
References
Hinchey J, Chaves C, Appignani B, Breen J, Pao L, Wang A, Pessin MS, Lamy C et al (1996) A reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. N Engl J Med 334:494–500
Bartynski WS (2008) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome, part 1: fundamental imaging and clinical features. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:1036–1042
Lamy C, Oppenheim C, Mas JL (2014) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Handb Clin Neurol 121:1687–1701
Staykov D, Schwab S (2012) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. J Intensive Care Med 27:11–24
Wu Q, Marescaux C, Wolff V, Jeung MY, Kessler R, Lauer V, Chen Y (2010) Tacrolimus-associated posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome after solid organ transplantation. Eur Neurol 64:169–177
Agildere AM, Basaran C, Cakir B, Ozgul E, Kural F, Haberal M (2006) Evaluation of neurologic complications by brain MRI in kidney and liver transplant recipients. Transplant Proc 38:611–618
McKinney AM, Short J, Truwit CL, McKinney ZJ, Kozak OS, SantaCruz KS, Teksam M (2007) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: incidence of atypical regions of involvement and imaging findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 189:904–912
Alexander S, David VG, Varughese S, Tamilarasi V, Jacob CK (2013) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in a renal allograft recipient: a complication of immunosuppression? Indian J Nephrol 23:137–139
Alparslan M, Bora U, Huseyin K, Ayhan D, Gultekin S (2013) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in a renal transplanted patient. Am J Case Rep 14:241–244
Apuri S, Carlin K, Bass E, Nguyen PT, Greene JN (2014) Tacrolimus associated posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome—a case series and review. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis 6:e2014014
Arimura FE, Camargo PC, Costa AN, Teixeira RH, Carraro RM, Afonso JE Jr, Campos SV, Samano MN et al (2014) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in lung transplantation: 5 case reports. Transplant Proc 46:1845–1848
Baldini M, Bartolini E, Gori S, Bonanni E, Cosottini M, Iudice A, Murri L (2010) Epilepsy after neuroimaging normalization in a woman with tacrolimus-related posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Epilepsy Behav 17:558–560
Barbas AS, Rege AS, Castleberry AW, Gommer J, Ellis MJ, Brennan TV, Collins BH, Martin AE et al (2013) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome independently associated with tacrolimus and sirolimus after multivisceral transplantation. Am J Transplant Off J Am Soc Transplant Am Soc Transplant Surg 13:808–810
Cordelli DM, Masetti R, Bernardi B, Barcia G, Gentile V, Biagi C, Prete A, Pession A et al (2012) Status epilepticus as a main manifestation of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome after pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Pediatr Blood Cancer 58:785–790
Cruz RJ Jr, DiMartini A, Akhavanheidari M, Iacovoni N, Boardman JF, Donaldson J, Humar A, Bartynski WS (2012) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in liver transplant patients: clinical presentation, risk factors and initial management. Am J Transplant Off J Am Soc Transplant Am Soc Transplant Surg 12:2228–2236
Fukuyama T, Tanaka M, Nakazawa Y, Motoki N, Inaba Y, Higuchi T, Koike K (2011) Prophylactic treatment for hypertension and seizure in a case of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation after posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Pediatr Transplant 15:E169–E173
Hammerstrom AE, Howell J, Gulbis A, Rondon G, Champlin RE, Popat U (2013) Tacrolimus-associated posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in hematopoietic allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Am J Hematol 88:301–305
Hayes D Jr, Adler B, Turner TL, Mansour HM (2014) Alternative tacrolimus and sirolimus regimen associated with rapid resolution of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome after lung transplantation. Pediatr Neurol 50:272–275
Heo S, Cho HJ, Jeon IS (2010) A case of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in a child with myelodysplastic syndrome following allogenic bone marrow transplantation. Pediatr Hematol Oncol 27:59–64
Jennane S, el Mahtat M, Konopacki J, Malfuson JV, Doghmi K, Mikdame M, De Revel T (2013) Cyclosporine-related posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome after cord blood stem cell transplantation. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther 6:71
Loar RW, Patterson MC, O’Leary PW, Driscoll DJ, Johnson JN (2013) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and hemorrhage associated with tacrolimus in a pediatric heart transplantation recipient. Pediatr Transplant 17:E67–E70
Moris D, Vernadakis S, Lionaki S, Daikos G, Zavos G (2014) An uncommon cause of acutely altered mental status in a renal transplant recipient. Ups J Med Sci 119:50–54
Qin W, Tan CY, Huang X, Huang Z, Tao Y, Fu P (2011) Rapamycin-induced posterior reversible encephalopathy in a kidney transplantation patient. Int Urol Nephrol 43:913–916
Rosso L, Nosotti M, Mendogni P, Palleschi A, Tosi D, Montoli M, Pappalettera M, Tarsia P et al (2012) Lung transplantation and posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: a case series. Transplant Proc 44:2022–2025
Santos MM, Tannuri AC, Gibelli NE, Ayoub AA, Maksoud-Filho JG, Andrade WC, Velhote MC, Silva MM et al (2011) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome after liver transplantation in children: a rare complication related to calcineurin inhibitor effects. Pediatr Transplant 15:157–160
Shao X, He Z, Tang L, Gao L (2012) Tacrolimus-associated ischemic optic neuropathy and posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome after small bowel transplantation. Transplantation 94:e58–e60
Shoji T, Bando T, Fujinaga T, Chen F, Kohno M, Yabe M, Yabe H, Date H (2012) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome due to immunosuppressant after living-donor lobar lung transplantation: report of a case. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 60:514–517
Torelli GF, Natalino F, Barberi W, Iori AP, Andreoli C, Valle V, Mercanti C, Perrone S et al (2011) Early onset of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) during Cyclosporine-A infusion. Leuk Res 35:1423–1424
Ueda N, Kawamura M, Nakazawa S, Hirai T, Kishikawa H, Nishimura K (2014) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) after kidney transplantation: a case report. Hinyokika Kiyo Acta Urologica Jpn 60:387–392
Yilmaz S, Gokben S, Arikan C, Calli C, Serdaroglu G (2010) Reversibility of cytotoxic edema in tacrolimus leukoencephalopathy. Pediatr Neurol 43:359–362
Zaman S R (2012) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome postautologous peripheral stem cell transplantation for multiple myeloma. BMJ Case Rep 2012
Bartynski WS, Tan HP, Boardman JF, Shapiro R, Marsh JW (2008) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome after solid organ transplantation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:924–930
Wong R, Beguelin GZ, de Lima M, Giralt SA, Hosing C, Ippoliti C, Forman AD, Kumar AJ et al (2003) Tacrolimus-associated posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome after allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Br J Haematol 122:128–134
Graham BR, Pylypchuk GB (2014) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in an adult patient undergoing peritoneal dialysis: a case report and literature review. BMC Nephrol 15:10
Nakajima N, Ueda M, Nagayama H, Yamazaki M, Katayama Y (2013) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome due to hypercalcemia associated with parathyroid hormone-related peptide: a case report and review of the literature. Intern Med 52:2465–2468
Tsang BK, Kermeen FD, Hopkins PM, Chambers DC (2010) Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome: diagnosis and management in the setting of lung transplantation. Int Med J 40:716–720
Rabinstein AA, Mandrekar J, Merrell R, Kozak OS, Durosaro O, Fugate JE (2012) Blood pressure fluctuations in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis Off J Natl Stroke Assoc 21:254–258
Fugate JE, Claassen DO, Cloft HJ, Kallmes DF, Kozak OS, Rabinstein AA (2010) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: associated clinical and radiologic findings. Mayo Clin Proc 85:427–432
Hefzy HM, Bartynski WS, Boardman JF, Lacomis D (2009) Hemorrhage in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: imaging and clinical features. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:1371–1379
Araz C, Camkiran A, Zeyneloglu P, Sezgin A, Moray G, Pirat A, Arslan G (2013) Early-onset posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome after solid organ transplantation in pediatric patients: a report of 2 cases. Transplant Proc 45:3555–3557
Hugonnet E, Da Ines D, Boby H, Claise B, Petitcolin V, Lannareix V, Garcier JM (2013) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES): features on CT and MR imaging. Diagn Interv Imaging 94:45–52
Zivkovic SA (2013) Neurologic complications after liver transplantation. World J Hepatol 5:409–416
Stevens CJ, Heran MK (2012) The many faces of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Br J Radiol 85:1566–1575
King JD, Rosner MH (2010) Osmotic demyelination syndrome. Am J Medi Sci 339:561–567
de Souza A (2013) Movement disorders and the osmotic demyelination syndrome. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 19:709–716
Alleman AM (2014) Osmotic demyelination syndrome: central pontine myelinolysis and extrapontine myelinolysis. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 35:153–159
Lake W, Chang JE, Kennedy T, Morgan A, Salamat S, Baskaya MK (2013) A case series of primary central nervous system posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disorder: imaging and clinical characteristics. Neurosurgery 72:960–970, discussion 970
Vegso G, Hajdu M, Sebestyen A (2011) Lymphoproliferative disorders after solid organ transplantation-classification, incidence, risk factors, early detection and treatment options. Pathol Oncol Res 17:443–454
Pruitt AA, Graus F, Rosenfeld MR (2013) Neurological complications of solid organ transplantation. Neurohospitalist 3:152–166
Fung JJ, Alessiani M, Abu-Elmagd K, Todo S, Shapiro R, Tzakis A, Van Thiel D, Armitage J et al (1991) Adverse effects associated with the use of FK 506. Transplant Proc 23:3105–3108
Hewer E, Kellner-Weldon F, Abu-Isa J, Schmitt AM (2014) Multiple cerebral lesions in a 60-year-old female patient with a history of liver transplantation. Neuropathol Off J Jpn Soc Neuropathol 34:425–427
Meriden Z, Bullock GC, Bagg A, Bonatti H, Cousar JB, Lopes MB, Robbins MK, Cathro HP (2010) Posttransplantation lymphoproliferative disease involving the pituitary gland. Hum Pathol 41:1641–1645
Baehring JM, Landry ML, Cooper D, Hui P, Bannykh S (2008) CSF IgH gene rearrangement analysis in isolated post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder of the central nervous system. J Neuro-Oncol 86:57–60
Shah R, Bag AK, Chapman PR, Cure JK (2010) Imaging manifestations of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Clin Radiol 65:431–439
Sahraian MA, Radue EW, Eshaghi A, Besliu S, Minagar A (2012) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: a review of the neuroimaging features and differential diagnosis. Eur J Neurol Off J Eur Fed Neurol Soc 19:1060–1069
Horger M, Beschorner R, Beck R, Nagele T, Schulze M, Ernemann U, Heckl S (2012) Common and uncommon imaging findings in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) with differential diagnostic considerations. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 114:1123–1130
Pruitt AA, Graus F, Rosenfeld MR (2013) Neurological complications of transplantation: part I: hematopoietic cell transplantation. Neurohospitalist 3:24–38
Weissert R (2011) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Neuroimmunol 231:73–77
Stott VL, Hurrell MA, Anderson TJ (2005) Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome: a misnomer reviewed. Int Med J 35:83–90
Dzudie A, Boissonnat P, Roussoulieres A, Cakmak, Mosbah K, Bejui FT, Obadia JF, Sebbag L (2009) Cyclosporine-related posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome after heart transplantation: should we withdraw or reduce cyclosporine?: case reports. Transplant Proc 41:716–720
Munoz R, Espinoza M, Espinoza O, Andrade A, Bravo E, Gonzalez F (2006) Cyclosporine-associated leukoencephalopathy in organ transplant recipients: experience of three clinical cases. Transplant Proc 38:921–923
Heidenhain C, Puhl G, Neuhaus P (2009) Late fulminant posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome after liver transplant. Exp Clin Transplant Off J Middle East Soc Organ Transplant 7:180–183
Schmidt D, Schachter SC (2014) Drug treatment of epilepsy in adults. BMJ 348:g254
Ruiz-Gimenez J, Sanchez-Alvarez JC, Canadillas-Hidalgo F, Serrano-Castro PJ, Andalusian Epilepsy S (2010) Antiepileptic treatment in patients with epilepsy and other comorbidities. Seizure 19:375–382
Aronow WS, Fleg JL, Pepine CJ, Artinian NT, Bakris G, Brown AS, Ferdinand KC, Ann Forciea M et al (2011) ACCF/AHA 2011 expert consensus document on hypertension in the elderly: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Clinical Expert Consensus documents developed in collaboration with the American Academy of Neurology, American Geriatrics Society, American Society for Preventive Cardiology, American Society of Hypertension, American Society of Nephrology, Association of Black Cardiologists, and European Society of Hypertension. J Am Soc Hypertens 5:259–352
Price RS, Kasner SE (2014) Hypertension and hypertensive encephalopathy. Handb Clin Neurol 119:161–167
Roth C, Ferbert A (2010) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome: long-term follow-up. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 81:773–777
Siegal D, Keller A, Xu W, Bhuta S, Kim DH, Kuruvilla J, Lipton JH, Messner H et al (2007) Central nervous system complications after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: incidence, manifestations, and clinical significance. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant J Am Soc Blood Marrow Transplant 13:1369–1379
Prasad N, Gulati S, Gupta RK, Kumar R, Sharma K, Sharma RK (2003) Is reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy with severe hypertension completely reversible in all patients? Pediatr Nephrol 18:1161–1166
Bartynski WS (2008) Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome, part 2: controversies surrounding pathophysiology of vasogenic edema. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:1043–1049
Dineen RA, Sibtain N, Karani JB, Lenthall RK (2008) Cerebral manifestations in liver disease and transplantation. Clin Radiol 63:586–599
Spencer CM, Goa KL, Gillis JC (1997) Tacrolimus. An update of its pharmacology and clinical efficacy in the management of organ transplantation. Drugs 54:925–975
Gerard M, Deleersnijder A, Demeulemeester J, Debyser Z, Baekelandt V (2011) Unraveling the role of peptidyl-prolyl isomerases in neurodegeneration. Mol Neurobiol 44:13–27
Ho S, Clipstone N, Timmermann L, Northrop J, Graef I, Fiorentino D, Nourse J, Crabtree GR (1996) The mechanism of action of cyclosporin A and FK506. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 80:S40–S45
Plosker GL, Foster RH (2000) Tacrolimus: a further update of its pharmacology and therapeutic use in the management of organ transplantation. Drugs 59:323–389
Schreiber SL, Crabtree GR (1992) The mechanism of action of cyclosporin A and FK506. Immunol Today 13:136–142
Dohgu S, Yamauchi A, Nakagawa S, Takata F, Kai M, Egawa T, Naito M, Tsuruo T et al (2004) Nitric oxide mediates cyclosporine-induced impairment of the blood–brain barrier in cocultures of mouse brain endothelial cells and rat astrocytes. Eur J Pharmacol 505:51–59
Kochi S, Takanaga H, Matsuo H, Naito M, Tsuruo T, Sawada Y (1999) Effect of cyclosporin A or tacrolimus on the function of blood–brain barrier cells. Eur J Pharmacol 372:287–295
Kochi S, Takanaga H, Matsuo H, Ohtani H, Naito M, Tsuruo T, Sawada Y (2000) Induction of apoptosis in mouse brain capillary endothelial cells by cyclosporin A and tacrolimus. Life Sci 66:2255–2260
Ozawa T (2008) Effects of FK506 on ca release channels (review). Perspect Med Chem 2:51–55
Wang J, Guo R, Liu S, Chen Q, Zuo S, Yang M, Zuo X (2014) Molecular mechanisms of FK506-induced hypertension in solid organ transplantation patients. Chin Med J 127:3645–3650
Cameron AM, Steiner JP, Roskams AJ, Ali SM, Ronnett GV, Snyder SH (1995) Calcineurin associated with the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor-FKBP12 complex modulates Ca2+ flux. Cell 83:463–472
Gold BG (1997) FK506 and the role of immunophilins in nerve regeneration. Mol Neurobiol 15:285–306
Abbott NJ, Revest PA (1991) Control of brain endothelial permeability. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev 3:39–72
De Bock M, Wang N, Decrock E, Bol M, Gadicherla AK, Culot M, Cecchelli R, Bultynck G et al (2013) Endothelial calcium dynamics, connexin channels and blood–brain barrier function. Prog Neurobiol 108:1–20
Hawkins BT, Davis TP (2005) The blood–brain barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev 57:173–185
Huber JD, Egleton RD, Davis TP (2001) Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of tight junctions in the blood–brain barrier. Trends Neurosci 24:719–725
Stuart RO, Sun A, Bush KT, Nigam SK (1996) Dependence of epithelial intercellular junction biogenesis on thapsigargin-sensitive intracellular calcium stores. J Biol Chem 271:13636–13641
Dohgu S, Sumi N, Nishioku T, Takata F, Watanabe T, Naito M, Shuto H, Yamauchi A et al (2010) Cyclosporin A induces hyperpermeability of the blood–brain barrier by inhibiting autocrine adrenomedullin-mediated up-regulation of endothelial barrier function. Eur J Pharmacol 644:5–9
Fernandes S, Salta S, Bravo J, Silva A P, Summavielle T (2014). Acetyl-L-carnitine prevents methamphetamine-induced structural damage on endothelial cells via ILK-related MMP-9 activity. Mol Neurobiol
Ishizaki T, Chiba H, Kojima T, Fujibe M, Soma T, Miyajima H, Nagasawa K, Wada I et al (2003) Cyclic AMP induces phosphorylation of claudin-5 immunoprecipitates and expression of claudin-5 gene in blood–brain-barrier endothelial cells via protein kinase A-dependent and -independent pathways. Exp Cell Res 290:275–288
Dohgu S, Takata F, Matsumoto J, Oda M, Harada E, Watanabe T, Nishioku T, Shuto H et al (2011) Autocrine and paracrine up-regulation of blood–brain barrier function by plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. Microvasc Res 81:103–107
Juhan-Vague I, Alessi MC, Mavri A, Morange PE (2003) Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, inflammation, obesity, insulin resistance and vascular risk. J Thromb Haemost 1:1575–1579
Ko HM, Lee SH, Kim KC, Joo SH, Choi WS, Shin CY (2015) The role of TLR4 and Fyn interaction on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated PAI-1 expression in astrocytes. Mol Neurobiol 52:8–25
Dohgu S, Kataoka Y, Ikesue H, Naito M, Tsuruo T, Oishi R, Sawada Y (2000) Involvement of glial cells in cyclosporine-increased permeability of brain endothelial cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 20:781–786
Takata F, Dohgu S, Yamauchi A, Sumi N, Nakagawa S, Naito M, Tsuruo T, Shuto H et al (2007) Inhibition of transforming growth factor-beta production in brain pericytes contributes to cyclosporin A-induced dysfunction of the blood–brain barrier. Cell Mol Neurobiol 27:317–328
Muzi M, Mankoff DA, Link JM, Shoner S, Collier AC, Sasongko L, Unadkat JD (2009) Imaging of cyclosporine inhibition of P-glycoprotein activity using 11C-verapamil in the brain: studies of healthy humans. J Nucl Med Off Publ Soc Nucl Med 50:1267–1275
Gurkan A, Emingil G, Oktem G, Selvi N, Afacan B, Tunc I, Toz H, Atilla G (2009) Immunohistochemical analysis of inducible and endothelial forms of nitric oxide synthase in cyclosporin A-induced gingival overgrowth. J Periodontol 80:1638–1647
Papachristou E, Papadimitropoulos A, Kotsantis P, Goumenos DS, Katsoris PG, Vlachojannis JG (2010) Interaction of endothelin-1 and nitric oxide pathways in human tubular epithelial cells under the influence of cyclosporine-A. Ren Fail 32:727–732
Ramzy D, Rao V, Tumiati LC, Xu N, Miriuka S, Delgado D, Ross HJ (2006) Role of endothelin-1 and nitric oxide bioavailability in transplant-related vascular injury: comparative effects of rapamycin and cyclosporine. Circulation 114:I214–I219
Yang L, Yang XC, Yang JK, Guo YH, Yi FF, Fan Q, Liu XL (2008) Cyclosporin A suppresses proliferation of endothelial progenitor cells: involvement of nitric oxide synthase inhibition. Intern Med 47:1457–1464
Minguillon J, Morancho B, Kim SJ, Lopez-Botet M, Aramburu J (2005) Concentrations of cyclosporin A and FK506 that inhibit IL-2 induction in human T cells do not affect TGF-beta1 biosynthesis, whereas higher doses of cyclosporin A trigger apoptosis and release of preformed TGF-beta1. J Leukoc Biol 77:748–758
Kalayci R, Kaya M, Uzun H, Bilgic B, Ahishali B, Arican N, Elmas I, Kucuk M (2009) Influence of hypercholesterolemia and hypertension on the integrity of the blood–brain barrier in rats. Int J Neurosci 119:1881–1904
Mayhan WG (1995) Role of nitric oxide in disruption of the blood–brain barrier during acute hypertension. Brain Res 686:99–103
Mohammadi MT, Shid Moosavi SM, Dehghani GA (2011) Contribution of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activity in blood–brain barrier disruption and edema after acute ischemia/reperfusion in aortic coarctation-induced hypertensive rats. Iran Biomed J 15:22–30
Nukhet Turkel A, Ziya Ziylan Y (2004) Protection of blood–brain barrier breakdown by nifedipine in adrenaline-induced acute hypertension. Int J Neurosci 114:517–528
Pires PW, Dams Ramos CM, Matin N, Dorrance AM (2013) The effects of hypertension on the cerebral circulation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 304:H1598–H1614
Poulet R, Gentile MT, Vecchione C, Distaso M, Aretini A, Fratta L, Russo G, Echart C et al (2006) Acute hypertension induces oxidative stress in brain tissues. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab Off J Int Soc Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:253–262
Mohammadi MT, Dehghani GA (2014) Acute hypertension induces brain injury and blood–brain barrier disruption through reduction of claudins mRNA expression in rat. Pathol Res Pract 210:985–990
Wilasrusmee C, Da Silva M, Siddiqui J, Bruch D, Kittur S, Wilasrusmee S, Kittur DS (2003) Role of endothelin-1 in microvascular dysfunction caused by cyclosporin A. J Am Coll Surg 196:584–591
Cauduro RL, Costa C, Lhulier F, Garcia RG, Cabral RD, Goncalves LF, Manfro RC (2005) Endothelin-1 plasma levels and hypertension in cyclosporine-treated renal transplant patients. Clin Transpl 19:470–474
Arii T, Kamiya T, Arii K, Ueda M, Nito C, Katsura KI, Katayama Y (2001) Neuroprotective effect of immunosuppressant FK506 in transient focal ischemia in rat: therapeutic time window for FK506 in transient focal ischemia. Neurol Res 23:755–760
Kumar P, Kalonia H, Kumar A (2010) Possible nitric oxide modulation in protective effect of FK-506 against 3-nitropropionic acid-induced behavioral, oxidative, neurochemical, and mitochondrial alterations in rat brain. Drug Chem Toxicol 33:377–392
Toung TJ, Bhardwaj A, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Traystman RJ, Hurn PD (1999) Neuroprotective FK506 does not alter in vivo nitric oxide production during ischemia and early reperfusion in rats. Stroke J Cereb Circ 30:1279–1285
Boger RH (2007) The pharmacodynamics of L-arginine. J Nutr 137:1650S–1655S
Puschel A, Lindenblatt N, Katzfuss J, Vollmar B, Klar E (2012) Immunosuppressants accelerate microvascular thrombus formation in vivo: role of endothelial cell activation. Surgery 151:26–36
Chiasson VL, Quinn MA, Young KJ, Mitchell BM (2011) Protein kinase CbetaII-mediated phosphorylation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase threonine 495 mediates the endothelial dysfunction induced by FK506 (tacrolimus). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 337:718–723
Agrawal S, Dixit A, Singh A, Tripathi P, Singh D, Patel DK, Singh MP (2015) Cyclosporine A and MnTMPyP alleviate alpha-synuclein expression and aggregation in cypermethrin-induced Parkinsonism. Mol Neurobiol 52:1619–1628
Gottschalk S, Cummins CL, Leibfritz D, Christians U, Benet LZ, Serkova NJ (2011) Age and sex differences in the effects of the immunosuppressants cyclosporine, sirolimus and everolimus on rat brain metabolism. Neurotoxicology 32:50–57
Serkova NJ, Christians U, Benet LZ (2004) Biochemical mechanisms of cyclosporine neurotoxicity. Mol Interv 4:97–107
Dohgu S, Nishioku T, Sumi N, Takata F, Nakagawa S, Naito M, Tsuruo T, Yamauchi A et al (2007) Adverse effect of cyclosporin A on barrier functions of cerebral microvascular endothelial cells after hypoxia-reoxygenation damage in vitro. Cell Mol Neurobiol 27:889–899
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Sheng Chen and Jun Hu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Hu, J., Xu, L. et al. Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome After Transplantation: a Review. Mol Neurobiol 53, 6897–6909 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9560-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9560-0