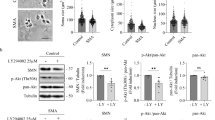
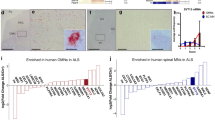
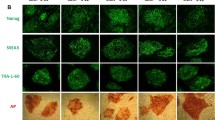
Abstract
Survival motor neuron (SMN) protein deficiency causes the genetic neuromuscular disorder spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), characterized by spinal cord motoneuron degeneration. Since SMN protein level is critical to disease onset and severity, analysis of the mechanisms involved in SMN stability is one of the central goals of SMA research. Here, we describe the role of several members of the NF-κB pathway in regulating SMN in motoneurons. NF-κB is one of the main regulators of motoneuron survival and pharmacological inhibition of NF-κB pathway activity also induces mouse survival motor neuron (Smn) protein decrease. Using a lentiviral-based shRNA approach to reduce the expression of several members of NF-κB pathway, we observed that IKK and RelA knockdown caused Smn reduction in mouse-cultured motoneurons whereas IKK or RelB knockdown did not. Moreover, isolated motoneurons obtained from the severe SMA mouse model showed reduced protein levels of several NF-κB members and RelA phosphorylation. We describe the alteration of NF-κB pathway in SMA cells. In the context of recent studies suggesting regulation of altered intracellular pathways as a future pharmacological treatment of SMA, we propose the NF-κB pathway as a candidate in this new therapeutic approach.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gallagher D, Gutierrez H, Gavalda N, O'Keeffe G, Hay R, Davies AM (2007) Nuclear factor-kappaB activation via tyrosine phosphorylation of inhibitor kappaB-alpha is crucial for ciliary neurotrophic factor-promoted neurite growth from developing neurons. J Neurosci 27:9664–9669
Gutierrez H, O'Keeffe GW, Gavalda N, Gallagher D, Davies AM (2008) Nuclear factor kappa B signaling either stimulates or inhibits neurite growth depending on the phosphorylation status of p65/RelA. J Neurosci 28:8246–8256
Albensi BC, Mattson MP (2000) Evidence for the involvement of TNF and NF-kappaB in hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Synapse 35:151–159
Nakai M, Qin ZH, Chen JF, Wang Y, Chase TN (2000) Kainic acid-induced apoptosis in rat striatum is associated with nuclear factor-kappaB activation. J Neurochem 74:647–658
Kaltschmidt B, Widera D, Kaltschmidt C (2005) Signaling via NF-kappaB in the nervous system. Biochim Biophys Acta 1745:287–299
Mincheva-Tasheva S, Soler RM (2013) NF-κB signaling pathways: role in nervous system physiology and pathology. Neuroscientist 19:175–194
Perkins ND (2007) Integrating cell-signalling pathways with NF-kappaB and IKK function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:49–62
Christian F, Smith EL, Carmody RJ (2016) The regulation of NF-κB subunits by phosphorylation. Cell 5
Bui NT, Livolsi A, Peyron JF, Prehn JH (2001) Activation of nuclear factor kappaB and Bcl-x survival gene expression by nerve growth factor requires tyrosine phosphorylation of IkappaBalpha. J Cell Biol 152:753–764
Saha RN, Liu X, Pahan K (2006) Up-regulation of BDNF in astrocytes by TNF-alpha: a case for the neuroprotective role of cytokine. J NeuroImmune Pharmacol 1:212–222
Simpson CS, Morris BJ (2000) Regulation of neuronal cell adhesion molecule expression by NF-kappa B. J Biol Chem 275:16879–16884
Rojo AI, Salinas M, Martín D, Perona R, Cuadrado A (2004) Regulation of Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase expression via the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase/Akt pathway and nuclear factor-kappaB. J Neurosci 24:7324–7334
Mincheva S, Garcera A, Gou-Fabregas M, Encinas M, Dolcet X, Soler RM (2011) The canonical nuclear factor-kappa B pathway regulates cell survival in a developmental model of spinal cord Motoneurons. J Neurosci 31:6493–6503
Bhakar AL, Tannis LL, Zeindler C, Russo MP, Jobin C, Park DS, MacPherson S, Barker PA (2002) Constitutive nuclear factor-kappa B activity is required for central neuron survival. J Neurosci 22:8466–8475
Kaltschmidt B, Uherek M, Volk B, Baeuerle PA, Kaltschmidt C (1997) Transcription factor NF-kappaB is activated in primary neurons by amyloid beta peptides and in neurons surrounding early plaques from patients with Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:2642–2647
Cardoso SM, Oliveira CR (2003) Inhibition of NF-kB renders cells more vulnerable to apoptosis induced by amyloid beta peptides. Free Radic Res 37:967–973
Lefebvre S, Burglen L, Reboullet S, Clermont O, Burlet P, Viollet L, Benichou B, Cruaud C et al (1995) Identification and characterization of a spinal muscular atrophy-determining gene. Cell 80:155–165
Lefebvre S, Burlet P, Liu Q, Bertrandy S, Clermont O, Munnich A, Dreyfuss G, Melki J (1997) Correlation between severity and SMN protein level in spinal muscular atrophy. Nat Genet 16:265–269
Sumner CJ (2006) Therapeutics development for spinal muscular atrophy. NeuroRx 3:235–245
Arce V, Garces A, de Bovis B, Filippi P, Henderson C, Pettmann B, deLapeyriere O (1999) Cardiotrophin-1 requires LIFRbeta to promote survival of mouse motoneurons purified by a novel technique. J Neurosci Res 55:119–126
Gou-Fabregas M, Garcera A, Mincheva S, Perez-Garcia MJ, Comella JX, Soler RM (2009) Specific vulnerability of mouse spinal cord motoneurons to membrane depolarization. J Neurochem 110:1842–1854
Perez-Garcia MJ, Cena V, de Pablo Y, Llovera M, Comella JX, Soler RM (2004) Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor increases intracellular calcium concentration. Role of calcium/calmodulin in the activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway. J Biol Chem 279:6132–6142
Encinas M, Rozen EJ, Dolcet X, Jain S, Comella JX, Milbrandt J, Johnson EM Jr (2008) Analysis of Ret knockin mice reveals a critical role for IKKs, but not PI 3-K, in neurotrophic factor-induced survival of sympathetic neurons. Cell Death Differ 15:1510–1521
Dolcet X, Llobet D, Encinas M, Pallares J, Cabero A, Schoenenberger JA, Comella JX, Matias-Guiu X (2006) Proteasome inhibitors induce death but activate NF-kappaB on endometrial carcinoma cell lines and primary culture explants. J Biol Chem 281:22118–22130
Lin YZ, Yao SY, Veach RA, Torgerson TR, Hawiger J (1995) Inhibition of nuclear translocation of transcription factor NF-kappa B by a synthetic peptide containing a cell membrane-permeable motif and nuclear localization sequence. J Biol Chem 270:14255–14258
Burnett BG, Muñoz E, Tandon A, Kwon DY, Sumner CJ, Fischbeck KH (2009) Regulation of SMN protein stability. Mol Cell Biol 29:1107–1115
Chang HC, Hung WC, Chuang YJ, Jong YJ (2004) Degradation of survival motor neuron (SMN) protein is mediated via the ubiquitin/proteasome pathway. Neurochem Int 45:1107–1112
Majumder S, Varadharaj S, Ghoshal K, Monani U, Burghes AH, Jacob ST (2004) Identification of a novel cyclic AMP-response element (CRE-II) and the role of CREB-1 in the cAMP-induced expression of the survival motor neuron (SMN) gene. J Biol Chem 279:14803–14811
Kaltschmidt B, Heinrich M, Kaltschmidt C (2002) Stimulus-dependent activation of NF-kappaB specifies apoptosis or neuroprotection in cerebellar granule cells. NeuroMolecular Med 2:299–309
Chu ZL, McKinsey TA, Liu L, Gentry JJ, Malim MH, Ballard DW (1997) Suppression of tumor necrosis factor-induced cell death by inhibitor of apoptosis c-IAP2 is under NF-kappaB control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:10057–10062
Li ZW, Chu W, Hu Y, Delhase M, Deerinck T, Ellisman M, Johnson R, Karin M (1999) The IKKbeta subunit of IkappaB kinase (IKK) is essential for nuclear factor kappaB activation and prevention of apoptosis. J Exp Med 189:1839–1845
Li Q, Estepa G, Memet S, Israel A, Verma IM (2000) Complete lack of NF-kappaB activity in IKK1 and IKK2 double-deficient mice: additional defect in neurulation. Genes Dev 14:1729–1733
Liu F, Xia Y, Parker AS, Verma IM (2012) IKK biology. Immunol Rev 246:239–253
Huang WC, Hung MC (2013) Beyond NF-κB activation: nuclear functions of IκB kinase α. J Biomed Sci 20:3
Olivotto E, Borzi RM, Vitellozzi R, Pagani S, Facchini A, Battistelli M, Penzo M, Li X et al (2008) Differential requirements for IKKalpha and IKKbeta in the differentiation of primary human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheum 58:227–239
Lamberti C, Lin KM, Yamamoto Y, Verma U, Verma IM, Byers S, Gaynor RB (2001) Regulation of beta-catenin function by the IkappaB kinases. J Biol Chem 276:42276–42286
Locatelli D, Terao M, Kurosaki M, Zanellati MC, Pletto DR, Finardi A, Colciaghi F, Garattini E et al (2015) Different stability and proteasome-mediated degradation rate of SMN protein isoforms. PLoS One 10:e0134163
Branchu J, Biondi O, Chali F, Collin T, Leroy F, Mamchaoui K, Makoukji J, Pariset C et al (2013) Shift from extracellular signal-regulated kinase to AKT/cAMP response element-binding protein pathway increases survival-motor-neuron expression in spinal-muscular-atrophy-like mice and patient cells. J Neurosci 33:4280–4294
Khoshnan A, Ko J, Tescu S, Brundin P, Patterson PH (2009) IKKalpha and IKKbeta regulation of DNA damage-induced cleavage of huntingtin. PLoS One 4:e5768
Thompson LM, Aiken CT, Kaltenbach LS, Agrawal N, Illes K, Khoshnan A, Martinez-Vincente M, Arrasate M et al (2009) IKK phosphorylates Huntingtin and targets it for degradation by the proteasome and lysosome. J Cell Biol 187:1083–1099
Husedzinovic A, Oppermann F, Draeger-Meurer S, Chari A, Fischer U, Daub H, Gruss OJ (2014) Phosphoregulation of the human SMN complex. Eur J Cell Biol 93:106–117
Kwon DY, Motley WW, Fischbeck KH, Burnett BG (2011) Increasing expression and decreasing degradation of SMN ameliorate the spinal muscular atrophy phenotype in mice. Hum Mol Genet 20:3667–3677
Foran E, Kwon DY, Nofziger JH, Arnold ES, Hall MD, Fischbeck KH, Burnett BG (2016) CNS uptake of bortezomib is enhanced by P-glycoprotein inhibition: implications for spinal muscular atrophy. Neurobiol Dis 88:118–124
Butchbach ME, Lumpkin CJ, Harris AW, Saieva L, Edwards JD, Workman E, Simard LR, Pellizzoni L et al (2016) Protective effects of butyrate-based compounds on a mouse model for spinal muscular atrophy. Exp Neurol 279:13–26
Tisdale S, Pellizzoni L (2015) Disease mechanisms and therapeutic approaches in spinal muscular atrophy. J Neurosci 35:8691–8700
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad, Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitarias (PI14/00060), Unión Europea, Fondo europeo de Desarrollo Regional (FEDER) “Una manera de hacer Europa”, and Generalitat de Catalunya (SGR740). AP holds a fellowship from Comissionat d’Universitats i Recerca, Departament d’Innovació, Universitats i Empresa de la Generalitat de Catalunya i Fons Social Europeu, SA and SdF hold a fellowship from Universitat de Lleida. We thank Elaine Lilly, Ph.D., for the English language revision of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Additional information
Rosa M. Soler and Ana Garcera last co-authors should be regarded as joint corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arumugam, S., Mincheva-Tasheva, S., Periyakaruppiah, A. et al. Regulation of Survival Motor Neuron Protein by the Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Pathway in Mouse Spinal Cord Motoneurons. Mol Neurobiol 55, 5019–5030 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0710-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0710-4