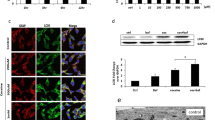
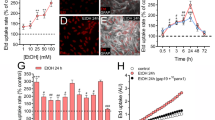
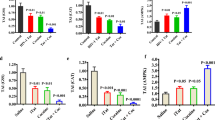
Abstract
Cocaine, a known psychostimulant, results in oxidative stress and inflammation. Recent studies from our group have shown that cocaine induces inflammation in glial cells. Our current study was aimed at investigating whether cocaine exposure could also induce inflammation in non-glial cells such as the pericytes with a focus on the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress/autophagy axis. Our in vitro findings demonstrated that exposure of pericytes to cocaine resulted in upregulation of the pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6) in both the intracellular as well as extracellular compartments, thus underpinning pericytes as yet another source of neuroinflammation. Cocaine exposure of pericytes resulted in increased formation of autophagosomes as demonstrated by a time-dependent increase of autophagy markers, with a concomitant defect in the fusion of the autophagosome with the lysosomes. Pharmacological blocking of the sigma 1 receptor underscored its role in cocaine-mediated activation of pericytes. Furthermore, it was also demonstrated that cocaine-mediated dysregulation of autophagy involved upstream activation of the ER stress pathways, with a subsequent downstream production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in pericytes. These findings were also validated in an in vivo model wherein pericytes in the isolated brain microvessels of cocaine injected mice (7 days) exhibited increased expression of both the autophagy marker—LC3 as well as the pro-inflammatory cytokine, IL-6. This is the first report describing the role of pericytes in cocaine-mediated neuroinflammation. Interventions aimed at blocking either the sigma-1 receptor or the upstream ER stress mediators could likely be envisioned as promising therapeutic targets for abrogating cocaine-mediated inflammation in pericytes.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolf ME (2016) Synaptic mechanisms underlying persistent cocaine craving. Nat Rev Neurosci 17(6):351–365. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2016.39
Barnett G, Hawks R, Resnick R (1981) Cocaine pharmacokinetics in humans. J Ethnopharmacol 3(2–3):353–366
CBHSQ CfBHSaQ (2011) Drug abuse warning network: 2011: selected tables of national estimates of drug-related emergency department visits. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration
Yao H, Duan M, Buch S (2011) Cocaine-mediated induction of platelet-derived growth factor: Implication for increased vascular permeability. Blood 117(8):2538–2547. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-10-313593
Yao H, Kim K, Duan M, Hayashi T, Guo M, Morgello S, Prat A, Wang J et al (2011) Cocaine hijacks sigma1 receptor to initiate induction of activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule: implication for increased monocyte adhesion and migration in the CNS. J Neurosci 31(16):5942–5955. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5618-10.2011
Buch S, Yao H, Guo M, Mori T, Su TP, Wang J (2011) Cocaine and HIV-1 interplay: molecular mechanisms of action and addiction. J NeuroImmune Pharmacol 6(4):503–515. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-011-9297-0
Dash S, Balasubramaniam M, Villalta F, Dash C, Pandhare J (2015) Impact of cocaine abuse on HIV pathogenesis. Front Microbiol 6:1111. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.01111
Hawkins BT, Davis TP (2005) The blood-brain barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev 57(2):173–185. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.57.2.4
Dhillon NK, Peng F, Bokhari S, Callen S, Shin SH, Zhu X, Kim KJ, Buch SJ (2008) Cocaine-mediated alteration in tight junction protein expression and modulation of CCL2/CCR2 axis across the blood-brain barrier: Implications for HIV-dementia. J NeuroImmune Pharmacol 3(1):52–56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-007-9091-1
Kolodgie FD, Wilson PS, Mergner WJ, Virmani R (1999) Cocaine-induced increase in the permeability function of human vascular endothelial cell monolayers. Exp Mol Pathol 66(2):109–122. https://doi.org/10.1006/exmp.1999.2253
Sharma HS, Muresanu D, Sharma A, Patnaik R (2009) Cocaine-induced breakdown of the blood-brain barrier and neurotoxicity. Int Rev Neurobiol 88:297–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0074-7742(09)88011-2
Ka M, Kook YH, Liao K, Buch S, Kim WY (2016) Transactivation of TrkB by Sigma-1 receptor mediates cocaine-induced changes in dendritic spine density and morphology in hippocampal and cortical neurons. Cell Death Dis 7(10):e2414. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2016.319
Periyasamy P, Guo ML, Buch S (2016) Cocaine induces astrocytosis through ER stress-mediated activation of autophagy. Autophagy 12(8):1310–1329. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2016.1183844
Rustenhoven J, Jansson D, Smyth LC, Dragunow M (2017) Brain pericytes as mediators of neuroinflammation. Trends Pharmacol Sci 38(3):291–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2016.12.001
Nakagawa S, Castro V, Toborek M (2012) Infection of human pericytes by HIV-1 disrupts the integrity of the blood-brain barrier. J Cell Mol Med 16(12):2950–2957. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2012.01622.x
Matsumoto J, Dohgu S, Takata F, Machida T, Bolukbasi Hatip FF, Hatip-Al-Khatib I, Yamauchi A, Kataoka Y (2018) TNF-alpha-sensitive brain pericytes activate microglia by releasing IL-6 through cooperation between IkappaB-NFkappaB and JAK-STAT3 pathways. Brain Res 1692:34–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2018.04.023
Liang XG, Tan C, Wang CK, Tao RR, Huang YJ, Ma KF, Fukunaga K, Huang MZ et al (2018) Myt1l induced direct reprogramming of pericytes into cholinergic neurons. CNS Neurosci Ther 24:801–809. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12821
Banks WA, Kovac A, Morofuji Y (2018) Neurovascular unit crosstalk: pericytes and astrocytes modify cytokine secretion patterns of brain endothelial cells. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 38(6):1104–1118. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X17740793
Sweeney MD, Ayyadurai S, Zlokovic BV (2016) Pericytes of the neurovascular unit: key functions and signaling pathways. Nat Neurosci 19(6):771–783. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4288
Li Y, Lucas-Osma AM, Black S, Bandet MV, Stephens MJ, Vavrek R, Sanelli L, Fenrich KK et al (2017) Pericytes impair capillary blood flow and motor function after chronic spinal cord injury. Nat Med 23(6):733–741. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4331
da Silva Meirelles L, Bellagamba BC, Camassola M, Nardi NB (2016) Mesenchymal stem cells and their relationship to pericytes. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 21:130–156
Stapor PC, Sweat RS, Dashti DC, Betancourt AM, Murfee WL (2014) Pericyte dynamics during angiogenesis: new insights from new identities. J Vasc Res 51(3):163–174. https://doi.org/10.1159/000362276
Proebstl D, Voisin MB, Woodfin A, Whiteford J, D'Acquisto F, Jones GE, Rowe D, Nourshargh S (2012) Pericytes support neutrophil subendothelial cell crawling and breaching of venular walls in vivo. J Exp Med 209(6):1219–1234. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20111622
Navarro R, Compte M, Alvarez-Vallina L, Sanz L (2016) Immune regulation by pericytes: modulating innate and adaptive immunity. Front Immunol 7:480. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2016.00480
Castro V, Skowronska M, Lombardi J, He J, Seth N, Velichkovska M, Toborek M (2018) Occludin regulates glucose uptake and ATP production in pericytes by influencing AMP-activated protein kinase activity. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 38(2):317–332. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X17720816
Cho HJ, Kuo AM, Bertrand L, Toborek M (2017) HIV alters gap junction-mediated intercellular communication in human brain Pericytes. Front Mol Neurosci 10:410. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2017.00410
Persidsky Y, Hill J, Zhang M, Dykstra H, Winfield M, Reichenbach NL, Potula R, Mukherjee A et al (2016) Dysfunction of brain pericytes in chronic neuroinflammation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 36(4):794–807. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X15606149
Hayashi T, Su TP (2003) Intracellular dynamics of sigma-1 receptors (sigma(1) binding sites) in NG108-15 cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 306(2):726–733. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.103.051292
Romieu P, Phan VL, Martin-Fardon R, Maurice T (2002) Involvement of the sigma(1) receptor in cocaine-induced conditioned place preference: possible dependence on dopamine uptake blockade. Neuropsychopharmacology 26(4):444–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-133X(01)00391-8
Maurice T, Martin-Fardon R, Romieu P, Matsumoto RR (2002) Sigma(1) (sigma(1)) receptor antagonists represent a new strategy against cocaine addiction and toxicity. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 26(4):499–527
Yao H, Yang Y, Kim KJ, Bethel-Brown C, Gong N, Funa K, Gendelman HE, Su TP et al (2010) Molecular mechanisms involving sigma receptor-mediated induction of MCP-1: implication for increased monocyte transmigration. Blood 115(23):4951–4962. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-01-266221
Matsumoto RR (2009) Targeting sigma receptors: novel medication development for drug abuse and addiction. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol 2(4):351–358. https://doi.org/10.1586/ecp.09.18
Yu L, Chen Y, Tooze SA (2018) Autophagy pathway: cellular and molecular mechanisms. Autophagy 14(2):207–215. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2017.1378838
Fields J, Dumaop W, Eleuteri S, Campos S, Serger E, Trejo M, Kosberg K, Adame A et al (2015) HIV-1 Tat alters neuronal autophagy by modulating autophagosome fusion to the lysosome: implications for HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders. J Neurosci 35(5):1921–1938. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3207-14.2015
Cho MH, Cho K, Kang HJ, Jeon EY, Kim HS, Kwon HJ, Kim HM, Kim DH et al (2014) Autophagy in microglia degrades extracellular beta-amyloid fibrils and regulates the NLRP3 inflammasome. Autophagy 10(10):1761–1775. https://doi.org/10.4161/auto.29647
Cai Y, Arikkath J, Yang L, Guo ML, Periyasamy P, Buch S (2016) Interplay of endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy in neurodegenerative disorders. Autophagy 12(2):225–244. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2015.1121360
Winslow AR, Rubinsztein DC (2011) The Parkinson disease protein alpha-synuclein inhibits autophagy. Autophagy 7(4):429–431
Guo ML, Liao K, Periyasamy P, Yang L, Cai Y, Callen SE, Buch S (2015) Cocaine-mediated microglial activation involves the ER stress-autophagy axis. Autophagy 11(7):995–1009. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2015.1052205
Niu F, Yao H, Zhang W, Sutliff RL, Buch S (2014) Tat 101-mediated enhancement of brain pericyte migration involves platelet-derived growth factor subunit B homodimer: implications for human immunodeficiency virus-associated neurocognitive disorders. J Neurosci 34(35):11812–11825. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1139-14.2014
Sil S, Periyasamy P, Guo ML, Callen S, Buch S (2018) Morphine-mediated brain region-specific astrocytosis involves the ER stress-autophagy axis. Mol Neurobiol 55:6713–6733. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-0878-2
Kimura S, Noda T, Yoshimori T (2007) Dissection of the autophagosome maturation process by a novel reporter protein, tandem fluorescent-tagged LC3. Autophagy 3(5):452–460
Kalasinsky KS, Bosy TZ, Schmunk GA, Ang L, Adams V, Gore SB, Smialek J, Furukawa Y et al (2000) Regional distribution of cocaine in postmortem brain of chronic human cocaine users. J Forensic Sci 45(5):1041–1048
Kalivas PW (2007) Cocaine and amphetamine-like psychostimulants: neurocircuitry and glutamate neuroplasticity. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 9(4):389–397
Prakash A, Das G (1993) Cocaine and the nervous system. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol 31(12):575–581
Nassogne MC, Louahed J, Evrard P, Courtoy PJ (1997) Cocaine induces apoptosis in cortical neurons of fetal mice. J Neurochem 68(6):2442–2450
Kousik SM, Napier TC, Carvey PM (2012) The effects of psychostimulant drugs on blood brain barrier function and neuroinflammation. Front Pharmacol 3:121. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2012.00121
Dhillon NK, Williams R, Peng F, Tsai YJ, Dhillon S, Nicolay B, Gadgil M, Kumar A et al (2007) Cocaine-mediated enhancement of virus replication in macrophages: implications for human immunodeficiency virus-associated dementia. J Neurovirol 13(6):483–495. https://doi.org/10.1080/13550280701528684
Poon HF, Abdullah L, Mullan MA, Mullan MJ, Crawford FC (2007) Cocaine-induced oxidative stress precedes cell death in human neuronal progenitor cells. Neurochem Int 50(1):69–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2006.06.012
Cao L, Walker MP, Vaidya NK, Fu M, Kumar S, Kumar A (2016) Cocaine-mediated autophagy in astrocytes involves sigma 1 receptor, PI3K, mTOR, Atg5/7, Beclin-1 and induces type II programed cell death. Mol Neurobiol 53(7):4417–4430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9377-x
Clark KH, Wiley CA, Bradberry CW (2013) Psychostimulant abuse and neuroinflammation: emerging evidence of their interconnection. Neurotox Res 23(2):174–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-012-9334-7
Daneman R, Zhou L, Kebede AA, Barres BA (2010) Pericytes are required for blood-brain barrier integrity during embryogenesis. Nature 468(7323):562–566. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09513
Armulik A, Genove G, Mae M, Nisancioglu MH, Wallgard E, Niaudet C, He L, Norlin J et al (2010) Pericytes regulate the blood-brain barrier. Nature 468(7323):557–561. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09522
Bergers G, Song S (2005) The role of pericytes in blood-vessel formation and maintenance. Neuro-Oncology 7(4):452–464. https://doi.org/10.1215/S1152851705000232
Saitoh T, Fujita N, Jang MH, Uematsu S, Yang BG, Satoh T, Omori H, Noda T et al (2008) Loss of the autophagy protein Atg16L1 enhances endotoxin-induced IL-1beta production. Nature 456(7219):264–268. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07383
Jones SA, Mills KH, Harris J (2013) Autophagy and inflammatory diseases. Immunol Cell Biol 91(3):250–258. https://doi.org/10.1038/icb.2012.82
Guha P, Harraz MM, Snyder SH (2016) Cocaine elicits autophagic cytotoxicity via a nitric oxide-GAPDH signaling cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113(5):1417–1422. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1524860113
Funakoshi-Hirose I, Aki T, Unuma K, Funakoshi T, Noritake K, Uemura K (2013) Distinct effects of methamphetamine on autophagy-lysosome and ubiquitin-proteasome systems in HL-1 cultured mouse atrial cardiomyocytes. Toxicology 312:74–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2013.07.016
Matus S, Glimcher LH, Hetz C (2011) Protein folding stress in neurodegenerative diseases: a glimpse into the ER. Curr Opin Cell Biol 23(2):239–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2011.01.003
Doyle KM, Kennedy D, Gorman AM, Gupta S, Healy SJ, Samali A (2011) Unfolded proteins and endoplasmic reticulum stress in neurodegenerative disorders. J Cell Mol Med 15(10):2025–2039. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01374.x
Ciechomska IA, Gabrusiewicz K, Szczepankiewicz AA, Kaminska B (2013) Endoplasmic reticulum stress triggers autophagy in malignant glioma cells undergoing cyclosporine a-induced cell death. Oncogene 32(12):1518–1529. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.174
Buch S, Yao H, Guo M, Mori T, Mathias-Costa B, Singh V, Seth P, Wang J et al (2012) Cocaine and HIV-1 interplay in CNS: cellular and molecular mechanisms. Curr HIV Res 10(5):425–428
Yang L, Yao H, Chen X, Cai Y, Callen S, Buch S (2016) Role of sigma receptor in cocaine-mediated induction of glial fibrillary acidic protein: implications for HAND. Mol Neurobiol 53(2):1329–1342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9094-5
Cai Y, Yang L, Niu F, Liao K, Buch S (2017) Role of Sigma-1 receptor in cocaine abuse and neurodegenerative disease. Adv Exp Med Biol 964:163–175. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-50174-1_12
Tsai SY, Chuang JY, Tsai MS, Wang XF, Xi ZX, Hung JJ, Chang WC, Bonci A et al (2015) Sigma-1 receptor mediates cocaine-induced transcriptional regulation by recruiting chromatin-remodeling factors at the nuclear envelope. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112(47):E6562–E6570. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1518894112
Nixon CC, Schwartz BH, Dixit D, Zack JA, Vatakis DN (2015) Cocaine exposure impairs multilineage hematopoiesis of human hematopoietic progenitor cells mediated by the sigma-1 receptor [corrected]. Sci Rep 5:8670. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep08670
Acknowledgements
The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health. The support by Nebraska Center for Substance Abuse Research is acknowledged. We are grateful to Drs. Guoku Hu, Minglei Guo, Ernest Chivero, Annadurai Thangaraj, and Ashutosh Tripathi for their useful discussions.
Funding
This work was supported by grants DA035203, DA040397, DA041751, DA044586 (SB), and DA043138 (SB & GH) from the National Institutes of Health and 2P30MH062261 from National Institute of Mental Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Supplementary Figure. 1
(A) Immunostaining of HBVPs using specific pericyte marker - PDGFRβ. Scale bar: 50 μm. (B) Immunostaining of HBVPs using specific pericyte marker - Desmin. Scale bar: 50 μm. (PNG 37 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sil, S., Niu, F., Tom, E. et al. Cocaine Mediated Neuroinflammation: Role of Dysregulated Autophagy in Pericytes. Mol Neurobiol 56, 3576–3590 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1325-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1325-0