Abstract
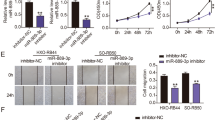
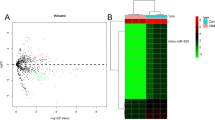
The expression pattern of microRNAs (miRNAs) and their potential target genes were investigated in acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) cell line NB4 cells during all-trans-retinoid acid (ATRA) treatment by using a miRNA microarrays platform and real-time quantitative PCR (RTQ-PCR). MiR-146a as one of the miRNAs down-regulated by ATRA during APL differentiation was identified. Direct interaction between miR146a and its predictive target gene Smad4 were confirmed by Luciferase assay. Down-regulation of miR-146a and upregulation of Smad4 at protein levels were demonstrated. These data suggested that miR-146a might influence proliferation of APL cells through TGF-β1/Smad signal transduction pathway during ATRA induction.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Massagué J, Blain SW, Lo RS. TGFbeta signaling in growth control, cancer, and heritable disorders. Cell. 2000;103(2):295–309.
Isufi I, Seetharam M, Zhou L, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta signaling in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2007;27(7):543–52.
Shi Y, Massague J. Mechanisms of TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell. 2003;113(6):685–700.
Imai Y, Kurokawa M, Izutsu K, et al. Mutation of the Smad4 gene in acute myelogeneous leukemia and their functional implications in leukemogenesis. Oncogene. 2001;20:88–96.
Zhang Y, Derynck R. Regulation of Smad signalling by protein associations and signalling crosstalk. Trends Cell Biol. 1999;9(7):274–9.
Shih HM, Chang CC, Kuo HY, Lin DY. Daxx mediates SUMO-dependent transcriptional control and subnuclear compartmentalization. Biochem Soc Trans. 2007;35(Pt 6):1397–400.
Hackanson B, Bennett KL, Brena RM, et al. Epigenetic modification of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha expression in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Res. 2008;68(9):3142–51.
Croce CM, Calin GA. miRNAs, cancer, and stem cell division. Cell. 2005;122(1):6–7.
Kluiver J, Kroesen B-J, Poppema S, et al. The role of microRNAs in normal hematopoiesis and hematopoietic malignancies. Leukemia. 2006;20:1931–6.
Garzon R, Pichiorri F, Palumbo T, et al. MicroRNA gene expression during retinoic acid-induced differentiation of human acute promyelocytic leukemia. Oncogene. 2007;26:4148–57.
Da MW. A preliminary report of a quick method for determining drug sensitivity of leukemic cells in vitro. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 1982;21(2):109–12.
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, et al. Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33:e179.
Saumet A, Vetter G, Bouttier M, et al. Transcriptional repression of microRNA genes by PML-RARA increases expression of key cancer proteins in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood. 2009;113(2):412–21.
Isken F, Steffen B, Merk S, et al. Identification of acute myeloid leukaemia associated microRNA expression patterns. Br J Haematol. 2008;140(2):153–61.
Garzon R, Volinia S, Liu CG, et al. MicroRNA signatures associated with cytogenetics and prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2008;111(6):3183–9.
John B, Enright AJ, Aravin A, Tuschl T, Sander C, Marks DS. Human microRNA targets. PLoS Biol. 2004;2(11):1862–79.
Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP, Burge CB. Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets. Cell. 2003;115(7):787–98.
Fazi F, Rosa A, Fatica A, et al. A minicircuitry comprised of microRNA-223 and transcription factors NFI-A and C/EBPalpha regulates human granulopoiesis. Cell. 2005;123(5):819–31.
Jongen-Lavrencic M, Sun SM, Dijkstra MK, Valk PJ, Löwenberg B. MicroRNA expression profiling in relation to the genetic heterogeneity of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2008;111(10):5078–85.
Debernardi S, Skoulakis S, Molloy G, Chaplin T, Dixon-McIver A, Young BD. MicroRNA miR-181a correlates with morphological sub-class of acute myeloid leukaemia and the expression of its target genes in global genome-wide analysis. Leukemia. 2007;21(5):912–6.
Zhong H, Chen FY, Wang HR, Lin JY, Xu R, Zhong JH, Huang HH. Modification of TGF-beta1 signaling pathway during NB4 cells differentiation by all-trans retinoid acid induction. Int J Hematol. 2009;89(4):438–44.
Imai Y, Kurokawa M, Izutsu K, Hangaishi A, Maki K, Ogawa S, Chiba S, Mitani K, Hirai H. Mutations of the Smad4 gene in acute myelogeneous leukemia and their functional implications in leukemogenesis. Oncogene. 2001;20(1):88–96.
Fatica A, Rosa A, Ballarino M, De Marchis ML, Rasmussen KD, Bozzoni I. Role of microRNAs in myeloid differentiation. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008;36(Pt 6):1201–5.
De Marchis ML, Ballarino M, Salvatori B, Puzzolo MC, Bozzoni I, Fatica A. A new molecular network comprising PU.1, interferon regulatory factor proteins and miR-342 stimulates ATRA-mediated granulocytic differentiation of acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Leukemia. 2009;23(5):856–62.
Acknowledgments
We thank Hui-juan Cui for RTQ-PCR technical assistance. This work was supported by Shanghai Municipal Commission of Sciences and Technology Grant 09ZR1418400 and Shanghai Municipal Education Commission Grant 06BZ031.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, H., Wang, Hr., Yang, S. et al. Targeting Smad4 links microRNA-146a to the TGF-β pathway during retinoid acid induction in acute promyelocytic leukemia cell line. Int J Hematol 92, 129–135 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-010-0626-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-010-0626-5