Abstract
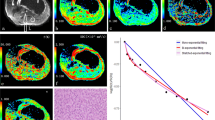
Our purpose was to assess the influence of liver steatosis on diffusion by triexponential analysis. Thirty-three patients underwent diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging with multiple b values for perfusion-related diffusion, fast free diffusion, and slow restricted diffusion coefficients (D p, D f, D s) and fractions (F p, F f, F s). They also underwent dual-echo gradient-echo imaging for measurement of the hepatic fat fraction (HFF). Of these, 13 patients were included in the control group and 20 in the fatty liver group with HFF >5 %. The parameters of the two groups were compared by use of the Mann–Whitney U test. The relationships between diffusion coefficients and HFFs were assessed by use of the Pearson correlation. D p and D f were reduced significantly in the steatotic liver group compared with those in the control group (D p = 27.72 ± 6.61 × 10−3 vs. 33.33 ± 6.47 × 10−3 mm2/s, P = 0.0072; D f = 1.70 ± 0.53 × 10−3 vs. 2.06 ± 0.40 × 10−3 mm2/s, P = 0.0224). There were no significant differences in the other parameters between the two groups. Furthermore, D p and D f were correlated with HFF (P < 0.0001, r = −0.64 and P = 0.0008, r = −0.56, respectively). Decreased liver perfusion in steatosis caused the reduction in D p, and extracellular fat accumulation and intracellular fat droplets in steatosis led to the reduction in D f. Thus, the influence of hepatic steatosis should be taken into consideration when triexponential function analysis is used for assessment of diffuse liver disease.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koinuma M, Ohashi I, Hanafusa K, Shibuya H. Apparent diffusion coefficient measurements with diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for evaluation of hepatic fibrosis. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2005;22:80–5.
Taouli B, Tolia AJ, Losada M, Babb JS, Chan ES, Bannan MA, et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI for quantification of liver fibrosis: preliminary experience. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;189:799–806.
Lewin M, Poujol-Robert A, Boëlle PY, Wendum D, Lasnier E, Viallon M, et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2007;46:658–65.
Padhani AR, Liu G, Koh DM, Chenevert TL, Thoeny HC, Takahara T, et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging as a cancer biomarker: consensus and recommendations. Neoplasia. 2009;11:102–25.
Xia D, Jing J, Shen H, Wu J. Value of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images for discrimination of focal benign and malignant hepatic lesions: a meta-analysis. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010;32:130–7.
Miller FH, Hammond N, Siddiqi AJ, Shroff S, Khatri G, Wang Y, et al. Utility of diffusion-weighted MRI in distinguishing benign and malignant hepatic lesions. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010;32:138–47.
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Aubin ML, Vignaud J, Laval-Jeantet M. Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology. 1988;168:497–505.
Yamada I, Aung W, Himeno Y, Nakagawa T, Shibuya H. Diffusion coefficients in abdominal organs and hepatic lesions: evaluation with intravoxel incoherent motion echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology. 1999;210:617–23.
Luciani A, Vignaud A, Cavet M, Nhieu JT, Mallat A, Ruel L. Liver cirrhosis: intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging—pilot study. Radiology. 2008;249:891–9.
Patel J, Sigmund EE, Rusinek H, Oei M, Babb JS, Taouli B. Diagnosis of cirrhosis with intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion MRI and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI alone and in combination: preliminary experience. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010;31:589–600.
Lemke A, Laun FB, Simon D, Stieltjes B, Schad LR. An in vivo verification of the intravoxel incoherent motion effect in diffusion-weighted imaging of the abdomen. Magn Reson Med. 2010;64:1580–5.
Rheinheimer S, Stieltjes B, Schneider F, Simon D, Pahernik S, Kauczor HU, et al. Investigation of renal lesions by diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging applying intravoxel incoherent motion-derived parameters—initial experience. Eur J Radiol. 2012;81:e310–6.
Chandarana H, Lee VS, Hecht E, Taouli B, Sigmund EE. Comparison of biexponential and monoexponential model of diffusion weighted imaging in evaluation of renal lesions: preliminary experience. Invest Radiol. 2011;46:285–91.
Shinmoto H, Tamura C, Soga S, Shiomi E, Yoshihara N, Kaji T, et al. An intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging study of prostate cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012;199:W496–500.
Lee JT, Liau J, Murphy P, Schroeder ME, Sirlin CB, Bydder M. Cross-sectional investigation of correlation between hepatic steatosis and IVIM perfusion on MR imaging. Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;30:572–8.
Poyraz AK, Onur MR, Kocakoç E, Oğur E. Diffusion-weighted MRI of fatty liver. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;35:1108–11.
Guiu B, Petit JM, Capitan V, Aho S, Masson D, Lefevre PH, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a 3.0-T MR study. Radiology. 2012;265:96–103.
Hayashi T, Miyati T, Takahashi J, Fukuzawa K, Sakai H, Tano M, et al. Diffusion analysis with triexponential function in liver cirrhosis. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013;38:148–53.
Marchesini G, Bugianesi E, Forlani G, Cerrelli F, Lenzi M, Manini R, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver, steatohepatitis, and the metabolic syndrome. Hepatology. 2003;37:917–23.
Caldwell SH, Crespo DM. The spectrum expanded: cryptogenic cirrhosis and the natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2004;40:578–84.
Lv W, Yan F, Zeng M, Zhang J, Yuan Y, Ma J. Value of abdominal susceptibility-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for quantitative assessment of hepatic iron deposition in patients with chronic hepatitis B: comparison with serum iron markers. J Int Med Res. 2012;40:1005–15.
Taouli B, Sandberg A, Stemmer A, Parikh T, Wong S, Xu J, et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging of the liver: comparison of navigator triggered and breathhold acquisitions. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009;30:561–8.
Griswold MA, Jakob PM, Heidemann RM, Nittka M, Jellus V, Wang J, et al. Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA). Magn Reson Med. 2002;47:1202–10.
Marquardt DW. An algorithm for least-squares estimation of nonlinear parameters. J Soc Ind Appl Math. 1963;11:431–41.
Qayyum A, Goh JS, Kakar S, Yeh BM, Merriman RB, Coakley FV. Accuracy of liver fat quantification at MR imaging: comparison of out-of-phase gradient-echo and fat-saturated fast spin-echo techniques—initial experience. Radiology. 2005;237:507–11.
Koelblinger C, Krššák M, Maresch J, Wrba F, Kaczirek K, Gruenberger T, et al. Hepatic steatosis assessment with 1H-spectroscopy and chemical shift imaging at 3.0 T before hepatic surgery: reliable enough for making clinical decisions? Eur J Radiol. 2012;81:2990–5.
Seifalian AM, Piasecki C, Agarwal A, Davidson BR. The effect of graded steatosis on flow in the hepatic parenchymal microcirculation. Transplantation. 1999;68:780–4.
Balci A, Karazincir S, Sumbas H, Oter Y, Egilmez E, Inandi T. Effects of diffuse fatty infiltration of the liver on portal vein flow hemodynamics. J Clin Ultrasound. 2008;36:134–40.
Ulusan S, Yakar T, Koc Z. Evaluation of portal venous velocity with Doppler ultrasound in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Korean J Radiol. 2011;12:450–5.
Tiniakos DG, Vos MB, Brunt EM. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: pathology and pathogenesis. Annu Rev Pathol. 2010;5:145–71.
Teramoto K, Bowers JL, Kruskal JB, Clouse ME. Hepatic microcirculatory changes after reperfusion in fatty and normal liver transplantation in the rat. Transplantation. 1993;56:1076–82.
Sharma P, Martin DR, Pineda N, Xu Q, Vos M, Anania F, et al. Quantitative analysis of T2-correction in single-voxel magnetic resonance spectroscopy of hepatic lipid fraction. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009;29:629–35.
Hayashi N, Miyati T, Minami T, Takeshita T, Ryu Y, Matsuda T, et al. Quantitative analysis of hepatic fat fraction by single-breathholding MR spectroscopy with T2 correction: phantom and clinical study with histologic assessment. Radiol Phys Technol. 2013;6:219–25.
Lemke A, Stieltjes B, Schad LR, Laun FB. Toward an optimal distribution of b values for intravoxel incoherent motion imaging. Magn Reson Imaging. 2011;29:766–76.
Chow AM, Gao DS, Fan SJ, Qiao Z, Lee FY, Yang J, et al. Liver fibrosis: an intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) study. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;36:159–67.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Hayashi, T., Miyati, T., Takahashi, J. et al. Diffusion analysis with triexponential function in hepatic steatosis. Radiol Phys Technol 7, 89–94 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-013-0235-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-013-0235-0