Abstract
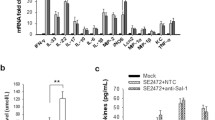
Salmonella enteritidis infection occurs in enterogenous diseases, such as gastroenteritis and parenteral focal infection, which often involve inflammation of intestinal epithelial cells. The nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway participates in the innate immune response to many gram-negative pathogenic bacteria and initiates inflammation in epithelial cells. KH-type splicing regulatory protein (KSRP) is a multi-domain RNA-binding protein that recruits the exosome-containing mRNA degradation complex to mRNAs coding for inflammatory response factors. However, it remains unclear whether KSRP is regulated by NF-κB signaling pathway in response to S. enteritidis infection and affects the development of inflammation. Accordingly, in this study, we investigated the role of KSRP in mediating the response to S. enteritidis in Caco-2 cells. The data revealed that S. enteritidis infection decreased KSRP expression, which was suppressed by blocking the NF-κB pathway. Additionally, S. enteritidis infection significantly increased the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2. Overexpression of KSRP reduced the expression levels of inflammatory factors in Caco-2 cells. KSRP was regulated by the NF-κB signaling pathway and participated in mediating the innate immune response to S. enteritidis infection in Caco-2 cells, and KSRP acted as a negative regulator of inflammatory gene expression.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angrisano T, Lembo F, Peluso S, Keller S, Chiariotti L, Pero R (2012) Helicobacter pylori regulates iNOS promoter by histone modifications in human gastric epithelial cells. Med Microbiol Immunol 201:249–257
Balakrishnan A, Chakravortty D (2017) Epithelial cell damage activates bactericidal/permeability increasing-protein (BPI) expression in intestinal epithelium. Front Microbiol 8:1567
Bertelsen LS, Paesold G, Eckmann L, Barrett KE (2003) Salmonella infection induces a hypersecretory phenotype in human intestinal xenografts by inducing cyclooxygenase 2. Infect Immun 71:2102–2109
Burrack KS, Morrison TE (2014) The role of myeloid cell activation and arginine metabolism in the pathogenesis of virus-induced diseases. Front Immunol 5:428
Casper I, Nowag S, Koch K, et al (2013) Post-transcriptional regulation of the human inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression by the cytosolic poly(A)-binding protein (PABP). Nitric Oxide 33:6–17
Chacón-Salinas R, Serafín-López J, Ramos-Payán R et al (2005) Differential pattern of cytokine expression by macrophages infected in vitro, with different Mycobacterium tuberculosis, genotypes. Clin Exp Immunol 140:443–449
Chen CYA, Shyu AB (1995) AU-rich elements: characterization and importance in mRNA degradation. Trends Biochem Sci 20:465–470
Chokshi NK, Guner YS, Hunter CJ, Upperman JS, Grishin A, Ford HR (2008) The role of nitric oxide in intestinal epithelial injury and restitution in neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin Perinatol 32:92–99
Cianciulli A, Calvello R, Cavallo P, Dragone T, Carofiglio V, Panaro MA (2012) Modulation of NF-κB activation by resveratrol in LPS treated human intestinal cells results in downregulation of PGE 2, production and COX-2 expression. Toxicol in Vitro 26:1122–1128
Clark JA, Coopersmith CM (2007) Intestinal crosstalk: a new paradigm for understanding the gut as the “motor” of critical illness. Shock 28:384–393
Dean JLE, Sully G, Clark AR, Saklatvala J (2004) The involvement of AU-rich element-binding proteins in p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway-mediated mRNA stabilization. Cell Signal 16:1113–1121
Dhamija S, Kuehne N, Winzen R, Doerrie A, Dittrich-Breiholz O, Thakur BK, Kracht M, Holtmann H (2011) Interleukin-1 activates synthesis of interleukin-6 by interfering with a KH-type splicing regulatory protein (KSRP)-dependent translational silencing mechanism. J Biol Chem 286:33279–33288
Díazmoreno I, Hollingworth D, Kelly G et al (2010) Orientation of the central domains of KSRP and its implications for the interaction with the RNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res 38:5193–5205
Eckmann L, Kagnoff MF, Fierer J (1993) Epithelial cells secrete the chemokine interleukin-8 in response to bacterial entry. Infect Immun 61:4569–4574
Egea L, Giménez R, Lúcia D, Modolell I, Badía J, Baldoma L, Aguilar J (2008) Increased production of the ether-lipid platelet-activating factor in intestinal epithelial cells infected by Salmonella enteritidis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1781:270–276
Fournier B, Williams IR, Gewirtz AT, Neish AS (2009) Toll-like receptor 5-dependent regulation of inflammation in systemic Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection. Infect Immun 77:4121–4129
Hayashi F, Smith KD, Ozinsky A, Hawn TR, Yi EC, Goodlett DR, Eng JK, Akira S, Underhill DM, Aderem A (2001) The innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by Toll-like receptor 5. Nature 410:1099–1103
Jobin C, Morteau O, Han DS et al (1998) Specific NF-κB blockade selectively inhibits tumor necrosis factor-α-induced COX-2 but not constitutive COX-1 gene expression in HT-29 cells. Immunology 95:537–543
Khabar KSA (2010) Post-transcriptional control during chronic inflammation and cancer: a focus on AU-rich elements. Cell Mol Life Sci 67:2937–2955
Kim JM, Kim JS, Jung HC, Song IS, Kim CY (2000a) Upregulated cyclooxygenase-2 inhibits apoptosis of human gastric epithelial cells infected with Helicobacter pylori. Dig Dis Sci 45:2436–2443
Kim H, Seo JY, Kim KH (2000b) Inhibition of lipid peroxidation, NF-kappaB activation and IL-8 production by rebamipide in Helicobacter pylori-stimulated gastric epithelial cells. Dig Dis Sci 45:621–628
Kim JM, Kim JS, Jung HC, Song IS, Kim CY (2002) Up-regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase and nitric oxide in Helicobacter pylori-infected human gastric epithelial cells: possible role of interferon-gamma in polarized nitric oxide secretion. Helicobacter 7:116–128
Kim SR, Jung YR, Kim DH, An HJ, Kim MK, Kim ND, Chung HY (2014) Caffeic acid regulates LPS-induced NF-κB activation through NIK/IKK and c-Src/ERK signaling pathways in endothelial cells. Arch Pharm Res 37:539–547
Kishore N, Sommers C, Mathialagan S, Guzova J, Yao M, Hauser S, Huynh K, Bonar S, Mielke C, Albee L, Weier R, Graneto M, Hanau C, Perry T, Tripp CS (2003) A selective IKK-2 inhibitor blocks NF-kappa B-dependent gene expression in interleukin-1 beta-stimulated synovial fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 278:32861–32871
Kleinert H, Pautz A, Linker K et al (2010) Regulation of the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Nitric Oxide Biol Chem 23:255–266
Lei Q, Qiang F, Chao D et al (2014) Amelioration of hypoxia and LPS-induced intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction by emodin through the suppression of the NF-κB and HIF-1α signaling pathways. Int J Mol Med 34:1629–1639
Li X, Lin W, Chen C et al (2012) KSRP: a checkpoint for inflammatory cytokine production in astrocytes. Glia 60:1773–1784
Linker K, Pautz A, Fechir M, Hubrich T, Greeve J, Kleinert H (2005) Involvement of KSRP in the post-transcriptional regulation of human iNOS expression-complex interplay of KSRP with TTP and HuR. Nucleic Acids Res 33:4813–4827
Min H, Turck CW, Nikolic JM, et al (1997) A new regulatory protein, KSRP, mediates exon inclusion through an intronic splicing enhancer. Genes Dev 11:1023–1036
Ogushi K, Wada A, Niidome T, Mori N, Oishi K, Nagatake T, Takahashi A, Asakura H, Makino SI, Hojo H, Nakahara Y, Ohsaki M, Hatakeyama T, Aoyagi H, Kurazono H, Moss J, Hirayama T (2001) Salmonella enteritidis FliC (flagella filament protein) induces human beta-defensin-2 mRNA production by Caco-2 cells. J Biol Chem 276:30521–30526
Panaro MA, Carofiglio V, Acquafredda A et al (2012) Anti-inflammatory effects of resveratrol occur via inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced NF-κB activation in Caco-2 and SW480 human colon cancer cells. Br J Nutr 108:1–10
Repetto E, Briata P, Kuziner N et al (2012) Let-7b/c enhance the stability of a tissue-specific mRNA during mammalian organogenesis as part of a feedback loop involving KSRP. PLoS Genet 8:470–471
Resta-Lenert S, Barrett KE (2002) Enteroinvasive bacteria alter barrier and transport properties of human intestinal epithelium: role of iNOS and COX-2. Gastroenterology 122:1070–1087
Spehlmann ME, Eckmann L (2009) Nuclear factor-kappa B in intestinal protection and destruction. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 25:92–99
Surh YJ, Chun KS, Cha HH, Han SS, Keum YS, Park KK, Lee SS (2001) Molecular mechanisms underlying chemopreventive activities of anti-inflammatory phytochemicals: down-regulation of COX-2 and iNOS through suppression of NF-kappa B activation. Mutat Res Fundam Mol Mech Mutagen 480-481:243–268
Takeda K, Akira S (2005) Toll-like receptors in innate immunity. Int Immunol 17:1–14
Trabucchi M, Briata P, Garcia-Mayoral M, et al (2009) The RNA-binding protein KSRP promotes the biogenesis of a subset of microRNAs. Nature 459:1010–1014
Tsujii M, Dubois RN (1995) Alterations in cellular adhesion and apoptosis in epithelial cells overexpressing prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase 2. Cell 83:493–501
Umesalma S, Sudhandiran G (2010) Differential inhibitory effects of the polyphenol ellagic acid on inflammatory mediators NF-kappaB, iNOS, COX-2, TNF-alpha, and IL-6 in 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced rat colon carcinogenesis. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 107:650–655
Vijaykumar M, Gewirtz AT (2009) Flagellin: key target of mucosal innate immunity. Mucosal Immunol 2:197–205
Yimlamai D, Konnikova L, Moss LG et al (2005) Involvement of KSRP in the post-transcriptional regulation of human iNOS expression-complex interplay of KSRP with TTP and HuR. Nucleic Acids Res 33:4813–4827
Zhou R, Gong A, Eischeid AN et al (2012) miR-27b targets KSRP to coordinate TLR4-mediated epithelial defense against Cryptosporidium parvum infection. PLoS Pathog 8:511–515
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Xianming Chen (Creighton University Medical Center, NE, USA) for providing the plasmid.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31270175); the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-13-0397); and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2013SCU04B14).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nie, Y., Cao, M., Wu, D. et al. KH-type splicing regulatory protein is regulated by nuclear factor-κB signaling to mediate innate immunity in Caco-2 cells infected by Salmonella enteritidis. Folia Microbiol 63, 669–676 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-018-0606-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-018-0606-3