Abstract
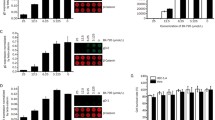
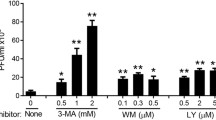
The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) can interact with and exploit the host cellular machinery to replicate and propagate itself. Numerous studies have shown that the Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signal pathway can positively regulate the replication of HIV-1, but exactly how each MAPK pathway affects HIV-1 infection and replication is not understood. In this study, we used the Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway inhibitor, PD98059, the Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway inhibitor, SP600125, and the p38 pathway inhibitor, SB203580, to investigate the roles of these pathways in HIV-1 replication. We found that application of PD98059 results in a strong VSV-G pseudotyped HIV-1NL4-3 luciferase reporter virus and HIV-1NL4-3 virus inhibition activity. In addition, SB203580 and SP600125 also elicited marked VSV-G pseudotyped HIV-1NL4-3 luciferase reporter virus inhibition activity but no HIV-1NL4-3 virus inhibition activity. We also found that SB203580 and SP600125 can enhance the HIV-1 inhibition activity of PD98059 when cells were treated with all three MAPK pathway inhibitors in combination. Finally, we show that HIV-1 virus inhibition activity of the MAPK pathway inhibitors was the result of the negative regulation of HIV-1 LTR promoter activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi A, Gendelman H E, Koenig S, et al. 1986. Production of acquired immunodeficiency syndromeassociated retrovirus in human and nonhuman cells transfected with an infectious molecular clone. J Virol, 59: 284–291.
Chen P, Flory E, Avots A, et al. 2000. Transactivation of naturally occurring HIV-1 long terminal repeats by the JNK signaling pathway. The most frequent naturally occurring length polymorphism sequence introduces a novel binding site for AP-1 factors. J Biol Chem, 275: 20382–20390.
Cohen P S, Schmidtmayerova H, Dennis J, et al. 1997. The critical role of p38 MAP kinase in T cell HIV-1 replication. Mol Med, 3: 339–346.
Connor R I, Chen B K, Choe S, et al. 1995. Vpr is required for efficient replication of human immunodeficiency virus type-1 in mononuclear phagocytes. Virology, 206: 935–944.
Cuenda A and Rousseau S. 2007. p38 MAP-kinases pathway regulation, function and role in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta, 1773: 1358–1375.
Davis R J. 2000. Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell, 103: 239–252.
DeFazio A, Chiew Y E, Sini R L, et al. 2000. Expression of c-erbB receptors, heregulin and oestrogen receptor in human breast cell lines. Int J Cancer, 87: 487–498.
Fang JY and Richardson BC. 2005. The MAPK signalling pathways and colorectal cancer. Lancet Oncol, 6: 322–327.
Gibellini D, Re MC, Bassini A, et al. 1999. HIV-1 gp120 induces the activation of both c-fos and c-jun immediateearly genes in HEL megakaryocytic cells. Br J Haematol, 104: 81–86.
Hommes D W, Peppelenbosch M, van Deventer S J. 2003. Mitogen activated protein (MAP) kinase signal transduction pathways and novel anti-inflammatory targets. Gut, 52: 144–151.
Jacque J M, Mann A, Enslen H, et al. 1998. Modulation of HIV-1 infectivity by MAPK, a virion-associated kinase. Embo J, 17: 2607–2618.
Ju S M, Song H Y, Lee J A, et al. 2009. Extracellular HIV-1 Tat up-regulates expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 via a MAPK-NF-kappaB dependent pathway in human astrocytes. Exp Mol Med, 41: 86–93.
Junttila M R, Li S P, Westermarck J. 2008. Phosphatase-mediated crosstalk between MAPK signaling pathways in the regulation of cell survival. Faseb J, 22: 954–965.
Krens S F, Spaink H P, Snaar-Jagalska B E. 2006. Functions of the MAPK family in vertebrate-development. FEBS Lett, 580: 4984–4990.
Mehrotra S, Chhabra A, Chattopadhyay S, et al. 2004. Rescuing melanoma epitope-specific cytolytic T lymphocytes from activation-induced cell death, by SP600125, an inhibitor of JNK: implications in cancer immunotherapy. J Immunol, 173: 6017–6024.
Muthumani K, Choo A Y, Shedlock D J, et al. 2008. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Nef induces programmed death 1 expression through a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent mechanism. J Virol, 82: 11536–11544.
Pereira L A, Bentley K, Peeters A, et al. 2000. A compilation of cellular transcription factor interactions with the HIV-1 LTR promoter. Nucl Acids Res, 28: 663–668.
Popik W, Hesselgesser J E, Pitha P M. 1998. Binding of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 to CD4 and CXCR4 receptors differentially regulates expression of inflammatory genes and activates the MEK/ERK signaling pathway. J Virol, 72: 6406–6413.
Reiners J J, Jr Lee J Y, Clift R E, et al. 1998. PD98059 is an equipotent antagonist of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. Mol Pharmacol, 53: 438–445.
Toschi E, Bacigalupo I, Strippoli R, et al. 2006. HIV-1 Tat regulates endothelial cell cycle progression via activation of the Ras/ERK MAPK signaling pathway. Mol Biol Cell, 17: 1985–1994.
Troppmair J, Bruder J T, Munoz H, et al. 1994. Mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signalregulated protein kinase activation by oncogenes, serum, and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate requires Raf and is necessary for transformation. J Biol Chem, 269: 7030–7035.
Wainberg M A, Jeang K T. 2008. 25 years of HIV-1 research — progress and perspectives. BMC Med, 6: 31.
Weston C R, Davis R J. 2002. The JNK signal transduction pathway. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 12: 14–21.
Weston C R, Davis R J. 2007. The JNK signal transduction pathway. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 19: 142–149.
Yamamoto K, Ichijo H, Korsmeyer S J. 1999. BCL-2 is phosphorylated and inactivated by an ASK1/Jun Nterminal protein kinase pathway normally activated at G (2)/M. Mol Cell Biol, 19: 8469–8478.
Yang X, Gabuzda D. 1998. Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylates and regulates the HIV-1 Vif protein. J Biol Chem, 273: 29879–29887.
Yang X, Chen Y, Gabuzda D. 1999. ERK MAP kinase links cytokine signals to activation of latent HIV-1 infection by stimulating a cooperative interaction of AP-1 and NF-kappaB. J Biol Chem, 274: 27981–27988.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation items: Key Projects in the National Science and Technology Pillar Program during the Eleventh Five-Year Plan Period of China (2008ZX10001-002); Major Science and Technology Innovation Cross Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KSCX1-YW-10).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, J., Shen, Xh., Chen, C. et al. Down-regulation of HIV-1 infection by inhibition of the MAPK signaling pathway. Virol. Sin. 26, 114–122 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12250-011-3184-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12250-011-3184-y