Abstract
Objective
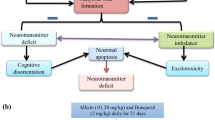
Excessive aluminum (Al) exposure impairs neurocognitive function in humans and animals. Epidemiologic studies have shown a potential linkage between chronic Al exposure and Alzheimer’s disease. The present study aims to evaluate the effects of tetrahydroxy stilbene glucoside (TSG), the extract from herbal medicine Polygoni Multiflori, on cognitive impairment and the over-expression of hippocampal amyloid precursor protein (APP) induced by chronic exposure to Al in rats
Methods
Rats were treated with 0.3% aluminum chloride (AlCl3) prepared in the drinking water for 90 d. AlCl3-treated animals were then randomly assigned to receive vehicle, TSG (4 g/kg), or Vitamin E (VE; 40 mg/kg) treatment for 5 months. VE served as a positive control. The effect of TSG was evaluated by passive avoidance task, and APP expression was evaluated by Western blotting.
Results
Following exposure to AlCl3 for 90 d, animals displayed a striking decrease (>80%) in step-through latency in the passive avoidance task and a significant increase in the expression of APP in the hippocampus. Both TSG and VE significantly ameliorated the performance impairment in the passive avoidance task, and suppressed the over-expression of APP. Moreover, the effects of TSG, but not of VE, were in a time-dependent manner.
Conclusion
TSG may possess therapeutic effects against Alzheimer’s disease.
摘要
目的
过量的铝盐可损害人和动物的神经认知功能。 流行病学研究提示, 慢性铝中毒和阿尔茨海默病有潜在的联系。 本实验旨在评估中药何首乌提取物—二苯乙烯苷(TSG)对铝盐慢性中毒的大鼠认知功能的保护作用及海马部位β-淀粉样前体蛋白(APP)表达的影响。
方法
以水配制0.3% 氯化铝, 连续喂养大鼠90 天。 随后铝盐暴露的大鼠随机分组, 采用溶媒, 进行TSG (4 g/kg)和VE (40 mg/kg)干预5 个月, 其中VE 作为对照药物。 结束后进行电刺激实验, 并用Western blot 法检测APP 的蛋白水平。
结果
连续服用90 天AlCl3 后, 大鼠躲避电刺激能力显著下降, 并且海马部位APP 的表达显著上调。 经过TSD 和VE 干预后, 大鼠躲避电刺激能力得到显著改善, APP表达的上升也被显著抑制。 与VE相比, TSG的效果随时间延长而变得更为显著。
结论
TSG对阿尔茨海默病有一定的治疗作用。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang XP, Ding HL. Alzheimer’s disease: epidemiology, genetics, and beyond. Neurosci Bull 2008, 24(2): 105–109.
Bharathi, Vasudevaraju P, Govindaraju M, Palanisamy AP, Sambamurti K, Rao KS. Molecular toxicity of aluminium in relation to neurodegeneration. Indian J Med Res 2008, 128(4): 545–556.
Akila R, Stollery BT, Riihimaki V. Decrements in cognitive performance in metal inert gas welders exposed to aluminium. Occup and Environ Med 1999, 56(9): 632–639.
Ribes D, Colomina MT, Vicens P, Domingo JL. Effects of oral aluminum exposure on behavior and neurogenesis in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Neurol 2008, 214(2): 293–300.
Hardy J. Alzheimer’s disease: the amyloid cascade hypothesis: an update and reappraisal. J Alzheimers Dis 2006, 9(3l): 151–153.
Kawahara M, Kato M, Kuroda Y. Effects of aluminum on the neurotoxicity of primary cultured neurons and on the aggregation of beta-amyloid protein. Brain Res Bull 2001, 55: 211–217.
Campbell A, Kumar A, La Rosa FG, Prasad KN, Bondy SC. Aluminum increases levels of beta-amyloid and ubiquitin in neuroblastoma but not in glioma cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 2000, 223(4): 397–402.
Kawahara M. Effects of aluminum on the nervous system and its possible link with neurodegenerative diseases. J Alzheimers Dis 2005, 8(2): 171–182.
Miu AC, Benga O. Aluminum and Alzheimer’s disease: a new look. J Alzheimers Dis 2006, 10(2): 179–201.
Song SJ, Li FF, Yue H. Study on the anti-aging effect of Radix polygonum multiflorum. J Hebei Med Univ 2003, 24(2): 90–91.
Liu HC, Chen WS. Study on antioxidation effect of 2,3,5,4′-tetrahydroxy stilbene -2-O-β-glucoside in vitro. J pharm Pract 2000, 18(4): 232–233.
Socci DJ, Crandall BM, Arendash GW. Chronic antioxidant treatment improves the cognitive performance of aged rats. Brain Res 1995, 693(1): 88–94.
Ichitani Y, Okaichi H, Yoshikawa T, Ibata Y. Learning behaviour in chronic vitamin E-deficient and -supplemented rats: radial arm maze learning and passive avoidance response. Behav Brain Res 1992, 51(2): 157–164.
Verstraeten SV, Aimo L, Oteiza PI. Aluminium and lead: molecular mechanisms of brain toxicity. Arch Toxicol 2008, 82(11): 789–802.
Ricchelli F, Drago D, Filippi B, Tognon G, Zatta P. Aluminumtriggered structural modifications and aggregation of β-amyloids. A comparison with copper and zinc. Cell Mol Life Sci 2005, 62(15): 1724–1733.
Bush AI, Tanzi RE. The galvanization of beta-amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002, 99(11): 7179–7317.
Kawahara M. Effects of aluminum on the nervous system and its possible link with neurodegenerative diseases. J Alzheimers Dis 2005, 8(2): 171–182.
Drago D, Bettella M, Bolognin S, Cendron L, Scancar J, Milacic R. Potential pathogenic role of beta-amyloid(1–42)-aluminum complex in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2008, 40(4): 731–746.
Jia Y, Zhong C, Wang Y. Effects of aluminum on amino acid neurotransmitters in hippocampus of rats. Chinese Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2001, 35(6): 397–400.
Nayak P, Chatterjee AK. Effects of aluminum exposure on brain glutamate and GABA systems: an experimental study in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 2001, 39(12): 1285–1289.
Platt B, Drysdale AJ, Nday C, Roloff EL, Drever BD, Salifoglou A. Differential toxicity of novel aluminium compounds in hippocampal culture. Neurotoxicology 2007, 28(3): 576–586.
Campbell A. The role of aluminum and copper on neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2006, 10(2): 165–172.
Ling Y, Morgan K, Kalsheker N. Amyloid precursor protein (APP) and the biology of proteolytic processing: relevance to Alzheimer. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2003, 35(4): 1505–1535.
Wan Y, Wang G, Chen SD. Genetic predisposition to inflammation: a new risk factor of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Bull 2008, 24(5): 314–322.
Nishida Y, Yokota T, Takahashi T, Uchihara T, Jishage K, Mizusawa H. Deletion of vitamin E enhances phenotype of Alzheimer disease model mouse. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006, 350(3): 530–536.
Zhang C, Yang SL, Yuan HL. Determination of stilbene in Radix Polygoni Multiflori by HPLC and its stability study. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 1997, 24(6): 357–359.
Wang W, Wang DQ. Progress of study on brain protective effect and mechanism of polygonum multiflorum. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med 2005, 25(10): 955–958.
Xie ZF, Lou ZQ, Huang XK. Classified dictionary of traditional Chinese medicine. New World Press, Beijing, 385–386.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, HB., Yang, JS., Shi, XQ. et al. Tetrahydroxy stilbene glucoside reduces the cognitive impairment and overexpression of amyloid precursor protein induced by aluminum exposure. Neurosci. Bull. 25, 391–396 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-009-0601-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-009-0601-4