Abstract
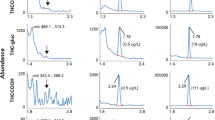
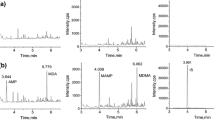
A gas chromatography-mass spectrometric (GC-MS) method was developed and validated for the simultaneous detection and quantification of four amphetamine-type stimulants (amphetamine (AP), methamphetamine (MA), 3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA) and 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA)) and two cannabinoids (Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and 11-nor-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol-9-carboxylic acid (THCCOOH)) in fingernails. Fingernail clippings (30 mg) were washed with distilled water and methanol, and then incubated in 1.0 M sodium hydroxide at 95°C for 30 min. The compounds of interest were isolated by liquid-liquid extraction followed by derivatization with N-methyl-N-trimethylsilyltrifluoroacetamide (MSTFA) at 70°C for 15 min. The derivatized compounds were analyzed by GC-MS in the selective ion monitoring (SIM) mode. The linear ranges were 0.1–15.0 ng/mg for AP, 0.2–15.0 ng/mg for MDA, Δ9-THC and THCCOOH, and 0.2–30.0 ng/mg for MA and MDMA, with good correlation coefficients (r2 > 0.9991). The intra-day, inter-day, and inter-person precisions were within 10.6%, 6.3%, and 5.3%, respectively. The intra-day, inter-day and inter-person accuracies were between −6.1 and 5.0%, −6.2 and 5.7%, and −6.4 and 5.6%, respectively. The limits of detection (LODs) and quantification (LOQs) for each compound were lower than 0.056 and 0.2 ng/mg, respectively. The recoveries were in the range of 74.0–94.8%. Positive GC-MS results were obtained from specimens of nine suspected MA or cannabis abusers. The concentration ranges of MA, AP, and THCCOOH were 0.10–1.41, 0.12–2.64, and 0.20 ng/mg, respectively. Based on these results, the method proved to be effective for the simultaneous qualification and quantification of amphetamine-type stimulants and cannabinoids in fingernails.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baden, H. P., Regeneration of the nail. Arch. Dermatol., 91, 619–620 (1965).
Caldwell, J., The metabolism of amphetamines in mammals. Drug Metab. Rev., 5, 219–280 (1976).
Cho, B. I., Methamphetamine abuse: epidemiologic issues and implications. In Miller, M. A. and Kozel, N. J. (Eds.). NIDA Research Monograph 115. US Department of Health and Human Services, Rockville, pp. 99–106 (1991).
Cingolani, M., Scavella, S., Mencarelli, R., Mirtella, D., Froldi, R., and Rodriguez, D., Simultaneous detection and quantitation of morphine, 6-acetylmorphine, and cocaine in toenails: comparison with hair analysis. J. Anal. Toxicol., 28, 128–131 (2004).
Cirimele, V., Kintz, P., and Mangin, P., Detection of amphetamines in fingernails: an alternative to hair analysis. Arch. Toxicol., 70, 68–69 (1995).
Clark, W. E. and LeGros Buxton, L. H. D., Studies in nail growth. Br. J. Dermatol., 50, 221–235 (1938).
Daniel, C. R., Piraccini, B. M., and Tosti, A., The nail and hair in forensic science. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol., 50, 258–261 (2004).
Garside, D., Ropero-Miller, J. D., Goldberger, B. A., Hamilton, W. F., and Maples, W. R., Identification of cocaine analytes in fingernail and toenail specimens. J. Forensic Sci., 43, 974–979 (1998).
Glennon, R. A., Pharmacology and toxicology of amphetamine and related designer drugs. In Asghar, K. and De Souza, E. (Eds.). NIDA Research Monograph 94. US Department of Health and Human Services, Rockville, pp. 43–67 (1989).
Hawks, R. L., The analysis of cannabinoids in biological fluids. In Hawks, R. L. (Ed.). NIDA Research Monograph 42. US Department of Health and Human Services, Rockville, pp. 125–137 (1982).
Horner, R. L. and Cohen B. I., Injuries to the fingernail. Rocky Mt. Med. J., 63, 60–62 (1966).
Irving, R. C. and Dickson, S. J., The detection of sedatives in hair and nail samples using tandem LC-MS-MS. Forensic Sci. Int., 166, 58–67 (2007).
Jenkins, A.J. and Engelhart, D. A., Phencyclidine detection in nails. J. Anal. Toxicol., 30, 643–644 (2006).
Jones, R., Marihuana research findings: 1976. In Petersen, R. C. (Ed.). NIDA Research Monograph 14, US Department of Health and Human Services, Rockville, pp. 128–178 (1977).
Kim J. Y., Jung K. S., Kim M. K., Lee J. I., and In M. K., Simultaneous determination of psychotropic phenylalkylamine derivatives in human hair by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom., 21, 1705–1720 (2007).
Klein, J., Forman, R., Eliopoulos, C., and Koren, G., A method for simultaneous measurement of cocaine and nicotine in neonatal hair. Ther. Drug Monit., 16, 67–70 (1994).
Lemos N. P., Anderson R. A., and Robertson J. R., Nail analysis for drugs of abuse: extraction and determination of cannabis in fingernails by RIA and GC-MS. J. Anal. Toxicol., 23, 147–152 (1999).
Lemos N. P., Anderson R. A., and Robertson J. R., The analysis of methadone in nail clippings from patients in a methadone-maintenance program. J. Anal. Toxicol., 24, 656–660 (2000a).
Lemos, N. P., Anderson, R. A., Valentini, R., Tagliaro, F., and Scott, R. T., Analysis of morphine by RIA and HPLC in fingernail clippings obtained from heroin users. J. Forensic Sci., 45, 407–412 (2000b).
Lim, H. K. and Foltz, R. L., Identification of metabolites of 3,4-(methylenedioxy)methamphetamine in human urine. Chem. Res. Toxicol., 2, 142–143 (1989).
Lin, D.-L., Yin, R.-M., Liu, H.-C., Wang, C.-Y., and Liu, R. H., Deposition characteristics of methamphetamine and amphetamine in fingernail clippings and hair sections. J. Anal. Toxicol., 28, 411–417 (2004).
Palmeri, A., Pichini, S., Pacifici, R., Zuccaro, P., and Lopez, A., Drugs in nails: physiology, pharmacokinetics and forensic toxicology. Clin. Pharmacokinet., 38, 95–110 (2000).
Ragoucy-Sengler, C. and Kintz, P., Detection of smoked cocaine marker (anhydroecgonine methylester) in nails. J. Anal. Toxicol., 29, 765–768 (2005).
Ropero-Miller, J. D., Goldberger, B. A., Cone, E. J., and Joseph, R. E. Jr., The disposition of cocaine and opiate analytes in hair and fingernails of humans following cocaine and codeine administration. J. Anal. Toxicol., 24, 496–508 (2000).
Skopp, G. and Pötsch, L., A case report on drug screening of nail clippings to detect prenatal drug exposure. Ther. Drug Monit., 19, 386–389 (1997).
Supreme Prosecutors’ Office, Drug Trend Report. vol. 12, Seoul, (2007).
Supreme Prosecutors’ Office, White Paper on Drug-Related Crimes. Seoul, pp. 95–122, (2004).
Suzuki, S., Inoue, T., Hori, H., and Inayama, S., Analysis of methamphetamine in hair, nail, sweat, and saliva by mass fragmentography. J. Anal. Toxicol., 13, 176–178 (1989).
Valente-Campos, S., Yonamine, M., de Moraes Moreau, R. L., and Silva, O. A., Validation of a method to detect cocaine and its metabolites in nails by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Forensic Sci. Int., 159, 218–222 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.Y., Cheong, J.C., Kim, M.K. et al. Simultaneous determination of amphetamine-type stimulants and cannabinoids in fingernails by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Arch. Pharm. Res. 31, 805–813 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-001-1230-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-001-1230-5