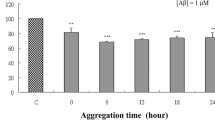
Abstract
Amyloid beta peptide (Aβ) oligomers increase intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) and calcium cation (Ca2+) concentrations, which causes neuronal cell death in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Thus, the use of neuroprotective agents with antioxidative activity might be effective in the treatment of AD. In the present study, the neuroprotective effects of the methanol extract from edible brown alga Eisenia bicyclis (Laminariaceae) and its solvent soluble fractions together with the isolated phlorotannins on Aβ-induced toxicity were assessed by cell viability, intracellular ROS, and Ca2+ levels in PC12 cells. The addition of the methanol extract as well as its ethyl acetate and n-butanol fractions of E. bicyclis markedly reversed the Aβ-induced toxicity. Among six phlorotannins, including phloroglucinol (1), dioxinodehydroeckol (2), eckol (3), phlorofucofuroeckol A (4), dieckol (5), and 7-phloroeckol (6), isolated from the most active ethyl acetate fraction, 3–6 significantly decreased Aβ-induced cell death. Furthermore, these compounds also inhibited intracellular ROS generation and Ca2+ generation, indicating the neuroprotective effects may be mediated through reduced intracellular ROS and Ca2+ generation. Thus, the results of the present study imply that E. bicyclis and its active components attenuated the oxidative stress and reduced neuronal cell death, suggesting that it may be used as a dietary neuroprotective agent in AD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agostinho, P., Cunha, R. A., and Oliveira, C., Neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Alzheimers disease. Curr. Pharm. Des., 16, 2766–2278 (2010).
Butterfield, D. A. and Boyd-Kimball, D., The critical role of methionine 35 in Alzheimer’s amyloid beta peptide (1–42)-induced oxidative stress and neurotoxicity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1703, 149–156 (2005).
Cecchi, C., Fiorillo, C., Sorbi, S., Latorraca, S., Nacmias, B., Bacnoli, S., Nassi, P., and Liguri, G., Oxidative stress and reduced antioxidant defenses in peripheral cells from familial Alzheimer’s patients. Free Radic. Biol. Med., 33, 1372–1379 (2002).
Choi, J. S., Lee, J. H., and Jung, J. H., The screening of nitrite scavenging effect of marine algae and active principles of Ecklonia stolonifera. J. Kor. Fish. Soc., 30, 909–915 (1997).
Christen, Y., Oxidative stress and Alzheimer disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr., 71, 621–629 (2000).
Clementi, M. E., Pezzotti, M., Orsini, F., Sampaolese, B., Mezzogori, D., Grassi, C., Giardina, B., and Misiti, F., Alzheimer’s amyloid beta-peptide (1–42) induces cell death in human neuroblastoma via bax/bcl-2 ratio increase: an intriguing role for methionine 35. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 342, 206–213 (2006).
Francesca, M., Alina, S., Bengt, W., Patrizia, M., and Miia, K., Alzheimer’s disease: clinical trials and drug development. Lancet Neurol., 9, 702–716 (2010).
Good, P. F., Werner, P., Hsu, A., Olanow, C. W., and Perl, D. P., Evidence for neuronal oxidative damage in Alzheimer’s disease. Am. J. Pathol., 149, 21–28 (1996).
Hao, L. N., Zhang, Q. Z., Yu, T. G., Cheng, Y. N., and Ji, S. L., Antagonistic effects of ultra-low-molecular-weight heparin on Aβ25–35-induced apoptosis in cultured rat cortical neurons. Brain Res., 1368, 1–10 (2011).
Hartman, D., Free radical theory of aging: Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. Age, 18, 97–119 (1995).
Hoi, C. P., Ho, Y. P., Baum, L., and Chow, A. H., Neuroprotec tive effect of honokiol and magnolol, compounds from Magnolia officinalis, on beta-amyloid-induced toxicity in PC12 cells. Phytother. Res., 24, 1538–1542 (2010).
Jhamandas, J. H., Wie, M. B., Harris, K., MacTavish, D., and Kar, S., Fucoidan inhibits cellular and neurotoxic effects of β-amyloid (Aβ) in rat cholinergic basal forebrain neurons. Eur. J. Neurosci., 21, 2649–2659 (2005).
Jung, H. A., Hyun, S. K., Kim, H. R., and Choi, J. S., Angiotensin-converting enzyme I inhibitory activity of phlorotannins from Ecklonia stolonifera. Fish. Sci., 72, 1292–1299 (2006).
Jung, H. A., Jin, S. E., Choi, R. J., Kim, D. H., Kim, Y. S., Ryu, J. H., Kim, D. W., Son, Y. K., Park, J. J., and Choi, J. S., Anti-amnesic activity of neferine with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capacities, as well as inhibition of ChEs and BACE1. Life Sci., 87, 420–430 (2010a).
Jung, H. A., Oh, S. H., and Choi, J. S., Molecular docking studies of phlorotannins from Eisenia bicyclis with BACE1 inhibitory activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 20, 3211–3215 (2010b).
Kang, H. S., Chung, H. Y., Jung, J. H., Son, B. W., and Choi, J. S., A new phlorotannin from the brown alga Ecklonia stolonifera. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 51, 1012–1014 (2003).
Kang, H. S., Chung, H. Y., Kim, J. Y., Son, B. W., Jung, H. A., and Choi, J. S., Inhibitory phlorotannins from the edible brown alga Ecklonia stolonifera on total reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. Arch. Pharm. Res., 27, 194–198 (2004).
Keller, J. N. and Mattson, M. P., 17 Beta-estradiol attenuates oxidative impairment of synaptic Na+/K+-ATPase activity, glucose transport and glutamate transport induced by amyloid beta-peptide and iron. J. Neurosci. Res., 50, 522–530 (1997).
Kim, A. R., Shin, T. S., Lee, M. S., Park, J. Y., Park, K. E., Yoon, N. Y., Kim, J. S., Choi, J. S., Jang, B. C., Byun, D. S., Park, N. K., and Kim, H. R., Isolation and identification of phlorotannins from Ecklonia stolonifera with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. J. Agric. Food Chem., 57, 3483–3489 (2009).
Kousaka, K., Ogi, N., Akazawa, Y., Fujieda, M., Yamamoto, Y., Takada, Y., and Kimura, J., Novel oxylipin metabolites from the brown alga Eisenia bicyclis. J. Nat. Prod., 66, 1318–1323 (2003).
Kurata, K., Taniguchi, K., Shiraishi, K., and Suzuki, M., A C26 sterol from the brown alga Eisenia bicyclis. Phytochemistry, 29, 3678–3680 (1990).
Launer, L. J., Andersen, K., Dewey, M. E., Letenneur, L., Ott, A., Amaducci, L. A., Brayne, C., Copeland, J. R., Dartigues, J. F., Kragh-Sorensen, P., Lobo, A., Martinez-Lage, J. M., Stijnen, T., and Hofman, A., Rates and risk factors for dementia and Alzheimer’s disease: results from EURODEM pooled analyses. Neurology, 1, 78–84 (1999).
Lee, J. H., Park, J. C., and Choi, J. S., The antioxidant activity of Ecklonia stolonifera. Arch. Pharm. Res., 19, 223–227 (1996).
Lee, S. H., Li, Y., Karadeniz, F., Kim, M. M., and Kim, S. K., α-Glucosidase and α-amylase inhibitory activities of phloroglucinal derivatives from edible marine brown alga, Ecklonia cava. J. Sci. Food Agric., 89, 1552–1558 (2009).
Li, Y., Qian, Z. J., Ryu, B., Lee, S. H., Kim, M. M., and Kim, S. K., Chemical components and its antioxidant properties in vitro: an edible marine brown alga, Ecklonia cava. Bioorg. Med. Chem., 17, 1963–1973 (2009).
Mark, R. J., Hensley, K., Butterfield, D. A., and Mattson, M. P., Amyloid beta-peptide impairs ion-motive ATPase activities: evidence for a role in loss of neuronal Ca2+ homeostasis and cell death. J. Neurosci., 15, 6239–6249 (1995).
Mark, R. J., Pang, Z., Geddes, J. W., and Mattson, M. P., Amyloid beta-peptide impairs glucose uptake in hippocampal and cortical neurons: involvement of membrane lipid peroxidation. J. Neurosci., 17, 1046–1054 (1997).
Mosmann, T., Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods, 65, 55–63 (1983).
Myung, C. S., Shin, H. C., Bao, H. Y., Yeo, S. J., Lee, B. H., and Kang, J. S., Improvement of memory by dieckol and phlorofucofuroeckol in ethanol-treated mice: possible involvement of the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase. Arch. Pharm. Res., 28, 691–698 (2005).
Noda, H., Amano, H., Arashima, K., Hashimoto, S., and Nishizawa, K., Studies on the antitumor activity of marine algae. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi, 55, 1259–1264 (1989).
Okada, Y., Ishimaru, A., Suzuki, R., and Okuyama, T., A new phloroglucinol derivatives from the brown alga Eisenia bicyclis: Potential for the effective treatment of diabetic complications. J. Nat. Prod., 67, 103–105 (2004).
Omodeo-Sale, F., Gramigna, D., and Campaniello, R., Lipid peroxidation and antioxidant systems in rat brain: effect of chronic alcohol consumption. Neurochem. Res., 22, 557–582 (1997).
Orhan, I. and Aslan, M., Appraisal of scopolamine-induced antiamnesic effect in mice and in vitro antiacetylcholinesterase and antioxidant activities of some traditionally used Lamiaceae plants. J. Ethnopharmacol., 122, 327–332 (2009).
Pangestuti, R. and Kim, S. K., Neuroprotective effects of marine algae. Mar. Drugs, 9, 803–818 (2011).
Ragan, M. A. and Glombitza, K. W., Phlorotannins, brown alga polyphenols. Prog. Phycol. Res., 4, 129–241 (1986).
Reddy, V. P., Zhu, X., Perry, G., and Smith, M. A., Oxidative stress in diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis., 16, 763–774 (2009).
Ryu, B., Li, Y., Qian, Z. J., Kim, M. M., and Kim, S. K., Differentiation of human osteosarcoma cells by isolated phlorotannins is subtly linked to COX-2, iNOS, MMPs, and MAPK signaling: implication for chronic articular disease. Chem. Biol. Interact., 179, 192–201 (2009).
Selkoe, D. J., The molecular pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron, 6, 487–498 (1991).
Selkoe, D. J., Alzheimer’s disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol. Rev., 81, 741–766 (2001).
Selkoe, D. J., Defining molecular targets to prevent Alzheimer disease. Arch. Neuron, 62, 192–195 (2005).
Shin, H. C., Hwang, H. J., Kang, K. J., and Lee, B. H., An antioxidative and anti-inflammatory agent for potential treatment of osteoarthritis from Ecklonia cava. Arch. Pharm. Res., 29, 165–171 (2006).
Stirk, W., Reinecke, D., and van Staden, J., Seasonal variation in antifungal, antibacterial and acetylcholinesterase activity in seven South African seaweeds. J. Appl. Phycol., 19, 271–276 (2007).
Tsang, C., Ina, A., Goto, T., and Kamei, Y., Sargachromenol, a novel nerve growth factor-potentiating substance isolated from Sargassum macrocarpum, promotes neurite outgrowth and survival via distinct signaling pathways in PC12D cells. Neuroscience, 132, 633–643 (2005).
Varadarajan, S., Kanski, J., Aksenova, M., Lauderback, C., and Butterfield, D. A., Different mechanisms of oxidative stress and neurotoxicity for Alzheimer’s A beta (1–42) and A beta (25–35). J. Am. Chem. Soc., 123, 5625–5631 (2001).
Wang, H. and Joseph, J. A., Quantifying cellular oxidative stress by dichlorofluorescein assay using microplate reader. Free Radic. Biol. Med., 27, 612–616 (1999).
Wang, X. J. and Xu, J. X., Possible involvement of Ca2+ signaling in rotenone-induced apoptosis in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Neurosci. Lett., 376, 127–132 (2005).
Xiaoyu, L., Kedi, X., Ming, Y., Yongping, W., and Xiaoxiang, Z., Protective effects of galantamine against Aβ-induced PC12 cell apoptosis by preventing mitochondrial dysfunction and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Neurochem. Int., 57, 588–599 (2010).
Yoon, N. Y., Chung, H. Y., Kim, H. R., and Choi, J. S., Acetyl and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitory activities of sterols and phlorotannins from Ecklonia stolonifera. Fish. Sci., 74, 200–207 (2008).
Yoon, N. Y., Lee, S. H., Yong, L., and Kim, S. K., Phlorotannins from Ishige okamurae and their acetyl- and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitory effects. J. Funct. Foods, 1, 331–335 (2009).
Zhou, Y., Li, W., Xu, L., and Chen, L., In Salvia miltiorrhiza, phenolic acids possess protective properties against amyloid α-induced cytotoxicity, and tanshinones act as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol., 31, 443–452 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahn, B.R., Moon, H.E., Kim, H.R. et al. Neuroprotective effect of edible brown alga Eisenia bicyclis on amyloid beta peptide-induced toxicity in PC12 cells. Arch. Pharm. Res. 35, 1989–1998 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-012-1116-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-012-1116-5