Abstract
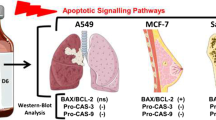
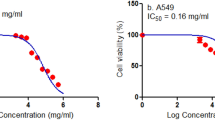
In the present study we experimented on a multimodal therapeutic approach, such as combining chemotherapy agent (Bee venom) with cellular (NK-92MI) immunotherapy. Previously bee venom has been found to show anti-cancer effect in various cancer cell lines. In lung cancer cells bee venom showed an IC50 value of 3 μg/ml in both cell lines. The co-culture of NK-92MI cell lines with lung cancer cells also show a decrease in viability upto 50 % at 48 h time point. Hence we used bee venom treated NK-92MI cells to co-culture with NSCLC cells and found that there is a further decrease in cell viability upto 70 and 75 % in A549 and NCI-H460 cell lines respectively. We further investigated the expression of various apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins and found that Bax, cleaved caspase-3 and -8 were increasing where as Bcl-2 and cIAP-2 was decreasing. The expression of various death receptor proteins like DR3, DR6 and Fas was also increasing. Concomitantly the expression of various death receptor ligands (TNFalpha, Apo3L and FasL) was also increasing of NK-92MI cells after co-culture. Further the DNA binding activity and luciferase activity of NF-κB was also inhibited after co-culture with bee venom treated NK-92MI cell lines. The knock down of death receptors with si-RNA has reversed the decrease in cell viability and NF-κB activity after co-culture with bee venom treated NK-92MI cells. Thus this new approach can enhance the anti-cancer effect of bee venom at a much lower concentration.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alizadehnohi, M., M. Nabiuni, Z. Nazari, Z. Safaeinejad, and S. Irian. 2012. The synergistic cytotoxic effect of cisplatin and honey bee venom on human ovarian cancer cell line A2780cp. Journal of Venom Research 3: 22–27.
Ashkenazi, A. 2008. Targeting the extrinsic apoptosis pathway in cancer. Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews 19(3–4): 325–331.
Bae, J.H., J.Y. Kim, M.J. Kim, S.H. Chang, Y.S. Park, C.H. Son, S.J. Park, J.S. Chung, E.Y. Lee, S.H. Kim, and C.D. Kang. 2010. Quercetin enhances susceptibility to NK cell-mediated lysis of tumor cells through induction of NKG2D ligands and suppression of HSP70. Journal of Immunotherapy 33(4): 391–401.
Bae, J.H., S.J. Kim, M.J. Kim, S.O. Oh, J.S. Chung, S.H. Kim, and C.D. Kang. 2012. Susceptibility to natural killer cell-mediated lysis of colon cancer cells is enhanced by treatment with epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors through UL16-binding protein-1 induction. Cancer Science 103(1): 7–16.
Baud, V., and M. Karin. 2009. Is NF-kappaB a good target for cancer therapy? Hopes and pitfalls. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 8(1): 33–40.
Brady, J., S. Carotta, R.P. Thong, C.J. Chan, Y. Hayakawa, M.J. Smyth, and S.L. Nutt. 2010. The interactions of multiple cytokines control NK cell maturation. Journal of Immunology 185(11): 6679–6688.
Burke, S., T. Lakshmikanth, F. Colucci, and E. Carbone. 2010. New views on natural killer cell-based immunotherapy for melanoma treatment. Trends in Immunology 31(9): 339–345.
Cerwenka, A., and L.L. Lanier. 2001. Natural killer cells, viruses and cancer. Nature Reviews Immunology 1(1): 41–49.
Cooper, M.A., T.A. Fehniger, and M.A. Caligiuri. 2001. The biology of human natural killer-cell subsets. Trends in Immunology 22(11): 633–640.
Dasgupta, A., J.E. Shields, and H.T. Spencer. 2012. Treatment of a solid tumor using engineered drug-resistant immunocompetent cells and cytotoxic chemotherapy. Human Gene Therapy 23(7): 711–721.
Du, G., L. Ye, G. Zhang, Q. Dong, K. Liu, and J. Tian. 2012. Human IL18-IL2 fusion protein as a potential antitumor reagent by enhancing NK cell cytotoxicity and IFN-gamma production. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology 138(10): 1727–1736.
Elrod, H.A., and S.Y. Sun. 2008. Modulation of death receptors by cancer therapeutic agents. Cancer Biology & Therapy 7(2): 163–173.
Glas, R., L. Franksson, C. Une, M.L. Eloranta, C. Ohlen, A. Orn, and K. Karre. 2000. Recruitment and activation of natural killer (NK) cells in vivo determined by the target cell phenotype. An adaptive component of NK cell-mediated responses. Journal of Experimental Medicine 191(1): 129–138.
Hercend, T., F. Farace, D. Baume, F. Charpentier, J.P. Droz, F. Triebel, and B. Escudier. 1990. Immunotherapy with lymphokine-activated natural killer cells and recombinant interleukin-2: A feasibility trial in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Journal of Biological Response Modifiers 9(6): 546–555.
Inoue, N., F. Matsuda, Y. Goto, and N. Manabe. 2011. Role of cell-death ligand-receptor system of granulosa cells in selective follicular atresia in porcine ovary. Journal of Reproduction and Development 57(2): 169–175.
Ip, S.W., Y.L. Chu, C.S. Yu, P.Y. Chen, H.C. Ho, J.S. Yang, H.Y. Huang, F.S. Chueh, T.Y. Lai, and J.G. Chung. 2012. Bee venom induces apoptosis through intracellular Ca2+-modulated intrinsic death pathway in human bladder cancer cells. International Journal of Urology 19(1): 61–70.
Ip, S.W., H.C. Wei, J.P. Lin, H.M. Kuo, K.C. Liu, S.C. Hsu, J.S. Yang, D. Mei, T.H. Chiu, S.M. Han, and J.G. Chung. 2008. Bee venom induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human cervical epidermoid carcinoma Ca Ski cells. Anticancer Research 28(2A): 833–842.
Jahangeer, S., P. Forde, D. Soden, and J. Hinchion. 2013. Review of current thermal ablation treatment for lung cancer and the potential of electrochemotherapy as a means for treatment of lung tumours. Cancer Treatment Reviews 39(8): 862–871.
Jang, M.H., M.C. Shin, S. Lim, S.M. Han, H.J. Park, I. Shin, J.S. Lee, K.A. Kim, E.H. Kim, and C.J. Kim. 2003. Bee venom induces apoptosis and inhibits expression of cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA in human lung cancer cell line NCI-H1299. Journal of Pharmacological Sciences 91(2): 95–104.
Jo, M., M.H. Park, P.S. Kollipara, B.J. An, H.S. Song, S.B. Han, J.H. Kim, M.J. Song, and J.T. Hong. 2012. Anti-cancer effect of bee venom toxin and melittin in ovarian cancer cells through induction of death receptors and inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 258(1): 72–81.
Kang, Y.J., I.Y. Kim, E.H. Kim, M.J. Yoon, S.U. Kim, T.K. Kwon, and K.S. Choi. 2011. Paxilline enhances TRAIL-mediated apoptosis of glioma cells via modulation of c-FLIP, survivin and DR5. Experimental & Molecular Medicine 43(1): 24–34.
Karin, M., and F.R. Greten. 2005. NF-kappaB: linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nature Reviews Immunology 5(10): 749–759.
Karin, M., and A. Lin. 2002. NF-kappaB at the crossroads of life and death. Nature Immunology 3(3): 221–227.
Latz, C., Q. Huang, M.K. Kapadia, and S.K. Freitag. 2009. Metastasis to eyelid as initial presentation of non-small cell carcinoma. Ophthalmic Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 25(5): 406–408.
Magne, N., J.O. Bay, J.Y. Blay, A. Goncalves, C. Massard, J. Thariat, M. Wislez, T. Andre, and S. Vignot. 2012. American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) 2012 essential data: the editorial board of the Bulletin du Cancer point of view. Bulletin du Cancer 99(12): 1209–1217.
Markovic, S.N., and D.M. Murasko. 1991. Role of natural killer and T-cells in interferon induced inhibition of spontaneous metastases of the B16F10L murine melanoma. Cancer Research 51(4): 1124–1128.
Mohammed, N., L.L. Kestin, I.S. Grills, M. Battu, D.L. Fitch, C.Y. Wong, J.H. Margolis, G.W. Chmielewski, and R.J. Welsh. 2011. Rapid disease progression with delay in treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics 79(2): 466–472.
Nakshatri, H., P. Bhat-Nakshatri, D.A. Martin, R.J. Goulet Jr, and G.W. Sledge Jr. 1997. Constitutive activation of NF-kappaB during progression of breast cancer to hormone-independent growth. Molecular and Cellular Biology 17(7): 3629–3639.
O’Donovan, T.R., G.C. O’Sullivan, and S.L. McKenna. 2011. Induction of autophagy by drug-resistant esophageal cancer cells promotes their survival and recovery following treatment with chemotherapeutics. Autophagy 7(5): 509–524.
Park, H.J., S.H. Lee, D.J. Son, K.W. Oh, K.H. Kim, H.S. Song, G.J. Kim, G.T. Oh, D.Y. Yoon, and J.T. Hong. 2004. Antiarthritic effect of bee venom: inhibition of inflammation mediator generation by suppression of NF-kappaB through interaction with the p50 subunit. Arthritis and Rheumatism 50(11): 3504–3515.
Park, M.H., M.S. Choi, D.H. Kwak, K.W. Oh, Y. Yoon do, S.B. Han, H.S. Song, M.J. Song, and J.T. Hong. 2011. Anti-cancer effect of bee venom in prostate cancer cells through activation of caspase pathway via inactivation of NF-kappaB. Prostate 71(8): 801–812.
Park, M.H., M.J. Song, M.C. Cho, D.C. Moon, Y. Yoon do, S.B. Han, and J.T. Hong. 2012. Interleukin-32 enhances cytotoxic effect of natural killer cells to cancer cells via activation of death receptor 3. Immunology 135(1): 63–72.
Putz, T., R. Ramoner, H. Gander, A. Rahm, G. Bartsch, K. Bernardo, S. Ramsay, and M. Thurnher. 2007. Bee venom secretory phospholipase A2 and phosphatidylinositol-homologues cooperatively disrupt membrane integrity, abrogate signal transduction and inhibit proliferation of renal cancer cells. Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy 56(5): 627–640.
Sancho-Martinez, I., and A. Martin-Villalba. 2009. Tyrosine phosphorylation and CD95: A FAScinating switch. Cell Cycle 8(6): 838–842.
Screpanti, V., R.P. Wallin, A. Grandien, and H.G. Ljunggren. 2005. Impact of FASL-induced apoptosis in the elimination of tumor cells by NK cells. Molecular Immunology 42(4): 495–499.
Smyth, M.J., E. Cretney, K. Takeda, R.H. Wiltrout, L.M. Sedger, N. Kayagaki, H. Yagita, and K. Okumura. 2001. Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) contributes to interferon gamma-dependent natural killer cell protection from tumor metastasis. Journal of Experimental Medicine 193(6): 661–670.
Smyth, M.J., Y. Hayakawa, K. Takeda, and H. Yagita. 2002. New aspects of natural-killer-cell surveillance and therapy of cancer. Nature Reviews Cancer 2(11): 850–861.
Sun, S.Y. 2011. Understanding the role of the death receptor 5/FADD/caspase-8 death signaling in cancer metastasis. Molecular and Cellular Pharmacology 3(1): 31–34.
Tam, Y.K., B. Miyagawa, V.C. Ho, and H.G. Klingemann. 1999. Immunotherapy of malignant melanoma in a SCID mouse model using the highly cytotoxic natural killer cell line NK-92. Journal of Hematotherapy 8(3): 281–290.
Triller, N., P. Korosec, I. Kern, M. Kosnik, and A. Debeljak. 2006. Multidrug resistance in small cell lung cancer: expression of P-glycoprotein, multidrug resistance protein 1 and lung resistance protein in chemo-naive patients and in relapsed disease. Lung Cancer 54(2): 235–240.
Wang, C., T. Chen, N. Zhang, M. Yang, B. Li, X. Lu, X. Cao, and C. Ling. 2009. Melittin, a major component of bee venom, sensitizes human hepatocellular carcinoma cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis by activating CaMKII-TAK1-JNK/p38 and inhibiting IkappaBalpha kinase-NFkappaB. Journal of Biological Chemistry 284(6): 3804–3813.
Yasumura, S., A. Amoscato, H. Hirabayashi, W.C. Lin, and T.L. Whiteside. 1994. Proliferation of hematopoietic cell lines induced by a soluble factor derived from human squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy 39(6): 407–415.
Yoshida, T., M. Horinaka, and T. Sakai. 2010. “Combination-oriented molecular-targeting prevention” of cancer: a model involving the combination of TRAIL and a DR5 inducer. Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine 15(4): 203–210.
Zhang, H.P., K. Takayama, B. Su, X.D. Jiao, R. Li, and J.J. Wang. 2011. Effect of sunitinib combined with ionizing radiation on endothelial cells. Journal of Radiation Research 52(1): 1–8.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (No. MRC, 2008-0062275), and by the Ministry of Trade, Industry, & Energy (MOTIE, 141526993) through fostering project of Osong Academy-Industry Convergence (BAIO).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kollipara, P.S., Kim, J.H., Won, D. et al. Co-culture with NK-92MI cells enhanced the anti-cancer effect of bee venom on NSCLC cells by inactivation of NF-κB. Arch. Pharm. Res. 37, 379–389 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0319-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-013-0319-8