Abstract
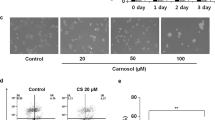
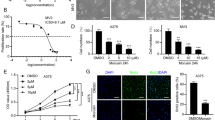
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) is associated with cancer progression in different cancers, including melanoma. It also affects specificity protein (Sp1), a transcription factor. Flavonoid morin is known to inhibit growth of cancer cells, including lung cancer and breast cancer. Herein, we hypothesized that morin can inhibit cancer activities in melanoma by altering ROS generation. The aim of this study is to determine the effects of morin and its underlying mechanisms in melanoma cells. Effects of morin on cell proliferation and apoptosis were determined using standardized assays. Changes in pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins were analyzed by western blot analysis. Cellular ROS levels and mitochondrial function were evaluated by measuring DCF-DA fluorescence and rhodamine-123 fluorescence intensities, respectively. Morin induced ROS production and apoptosis, as presented by increased proportion of cells with Annexin V-PE(+) staining and sub-G0/G1 peak in cell cycle analysis. It also downregulated Sp1, Mcl-1, Bcl-2, and caspase-3 but upregulated cleaved caspase-3, Bax, and PUMA. In immunohistochemical staining, Sp1 was overexpressed in melanoma tissues compared to normal skin tissues. Collectively, our data suggest that morin can induce apoptosis of melanoma cells by regulating pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins through ROS, and may be a potential substance for treatment of melanoma.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbour N, Vanderluit JL, Le Grand JN, Jahani-Asl A, Ruzhynsky VA, Cheung EC, Kelly MA, Mackenzie AE, Park DS, Opferman JT, Slack RS (2008) Mcl-1 is a key regulator of apoptosis during CNS development and after DNA damage. J Neurosci 28:6068–6078
Bajpai R, Nagaraju GP (2017) Specificity protein 1: its role in colorectal cancer progression and metastasis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 113:1–7
Baldelli S, Aquilano K, Rotilio G, Ciriolo MR (2008) Glutathione and copper, zinc superoxide dismutase are modulated by overexpression of neuronal nitric oxide synthase. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40:2660–2670
Beroukhim R, Mermel CH, Porter D, Wei G, Raychaudhuri S, Donovan J, Barretina J, Boehm JS, Dobson J, Urashima M, Mc Henry KT, Pinchback RM, Ligon AH, Cho YJ, Haery L, Greulich H, Reich M, Winckler W, Lawrence MS, Weir BA, Tanaka KE, Chiang DY, Bass AJ, Loo A, Hoffman C, Prensner J, Liefeld T, Gao Q, Yecies D, Signoretti S, Maher E, Kaye FJ, Sasaki H, Tepper JE, Fletcher JA, Tabernero J, Baselga J, Tsao MS, Demichelis F, Rubin MA, Janne PA, Daly MJ, Nucera C, Levine RL, Ebert BL, Gabriel S, Rustgi AK, Antonescu CR, Ladanyi M, Letai A, Garraway LA, Loda M, Beer DG, True LD, Okamoto A, Pomeroy SL, Singer S, Golub TR, Lander ES, Getz G, Sellers WR, Meyerson M (2010) The landscape of somatic copy-number alteration across human cancers. Nature 463:899–905
Black AR, Black JD, Azizkhan-Clifford J (2001) Sp1 and kruppel-like factor family of transcription factors in cell growth regulation and cancer. J Cell Physiol 188:143–160
Briggs MR, Kadonaga JT, Bell SP, Tjian R (1986) Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science 234:47–52
Brown J, O’prey J, Harrison PR (2003) Enhanced sensitivity of human oral tumours to the flavonol, morin, during cancer progression: involvement of the Akt and stress kinase pathways. Carcinogenesis 24:171–177
Cabello CM, Lamore SD, Bair WB 3rd, Qiao S, Azimian S, Lesson JL, Wondrak GT (2012) The redox antimalarial dihydroartemisinin targets human metastatic melanoma cells but not primary melanocytes with induction of NOXA-dependent apoptosis. Invest New Drugs 30:1289–1301
Chiefari E, Brunetti A, Arturi F, Bidart JM, Russo D, Schlumberger M, Filetti S (2002) Increased expression of AP2 and Sp1 transcription factors in human thyroid tumors: a role in NIS expression regulation? BMC Cancer 2:35
Choi ES, Han G, Park SK, Lee K, Kim HJ, Cho SD, Kim HM (2013) A248, a novel synthetic HDAC inhibitor, induces apoptosis through the inhibition of specificity protein 1 and its downstream proteins in human prostate cancer cells. Mol Med Rep 8:195–200
Choi CY, Kim JY, Wee SY, Lee JH, Nam DH, Kim CH, Cho MK, Lee YJ, Nam HS, Lee SH, Cho SW (2014) Expression of nuclear factor erythroid 2 protein in malignant cutaneous tumors. Arch Plast Surg 41:654–660
Chuang JY, Kao TJ, Lin SH, Wu AC, Lee PT, Su TP, Yeh SH, Lee YC, Wu CC, Chang WC (2017) Specificity protein 1-zinc finger protein 179 pathway is involved in the attenuation of oxidative stress following brain injury. Redox Biol 11:135–143
Deniaud E, Baguet J, Mathieu AL, Pages G, Marvel J, Leverrier Y (2006) Overexpression of Sp1 transcription factor induces apoptosis. Oncogene 25:7096–7105
Du Y, Qu J, Zhang W, Bai M, Zhou Q, Zhang Z, Li Z, Miao J (2016) Morin reverses neuropathological and cognitive impairments in APPswe/PS1dE9 mice by targeting multiple pathogenic mechanisms. Neuropharmacology 108:1–13
Duan H, Heckman CA, Boxer LM (2005) Histone deacetylase inhibitors down-regulate bcl-2 expression and induce apoptosis in t(14;18) lymphomas. Mol Cell Biol 25:1608–1619
Dzhagalov I, St John A, He YW (2007) The antiapoptotic protein Mcl-1 is essential for the survival of neutrophils but not macrophages. Blood 109:1620–1626
Dzhagalov I, Dunkle A, He YW (2008) The anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family member Mcl-1 promotes T lymphocyte survival at multiple stages. J Immunol 181:521–528
Gandhy SU, Kim K, Larsen L, Rosengren RJ, Safe S (2012) Curcumin and synthetic analogs induce reactive oxygen species and decreases specificity protein (Sp) transcription factors by targeting microRNAs. BMC Cancer 12:564
Guan H, Cai J, Zhang N, Wu J, Yuan J, Li J, Li M (2012) Sp1 is upregulated in human glioma, promotes MMP-2-mediated cell invasion and predicts poor clinical outcome. Int J Cancer 130:593–601
Guo Z, Zhang W, Xia G, Niu L, Zhang Y, Wang X, Zhang Y, Jiang B, Wang J (2010) Sp1 upregulates the four and half lim 2 (FHL2) expression in gastrointestinal cancers through transcription regulation. Mol Carcinog 49:826–836
Guterres FA, Martinez GR, Rocha ME, Winnischofer SM (2013) Simvastatin rises reactive oxygen species levels and induces senescence in human melanoma cells by activation of p53/p21 pathway. Exp Cell Res 319:2977–2988
Hambright HG, Meng P, Kumar AP, Ghosh R (2015) Inhibition of PI3 K/AKT/mTOR axis disrupts oxidative stress-mediated survival of melanoma cells. Oncotarget 6:7195–7208
Hofmann UB, Westphal JR, Van Muijen GN, Ruiter DJ (2000) Matrix metalloproteinases in human melanoma. J Invest Dermatol 115:337–344
Hsu TI, Wang MC, Chen SY, Yeh YM, Su WC, Chang WC, Hung JJ (2012) Sp1 expression regulates lung tumor progression. Oncogene 31:3973–3988
Hyun HB, Lee WS, Go SI, Nagappan A, Park C, Han MH, Hong SH, Kim G, Kim GY, Cheong J, Ryu CH, Shin SC, Choi YH (2015) The flavonoid morin from Moraceae induces apoptosis by modulation of Bcl-2 family members and Fas receptor in HCT 116 cells. Int J Oncol 46:2670–2678
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61:69–90
Jiang NY, Woda BA, Banner BF, Whalen GF, Dresser KA, Lu D (2008) Sp1, a new biomarker that identifies a subset of aggressive pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 17:1648–1652
Jin M, Ande A, Kumar A, Kumar S (2013) Regulation of cytochrome P450 2e1 expression by ethanol: role of oxidative stress-mediated pkc/jnk/sp1 pathway. Cell Death Dis 4:e554
Jin H, Lee WS, Eun SY, Jung JH, Park HS, Kim G, Choi YH, Ryu CH, Jung JM, Hong SC, Shin SC, Kim HJ (2014) Morin, a flavonoid from Moraceae, suppresses growth and invasion of the highly metastatic breast cancer cell line MDA-MB231 partly through suppression of the Akt pathway. Int J Oncol 45:1629–1637
Karlseder J, Rotheneder H, Wintersberger E (1996) Interaction of Sp1 with the growth- and cell cycle-regulated transcription factor E2F. Mol Cell Biol 16:1659–1667
Kawabata K, Tanaka T, Honjo S, Kakumoto M, Hara A, Makita H, Tatematsu N, Ushida J, Tsuda H, Mori H (1999) Chemopreventive effect of dietary flavonoid morin on chemically induced rat tongue carcinogenesis. Int J Cancer 83:381–386
Kim HK, Namgoong SY, Kim HP (1993) Antiinflammatory activity of flavonoids: mouse ear edema inhibition. Arch Pharm Res 16:18
Klaunig JE, Xu Y, Bachowski S, Ketcham CA, Isenberg JS, Kolaja KL, Baker TK, Walborg EF Jr, Stevenson DE (1995) Oxidative stress in nongenotoxic carcinogenesis. Toxicol Lett 82–83:683–691
Kuo HM, Chang LS, Lin YL, Lu HF, Yang JS, Lee JH, Chung JG (2007) Morin inhibits the growth of human leukemia HL-60 cells via cell cycle arrest and induction of apoptosis through mitochondria dependent pathway. Anticancer Res 27:395–405
Lau AT, Wang Y, Chiu JF (2008) Reactive oxygen species: current knowledge and applications in cancer research and therapeutic. J Cell Biochem 104:657–667
Lee SJ, Son KH, Chang HW, Do JC, Jung KY, Kang SS, Kim HP (1993) Antiinflammatory activity of naturally occurring flavone and flavonol glycosides. Arch Pharmacal Res 16:25
Lee HS, Jung K-H, Hong S-W, Park I-S, Lee C, Han H-K, Lee D-H, Hong S-S (2008) Morin protects acute liver damage by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) in rat. Arch Pharm Res 31:1160–1165
Lee JH, Won YS, Park KH, Lee MK, Tachibana H, Yamada K, Seo KI (2012) Celastrol inhibits growth and induces apoptotic cell death in melanoma cells via the activation ROS-dependent mitochondrial pathway and the suppression of PI3 K/AKT signaling. Apoptosis 17:1275–1286
Lee J, Jin H, Lee WS, Nagappan A, Choi YH, Kim GS, Jung J, Ryu CH, Shin SC, Hong SC, Kim HJ (2016) Morin, a flavonoid from Moraceae, inhibits cancer cell adhesion to endothelial cells and EMT by downregulating VCAM1 and Ncadherin. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 17:3071–3075
Lee MH, Cha HJ, Choi EO, Han MH, Kim SO, Kim GY, Hong SH, Park C, Moon SK, Jeong SJ, Jeong MJ, Kim WJ, Choi YH (2017) Antioxidant and cytoprotective effects of morin against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress are associated with the induction of Nrf-2mediated HO-1 expression in V79-4 Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts. Int J Mol Med 39:672–680
Marnett LJ, Riggins JN, West JD (2003) Endogenous generation of reactive oxidants and electrophiles and their reactions with DNA and protein. J Clin Invest 111:583–593
Nguyen T, Nioi P, Pickett CB (2009) The Nrf2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway and its activation by oxidative stress. J Biol Chem 284:13291–13295
Noor H, Cao P, Raleigh DP (2012) Morin hydrate inhibits amyloid formation by islet amyloid polypeptide and disaggregates amyloid fibers. Protein Sci 21:373–382
Ola MS, Aleisa AM, Al-Rejaie SS, Abuohashish HM, Parmar MY, Alhomida AS, Ahmed MM (2014) Flavonoid, morin inhibits oxidative stress, inflammation and enhances neurotrophic support in the brain of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Neurol Sci 35:1003–1008
Opferman JT, Letai A, Beard C, Sorcinelli MD, Ong CC, Korsmeyer SJ (2003) Development and maintenance of B and T lymphocytes requires antiapoptotic MCL-1. Nature 426:671–676
Opferman JT, Iwasaki H, Ong CC, Suh H, Mizuno S, Akashi K, Korsmeyer SJ (2005) Obligate role of anti-apoptotic MCL-1 in the survival of hematopoietic stem cells. Science 307:1101–1104
Pervaiz S, Clement MV (2007) Superoxide anion: oncogenic reactive oxygen species? Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39:1297–1304
Prathyusha AMVN, Nawadkar R, Chari B (2017) Role of Sp1 Transcriptional Factor in Gastrointestinal Carcinogenesis. In: Nagaraju GP (ed) Role of transcription factors in gastrointestinal malignancies, 1st edn. Springer, Singapore, pp 191–201
Reuter S, Gupta SC, Chaturvedi MM, Aggarwal BB (2010) Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: how are they linked? Free Radic Biol Med 49:1603–1616
Sander CS, Hamm F, Elsner P, Thiele JJ (2003) Oxidative stress in malignant melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer. Br J Dermatol 148:913–922
Sithara T, Arun KB, Syama HP, Reshmitha TR, Nisha P (2017) Morin inhibits proliferation of SW480 colorectal cancer cells by inducing apoptosis mediated by reactive oxygen species formation and uncoupling of warburg effect. Front Pharmacol 8:640
Sivaramakrishnan V, Niranjali Devaraj S (2009) Morin regulates the expression of NF-kappaB-p65, COX-2 and matrix metalloproteinases in diethylnitrosamine induced rat hepatocellular carcinoma. Chem Biol Interact 180:353–359
Tsujimoto Y, Shimizu S (2007) Role of the mitochondrial membrane permeability transition in cell death. Apoptosis 12:835–840
Wang L, Wei D, Huang S, Peng Z, Le X, Wu TT, Yao J, Ajani J, Xie K (2003) Transcription factor Sp1 expression is a significant predictor of survival in human gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res 9:6371–6380
Wang XB, Peng WQ, Yi ZJ, Zhu SL, Gan QH (2007) Expression and prognostic value of transcriptional factor sp1 in breast cancer. Ai Zheng 26:996–1000
Wang X, Wang J, Lin S, Geng Y, Wang J, Jiang B (2008) Sp1 is involved in H2O2-induced PUMA gene expression and apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 27:44
Yao JC, Wang L, Wei D, Gong W, Hassan M, Wu TT, Mansfield P, Ajani J, Xie K (2004) Association between expression of transcription factor Sp1 and increased vascular endothelial growth factor expression, advanced stage, and poor survival in patients with resected gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10:4109–4117
Yao D, Cui H, Zhou S, Guo L (2017) Morin inhibited lung cancer cells viability, growth, and migration by suppressing miR-135b and inducing its target CCNG2. Tumour Biol 39:1010428317712443
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, Y.J., Kim, W.I., Kim, S.Y. et al. Flavonoid morin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of melanoma cells by regulating reactive oxygen species, Sp1 and Mcl-1. Arch. Pharm. Res. 42, 531–542 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-019-01158-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-019-01158-5