Abstract
Background
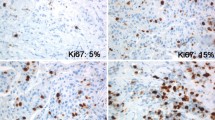
Ki67 is a protein associated with cell cycle activity and shows a good correlation with the growth fraction, which has been proposed as a prognostic or predictive marker in breast cancer. In this study, we aimed to analyze the expression levels of Ki67 (MKI67) messenger RNA (mRNA) derived from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissues for comparison with the immunohistochemical Ki67 labeling index, and investigate the correlation coefficients with clinical outcomes.
Methods
We analyzed the data of Ki67 mRNA from FFPE and matched fresh-frozen (FF) tissues based on a real-time quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) assay system in 203 cases of primary invasive breast cancer.
Results
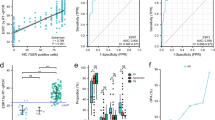
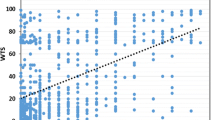
The correlation between Ki67 mRNA expression of either FFPE or FF specimens and Ki67 labeling index was positive, as was the correlation between the FFPE and FF results (P < 0.0001). Ki67 mRNA expression of FFPE specimens was significantly associated with clinicopathological characteristics: tumor size, lymph node status, nuclear grade, hormone receptors, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (Her2) status, and tumor subtype. In prognostic results, Ki67 gene expression in the FFPE specimens revealed almost similar patterns of significance in Kaplan–Meier curves and univariate and multivariate relapse-free survival results as the Ki67 labeling index.
Conclusions
Gene expression analysis of Ki67 of FFPE specimens could be successfully performed using RT-qPCR, closely resembling the significant clinical characteristics of Ki67 labeling index. These results confirm that Ki67 gene expression of FFPE specimens has potential for evaluation of cell cycle activity of breast cancer specimens.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yerushalmi R, Woods R, Ravdin PM, Hayes MM, Gelmon KA. Ki67 in breast cancer: prognostic and predictive potential. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:174–83.
Potemski P, Pluciennik E, Bednarek AK, Kusinska R, Kubiak R, Jesionek-Kupnicka D, et al. Ki-67 expression in operable breast cancer: a comparative study of immunostaining and a real-time RT-PCR assay. Pathol Res Pract. 2006;202:491–5.
Wiesner FG, Magener A, Fasching PA, Wesse J, Bani MR, Rauh C, et al. Ki-67 as a prognostic molecular marker in routine clinical use in breast cancer patients. Breast. 2009;18:135–41.
Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Coates AS, Gelber RD, Thurlimann B, Senn HJ. Strategies for subtypes-dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann Oncol. 2011;22:1736–47.
Goldhirsch A, Ingle JN, Gelber RD, Coates AS, Thurlimann B, Senn HJ. Thresholds for therapies: highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2009. Ann Oncol. 2009;20:1319–29.
Toi M, Saji S, Masuda N, Kuroi K, Sato N, Takei H, et al. Ki67 index changes, pathological response and clinical benefits in primary breast cancer patients treated with 24 weeks of aromatase inhibition. Cancer Sci. 2011;102:858–65.
Tanei T, Shimomura A, Shimazu K, Nakayama T, Kim SJ, Iwamoto T, et al. Prognostic significance of Ki67 index after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2011;37:155–61.
Mello-Grand M, Singh V, Ghimenti C, Scatolini M, Regolo L, Grosso E, et al. Gene expression profiling and prediction of response to hormonal neoadjuvant treatment with anastrozole in surgically resectable breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010;121:399–411.
Endo Y, Toyama T, Takahashi S, Sugiura H, Yoshimoto N, Iwasa M, et al. High estrogen receptor expression and low Ki67 expression are associated with improved time to progression during first-line endocrine therapy with aromatase inhibitors in breast cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 2011;16:512–8.
Dowsett M, Smith IE, Ebbs SR, Dixon JM, Skene A, A’Hern R, et al. Prognostic value of Ki67 expression after short-term presurgical endocrine therapy for primary breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99:167–70.
Cheang MC, Chia SK, Voduc D, Gao D, Leung S, Snider J, et al. Ki67 index, HER2 status, and prognosis of patients with luminal B breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009;101:736–50.
Konsti J, Lundin M, Joensuu H, Lehtimaki T, Sihto H, Holli K, et al. Development and evaluation of a virtual microscopy application for automated assessment of Ki-67 expression in breast cancer. BMC Clin Pathol. 2011;11:3.
Scicchitano MS, Dalmas DA, Bertiaux MA, Anderson SM, Turner LR, Thomas RA, et al. Preliminary comparison of quantity, quality, and microarray performance of RNA extracted from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded, and unfixed frozen tissue samples. J Histochem Cytochem. 2006;54:1229–37.
Abdueva D, Wing M, Schaub B, Triche T, Davicioni E. Quantitative expression profiling in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples by affymetrix microarrays. J Mol Diagn. 2010;12:409–17.
Sanchez-Navarro I, Gamez-Pozo A, Gonzalez-Baron M, Pinto-Marin A, Hardisson D, Lopez R, et al. Comparison of gene expression profiling by reverse transcription quantitative PCR between fresh frozen and formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded breast cancer tissues. Biotechniques. 2010;48:389–97.
Farragher SM, Tanney A, Kennedy RD, Paul Harkin D. RNA expression analysis from formalin fixed paraffin embedded tissues. Histochem Cell Biol. 2008;130:435–45.
Mittempergher L, de Ronde JJ, Nieuwland M, Kerkhoven RM, Simon I, Rutgers EJ, et al. Gene expression profiles from formalin fixed paraffin embedded breast cancer tissue are largely comparable to fresh frozen matched tissue. PLoS One. 2011;6:e17163.
Ramaswamy S. Translating cancer genomics into clinical oncology. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1814–6.
April C, Klotzle B, Royce T, Wickham-Garcia E, Boyaniwsky T, Izzo J, et al. Whole-genome gene expression profiling of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue samples. PLoS One. 2009;4:e8162.
Gur-Dedeoglu B, Konu O, Bozkurt B, Ergul G, Seckin S, Yulug IG. Identification of endogenous reference genes for qRT-PCR analysis in normal matched breast tumor tissues. Oncol Res. 2009;17:353–65.
Fu P, Ibusuki M, Yamamoto Y, Yamamoto S, Fujiwara S, Murakami K, et al. Quantitative determination of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor mRNA in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues of invasive breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 2011. doi:10.1007/s12282-011-0299-9.
Hammond ME, Hayes DF, Dowsett M, Allred DC, Hagerty KL, Badve S, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College Of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:2784–95.
Jung SY, Han W, Lee JW, Ko E, Kim E, Yu JH, et al. Ki-67 expression gives additional prognostic information on St. Gallen 2007 and Adjuvant! Online risk categories in early breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16:1112–21.
Reis-Filho JS, Pusztai L. Gene expression profiling in breast cancer: classification, prognostication, and prediction. Lancet. 2011;378:1812–23.
Paik S, Shak S, Tang G, Kim C, Baker J, Cronin M, et al. A multigene assay to predict recurrence of tamoxifen-treated, node-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:2817–26.
Parker JS, Mullins M, Cheang MC, Leung S, Voduc D, Vickery T, et al. Supervised risk predictor of breast cancer based on intrinsic subtypes. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:1160–7.
Acknowledgments
We thank Y. Azakami and Y. Sonoda for excellent technical support, and A. Okabe for clinical data management.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Yamamoto, S., Ibusuki, M., Yamamoto, Y. et al. Clinical relevance of Ki67 gene expression analysis using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded breast cancer specimens. Breast Cancer 20, 262–270 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-012-0332-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-012-0332-7