Abstract
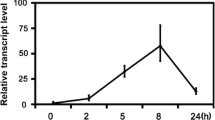
WRKY proteins are a superfamily of transcription factors involved in many plant processes including plant defense responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. We isolated a WRKY gene from pepper during the incompatible interaction between the pepper cultivar HDA149 and Meloidogyne incognita. The full-length gene, named as CaWRKY30, has a 1,533-bp cDNA sequence and contains an open reading frame of 1,095 bp, encodes a putative polypeptide of 364 amino acids with a theoretical protein size of 41.2 kDa, and contains one WRKY domain followed by a zinc-finger motif. The genomic sequence of CaWRKY30 contains three exons and two introns. Southern blot analysis confirmed that CaWRKY30 exists as a single copy in the pepper cultivar HDA149 genome. Quantitative RT-PCR showed that CaWRKY30 is up-regulated by application of various pathogens including avirulent M. incognita, Tobacco mosaic virus, Ralstonia solanacerum, and Phytophthora capsici Leonian. Furthermore, the transcripts of CaWRKY30 were rapidly induced after treatment with phytohormones salicylic acid (SA). However, the expression of CaWRKY30 was down-regulated by virulent M. incognita and phytohormones methyl jasmonic acid (MeJA). In addition, the nuclear localization of CaWRKY30 was determined when a CaMV35s::CaWRKY30-eGFP fusion construct was expressed in onion epidermal cells. These results suggested that CaWRKY30 might be involved in plant defense mechanisms against the diverse pathogen infection.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bostock RM (2005) Signal crosstalk and induced resistance: straddling the line between cost and benefit. Annu Rev Phytopathol 43:545–580
Chen C, Chen Z (2000) Isolation and characterization of two pathogen- and salicylic acid-induced genes encoding WRKY DNA-binding proteins from tobacco. Plant Mol Biol 42:387–396
Chen C, Chen Z (2002) Potentiation of developmentally regulated plant defense response by AtWRKY18, a pathogen-induced Arabidopsis transcription factor. Plant Physiol 129:706–716
Chujo T, Takai R, Akimoto-Tomiyama C, Ando S, Minami E, Nagamura Y, Kaku H, Shibuya N, Yasuda M, Nakashita H, Umemura K, Okada A, Okada K, Nojiri H, Yamane H (2007) Involvement of the elicitor-induced gene OsWRKY53 in the expression of defense-related genes in rice. Biochim Biophys Acta 1769:497–505
Dong J, Chen C, Chen Z (2003) Expression profiles of the Arabidopsis WRKY gene superfamily during plant defense response. Plant Mol Biol 51:21–37
Eulgem T (2005) Regulation of the Arabidopsis defense transcriptome. Trends Plant Sci 10:71–78
Eulgem T, Somssich IE (2007) Networks of WRKY transcription factors in defense signaling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:366–371
Eulgem T, Rushton PJ, Schmelzer E, Hahlbrock K, Somssich IE (1999) Early nuclear events in plant defence signalling: rapid gene activation by WRKY transcription factors. EMBO J 18:4689–4699
Eulgem T, Rushton PJ, Robatzek S, Somssich IE (2000) The WRKY superfamily of plant transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci 5:199–206
Fan H, Wang F, Gao H, Wang L, Xu J, Zhao Z (2011) Pathogen-induced MdWRKY1 in ‘Qinguan’ apple enhances disease resistance. J Plant Biol 54(3):150–158
Giacomelli JI, Ribichich KF, Dezar CA, Chan RL (2010) Expression analyses indicate the involvement of sunflower WRKY transcription factors in stress responses, and phylogenetic reconstructions reveal the existence of a novel clade in the Asteraceae. Plant Sci 178:398–410
Grunewald W, Karimi M, Wieczorek K, Van de Cappelle E, Wischnitzki E, Grundler F, Inze D, Beeckman T, Gheysen G (2008) A role for AtWRKY23 in feeding site establishment of plant-parasitic nematodes. Plant Physiol 148:358–368
Guo R, Yu F, Gao Z, An H, Cao X, Guo X (2011) GhWRKY3, a novel cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) WRKY gene, is involved in diverse stress responses. Mol Biol Rep 38:49–58
Higashi K, Ishiga Y, Inagaki Y, Toyoda K, Shiraishi T, Ichinose Y (2008) Modulation of defense signal transduction by flagellin-induced WRKY41 transcription factor in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Genet Genomics 279:303–312
Huang S, Yamamoto H, Ide N, Mizuno S, Shiraishi N, Sato T, Nakagawa H, Sonoda M (2010) Isolation and molecular characterization of a SoWRKY1 transcription factor from spinach (Spinacia oleracea). Plant Biotechnol 27:121–129
Jammes F, Lecomte P, de Almeida-Engler J, Bitton F, Martin-Magniette ML, Renou JP, Abad P, Favery B (2005) Genome-wide expression profiling of the host response to root-knot nematode infection in Arabidopsis. Plant J 44:447–458
Kalde M, Barth M, Somssich IE, Lippok B (2003) Members of the Arabidopsis WRKY group III transcription factors are part of different plant defense signaling pathways. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 16:295–305
Knoth C, Ringler J, Dangl JL, Eulgem T (2007) Arabidopsis WRKY70 is required for full RPP4-mediated disease resistance and basal defense against Hyaloperonospora parasitica. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 20:120–128
Lee SJ, Lee MY, Yi SY, Oh SK, Choi SH, Her NH, Choi D, Min BW, Yang SG, Harn CH (2002) PPI1: a novel pathogen-induced basic region-leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factor from pepper. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15:540–548
Li J, Brader G, Palva ET (2004) The WRKY70 transcription factor: a node of convergence for jasmonate-mediated and salicylate-mediated signals in plant defense. Plant Cell 16:319–331
Li J, Brader G, Kariola T, Palva ET (2006) WRKY70 modulates the selection of signaling pathways in plant defense. Plant J 46:477–491
Marchive C, Mzid R, Deluc L, Barrieu F, Pirrello J, Gauthier A, Corio-Costet MF, Regad F, Cailleteau B, Hamdi S, Lauvergeat V (2007) Isolation and characterization of a Vitis vinifera transcription factor, VvWRKY1, and its effect on responses to fungal pathogens in transgenic tobacco plants. J Exp Bot 58:1999–2010
Naoumkina MA, He X, Dixon RA (2008) Elicitor-induced transcription factors for metabolic reprogramming of secondary metabolism in Medicago truncatula. BMC Plant Biol 8:132
Oh SK, Baek KH, Park JM, Yi SY, Yu SH, Kamoun S, Choi D (2008) Capsicum annuum WRKY protein CaWRKY1 is a negative regulator of pathogen defense. New Phytol 177:977–989
Park CJ, Shin YC, Lee BJ, Kim KJ, Kim JK, Paek KH (2006) A hot pepper gene encoding WRKY transcription factor is induced during hypersensitive response to Tobacco mosaic virus and Xanthomonas campestris. Planta 223:168–179
Reymond P, Farmer EE (1998) Jasmonate and salicylate as global signals for defense gene expression. Curr Opin Plant Biol 1:404–411
Rushton PJ, Somssich IE (1998) Transcriptional control of plant genes responsive to pathogens. Curr Opin Plant Biol 1:311–315
Rushton PJ, Somssich IE, Ringler P, Shen QJ (2010) WRKY transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci 15:247–258
Singh K, Foley RC, Onate-Sanchez L (2002) Transcription factors in plant defense and stress responses. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:430–436
Yang Y, Shah J, Klessig D (1997) Signal perception and transduction in plant defense responses. Genes Dev 11:1621
Yang P, Chen C, Wang Z, Fan B, Chen Z (1999) A pathogen-and salicylic acid-induced WRKY DNA-binding activity recognizes the elicitor response element of the tobacco class I chitinase gene promoter. Plant J 18:141–149
Yang B, Jiang Y, Rahman MH, Deyholos MK, Kav NN (2009) Identification and expression analysis of WRKY transcription factor genes in canola (Brassica napus L.) in response to fungal pathogens and hormone treatments. BMC Plant Biol 9:68
Zhang ZL, Xie Z, Zou X, Casaretto J, Ho TH, Shen QJ (2004) A rice WRKY gene encodes a transcriptional repressor of the gibberellin signaling pathway in aleurone cells. Plant Physiol 134:1500–1513
Zhang J, Peng Y, Guo Z (2008) Constitutive expression of pathogen-inducible OsWRKY31 enhances disease resistance and affects root growth and auxin response in transgenic rice plants. Cell Res 18:508–521
Zheng Z, Qamar SA, Chen Z, Mengiste T (2006) Arabidopsis WRKY33 transcription factor is required for resistance to necrotrophic fungal pathogens. Plant J 48:592–605
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (2009CB11900) and the National Science Foundation of China (30671412 and 30971905).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jingyuan, Z., Xuexiao, Z., Zhenchuan, M. et al. A Novel Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) WRKY Gene, CaWRKY30, Is Involved in Pathogen Stress Responses. J. Plant Biol. 54, 329–337 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-011-9171-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-011-9171-x