Abstract
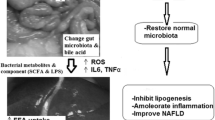
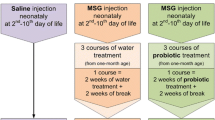
Today probiotics have been suggested as a treatment for the prevention of NAFLD. Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation may have beneficial effects in regulating hepatic lipid metabolism, adipose tissue function and inflammation. The present study was designed to determine whether probiotics plus omega-3 are superior to probiotics alone on the monosodium glutamate (MSG)-induced NAFLD model in rats. We included 60 rats divided into four groups, 15 animals in each. Rats of group I were intact. Newborn rats of groups II–IV were injected with MSG. The III (Symbiter) group received 2.5 ml/kg of multiprobiotic “Symbiter” containing concentrated biomass of 14 probiotic bacteria genera. The IV (Symbiter-Omega) groups received “Symbiter-Omega” combination of probiotic biomass supplemented with flax and wheat germ oil (250 mg of each, concentration of omega-3 fatty acids 1–5 %). In both interventional groups reduction in total NAS score was observed. Supplementation of alive probiotic mixture with omega-3 fatty acids lead to 20 % higher decrease in steatosis score (0.73 ± 0.11 vs 0.93 ± 0.22, p = 0.848) and reduction by 16.6 % of triglycerides content in liver as compared to probiotic alone. Our study demonstrated more pronounced reduction in hepatic steatosis and hepatic lipid accumulation after treatment with combination of alive probiotics and omega-3 as compared to probiotics alone.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Byrne CD, Targher G (2016) EASL–EASD–EASO clinical practice guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: is universal screening appropriate? Diabetology 59:141–144. doi:10.1007/s00125-016-3910-y
Kobyliak N, Abenavoli L (2014) The role of liver biopsy to assess non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Rev Recent Clin Trials 9:159–169
Vernon G, Baranova A, Younossi ZM (2011) Systematic review: the epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in adults. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 34:274–285. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2011.04724.x
Farrell GS, Larter CZ (2006) Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: from steatosis to cirrhosis. Hepatology 43(Suppl 1):S99–S112
Weston SR, Leyden W, Murphy R, Bass NM, Bell BP, Manos MM, Terrault NA (2005) Racial and ethnic distribution of nonalcoholic fatty liver in persons with newly diagnosed chronic liver disease. Hepatology 41:372–379
Musso G, Gambino R, Cassader M, Pagano G (2011) Meta-analysis: natural history of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and diagnostic accuracy of non-invasive tests for liver disease severity. Ann Med 43:617–649. doi:10.3109/07853890.2010.518623
Kobyliak N, Virchenko O, Falalyeyeva T (2016) Pathophysiological role of host microbiota in the development of obesity. Nutr J 15:43. doi:10.1186/s12937-016-0166-9
Federico A, Dallio M, Godos J, Loguercio C, Salomone F (2016) Targeting gut-liver axis for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: translational and clinical evidence. Transl Res 167:116–124. doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2015.08.002
Cani PD, Van Hul M (2015) Novel opportunities for next-generation probiotics targeting metabolic syndrome. Curr Opin Biotechnol 32:21–27. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2014.10.006
Kobyliak N, Conte C, Cammarota G, Haley AP, Styriak I, Gaspar L, Fusek J, Rodrigo L, Kruzliak P (2016) Probiotics in prevention and treatment of obesity: a critical view. Nutr Metab (Lond) 13:14. doi:10.1186/s12986-016-0067-0
Savcheniuk O, Kobyliak N, Kondro M, Virchenko O, Falalyeyeva T, Beregova T (2014) Short-term periodic consumption of multiprobiotic from childhood improves insulin sensitivity, prevents development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and adiposity in adult rats with glutamate-induced obesity. BMC Complement Altern Med 14:247. doi:10.1186/1472-6882-14-247
Scorletti E, Byrne CD (2013) Omega-3 fatty acids, hepatic lipid metabolism, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Annu Rev Nutr 33:231–248. doi:10.1146/annurev-nutr-071812-161230
Pettinelli P, Del Pozo T, Araya J, Rodrigo R, Araya AV, Smok G, Csendes A, Gutierrez L, Rojas J, Korn O, Maluenda F, Diaz JC, Rencoret G, Braghetto I, Castillo J, Poniachik J, Videla LA (2009) Enhancement in liver SREBP-1c/PPAR-alpha ratio and steatosis in obese patients: correlations with insulin resistance and n_3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid depletion. Biochim Biophys Acta 1792(11):1080–1086. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2009.08.015
Parker HM, Johnson NA, Burdon CA, Cohn JS, O’Connor HT, George J (2012) Omega-3 supplementation and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hepatol 56:944–951. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2011.08.018
Zivkovic AM, German JB, Sanyal AJ (2007) Comparative review of diets for the metabolic syndrome: implications for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Am J Clin Nutr 86:285–300
Kobyliak N, Abenavoli L, Falalyeyeva T, Virchenko O, Natalia B, Beregova T, Bodnar P, Spivak M (2016) Prevention of NAFLD development in rats with obesity via the improvement of pro/antioxidant state by cerium dioxide nanoparticles. Clujul Med 89:229–235. doi:10.15386/cjmed-632
Nakagawa T, Ukai K, Ohyama T, Gomita Y, Okamura H (2000) Effects of chronic administration of sibutramine on body weight, food intake and motor activity in neonatally monosodium glutamate-treated obese female rats: relationship of antiobesity effect with monoamines. Exp Anim 49:239–249
Kondro M, Mykhalchyshyn G, Bodnar P, Kobyliak N, Falalyeyeva T (2013) Metabolic profile and morpho-functional state of the liver in rats with glutamate-induced obesity. Curr Issues Pharm Med Sci 26:379–381. doi:10.12923/j.2084-980X/26.4/a.05
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, Behling C, Contos MJ, Cummings OW, Ferrell LD, Liu YC, Torbenson MS, Unalp-Arida A, Yeh M, McCullough AJ, Sanyal AJ (2005) Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 41:1313–1321
Folch J, Lees M, Stanley GHS (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226:497–509
Vitetta L, Hall S, Linnane AW (2014) Live probiotic cultures and the gastrointestinal tract: symbiotic preservation of tolerance whilst attenuating pathogenicity. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 4:143. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2014.00143
Kobyliak N, Falalyeyeva T, Virchenko O, Mykhalchyshyn G, Bodnar P, Spivak M, Yankovsky D, Beregova T, Ostapchenko L (2016) Comparative experimental investigation on the efficacy of mono- and multiprobiotic strains in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease prevention. BMC Gastroenterol 16:34. doi:10.1186/s12876-016-0451-2
Mei L, Tang Y, Li M, Yang P, Liu Z, Yuan J, Zheng P (2015) Co-administration of cholesterol-lowering probiotics and anthraquinone from Cassia obtusifolia L. ameliorate non-alcoholic fatty liver. PLoS ONE 10:e0138078. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0138078
Yoo SR, Kim YJ, Park DY, Jung UJ, Jeon SM, Ahn YT, Huh CS, McGregor R, Choi MS (2013) Probiotics L. plantarum and L. curvatus in combination alter hepatic lipid metabolism and suppress diet-induced obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring) 21:2571–2578. doi:10.1002/oby.20428
Kim SW, Park KY, Kim B, Kim E, Hyun CK (2013) Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG improves insulin sensitivity and reduces adiposity in high-fat diet-fed mice through enhancement of adiponectin production. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 431:258–263. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.12.121
Briskey D, Heritage M, Jaskowski L, Peake J, Gobe G, Subramaniam VN, Crawford D, Campbell C, Vitetta L (2016) Probiotics modify tight-junction proteins in an animal model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. doi:10.1177/1756283X16645055
Ritze Y, Bárdos G, Claus A, Ehrmann V, Bergheim I, Schwiertz A, Bischoff SC (2014) Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG protects against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. PLoS ONE 9:e80169. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0080169
Plaza-Diaz J, Gomez-Llorente C, Abadia-Molina F, Saez-Lara MJ, Campaña-Martin L, Muñoz-Quezada S, Romero F, Gil A, Fontana L (2014) Effects of Lactobacillus paracasei CNCM I-4034, Bifidobacterium breve CNCM I-4035 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus CNCM I-4036 on hepatic steatosis in Zucker rats. PLoS ONE 9:e98401. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0098401
Reichold A, Brenner SA, Spruss A, Förster-Fromme K, Bergheim I, Bischoff SC (2014) Bifidobacterium adolescentis protects from the development of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in a mouse model. J Nutr Biochem 25:118–125. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2013.09.011
Neschen S, Morino K, Dong J, Wang-Fischer Y, Cline GW, Romanelli AJ, Rossbacher JC, Moore IK, Regittnig W, Munoz DS, Kim JH, Shulman GI (2007) n-3 fatty acids preserve insulin sensitivity in vivo in a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α-dependent manner. Diabetes 56:1034–1041
Takeuchi Y, Yahagi N, Izumida Y, Nishi M, Kubota M, Teraoka Y, Yamamoto T, Matsuzaka T, Nakagawa Y, Sekiya M, Iizuka Y, Ohashi K, Osuga J, Gotoda T, Ishibashi S, Itaka K, Kataoka K, Nagai R, Yamada N, Kadowaki T, Shimano H (2010) Polyunsaturated fatty acids selectively suppress sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 through proteolytic processing and autoloop regulatory circuit. J Biol Chem 285:11681–11691. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.096107
Opreanu M, Lydic TA, Reid GE, McSorley KM, Esselman WJ, Busik JV (2010) Inhibition of cytokine signaling in human retinal endothelial cells through downregulation of sphingomyelinases by docosahexaenoic acid. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 51:3253–3263. doi:10.1167/iovs.09-4731
Borengasser SJ, Rector RS, Uptergrove GM, Morris EM, Perfield JW 2nd, Booth FW, Fritsche KL, Ibdah JA, Thyfault JP (2012) Exercise and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation for the treatment of hepatic steatosis in hyperphagic OLETF rats. J Nutr Metab 2012:268680. doi:10.1155/2012/268680
Rajkumar H, Mahmood N, Kumar M, Varikuti SR, Challa HR, Myakala SP (2014) Effect of probiotic (VSL#3) and omega-3 on lipid profile, insulin sensitivity, inflammatory markers, and gut colonization in overweight adults: a randomized, controlled trial. Mediators Inflamm 2014:348959. doi:10.1155/2014/348959
Acknowledgments
The authors express their sincere thanks to Dr. Yankovsky Dmitro Stanislavovych for the help, advice and financial support of this work.
Authors’ Contribution
Petro Bodnar and Tetyana Beregova conceived and designed the study. Nazarii Kobyliak and Tetyana Falalyeyeva carried out experiments, collected data, analyzed data and wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final version to be published.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This study was carried out in strict accordance with the recommendations in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the National Institutes of Health and the general ethical principles of animal experiments, approved by the First National Congress on Bioethics Ukraine (September 2001). The protocol was approved by the Committee on the Ethics of Animal Experiments of the Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv (Protocol Number: 17/2015).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kobyliak, N., Falalyeyeva, T., Bodnar, P. et al. Probiotics Supplemented with Omega-3 Fatty Acids are More Effective for Hepatic Steatosis Reduction in an Animal Model of Obesity. Probiotics & Antimicro. Prot. 9, 123–130 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-016-9230-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12602-016-9230-1