Abstract
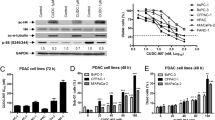
The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) pathway is one of the most commonly activated signaling pathways in pancreatic cancer and is a target of interest for new therapeutic approaches. NVP-BGT226 is a novel dual class PI3K/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor that has entered Phase I/II clinical trials. We analyzed the effect of NVP-BGT226 (10–100 nM) on the pancreatic cell lines Panc-1, BxPc-3, AsPC-1 and MiaPaCa-2 in regard to cell viability, induction of apoptosis, cell cycle, and expression of the antiapoptotic genes Survivin, MCL-1, BCL-2 and BCL-xL. Cell viability decreased within 24–72 h after exposure to about 50% compared to untreated control cells in a concentration- but not time-dependent manner. Cell cycle analysis revealed that NVP-BGT226 induced predominantly G0/G1 cell cycle arrest. Additionally, real-time RT-PCR and Western blot analysis showed a remarkable decrease of Survivin expression. Originally designed as a dual inhibitor, there was only a significant inhibition of p-mTOR. In summary, the dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor NVP-BGT226 induces G0/G1 arrest and acts, at least, partially via downregulation of Survivin.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Murray T, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics 2007. CA Cancer J Clin. 2007;57:43–66.
Duffy JP, Eibl G, Hines OJ. Influence of hypoxia and neoangiogenesis on the growth of pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer. 2003;2:12–22.
Hidalgo M. Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1605–17.
Okami K, Wu L, Riggins G, Cairns P, Goggins M, Evron E, Halachmi N, Ahrendt SA, Reed AL, Hilgers W, Kern SE, Koch WM, Sidransky D, Jen J. Analysis of PTEN/MMAC1 alterations in aerodigestive tract tumors. Cancer Res. 1998;58:509–11.
Perugini RA, McDade TP, Vittimberga FJ, Callery MP. Pancreatic cancer cell. Proliferation is phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase dependent. J Surg Res. 2000;90:39–44.
Carracedo A, Pandolfi PP. The PTEN–PI3K pathway: of feedback and cross-talks. Oncogene. 2008;27:5527–41.
Cantley LC. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science. 2002;296:1655–7.
Yamamoto S, Tomita Y, Hoshida S, Morooka T, Nagano H, Dono K, Umeshita K, Sakon M, Ishikawa O, Ohigashi H, Nakamori S, Monden M, Aozasa K. Prognostic significance of activated Akt expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;8:2846–50.
Cheng JQ, Ruggeri B, Klein W, Sonoda G, Altomare D, Watson D, Testa J. Amplification of AKT2 in human pancreatic cancer cells and inhibition of AKT2 expression and tumorigenicity by antisense RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996;93:3636–41.
Altomare D, Tanno S, Rienzo D, Klein-Szanto A, Tanno S, Skele K, Hoffman J, Testa J. Frequent activation of AKT2 kinase in human pancreatic carcinomas. J Cell Biochem. 2002;87:470–6.
Ruggeri BA, Huang L, Wood M, Cheng J, Testa JR. Amplification and overexpression of the AKT2 oncogene in a subset of human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. Mol Carcinog. 1998;21:81–6.
Weng D, Song X, Xing H, Ma X, Xia X, Yanjie W, Zhou J, Xu G, Zhu T, Wang S, Ma D. Implication of the Akt2/Survivin pathway as a critical target in paclitaxel treatment in human ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2009;273:257–65.
Asano T, Yao Y, Zhu J, Li D, Abbruzzese JL, Reddy SA. The rapamycin analog CCI-779 is a potent inhibitor of pancreatic cancer cell proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;331:295–302.
Paz-Ares L, Blanco-Aparicio C, Garcia-Carbonero R, Carnero A. Inhibiting PI3K as a therapeutic strategy against cancer. Clin Transl Oncol. 2009;11:572–9.
Miao G, Lu Q, Zhang X. Downregulation of survivin by RNAi inhibits growth of human gastric carcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13:1170–4.
Liu W, Yan H, Qin R, Tian R, Wang M, Jiang J, Shen M, Shi C. siRNA directed against Survivin enhances pancreatic cancer cell Gemcitabine chemosensitivity. Dig Dis Sci. 2009;54:89–96.
Ning Fuessel S, Kotzsch M, Kraemer K, Kappler M, Schmidt U, Taubert H, Wirth MP, Meye A. siRNA-mediated down-regulation of survivin inhibits bladder cancer cell growth. Int J Oncol. 2004;4:1065–71.
Kappler M, Bache M, Bartel F, Kotzsch M, Panian M, Würl P, Blümke K, Schmidt H, Meye A, Taubert H. Knockdown of survivin expression by small interfering RNA reduces the clonogenic survival of human sarcoma cell lines independently of p53. Cancer Gene Ther. 2004;3:186–93.
Rödel F, Hoffmann J, Distel L, Herrmann M, Noisternig T, Papadopoulos T, Sauer R, Rödel C. Survivin as a radioresistance factor, and prognostic and therapeutic target for radiotherapy in rectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;11:4881–7.
Wanner K, Hipp S, Oelsner M, Ringshausen I, Bogner C, Peschel C, Decker T. Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition induces cell cycle arrest in diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) cells and sensitises DLBCL cells to rituximab. Br J Haematol. 2006;5:475–84.
Baumann P, Schneider L, Mandl-Weber S, Oduncu F, Schmidmaier R. Simultaneous targeting of PI3K and mTOR with NVP-BGT226 is highly effective in multiple myeloma. Anticancer Drugs. Sept. 2011.
Zitzman K, De Toni E, Brand S, Goeke B, Meinecke J, Spoetll G, Meyer H, Auernhammer C. The novel mTOR inhibitor RAD001 (Everolimus) induces antiproliferative effects in human pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor cells. Neuroendocrinology. 2007;85:54–60.
Janes MR, Limon JJ, So L, Chen J, Lim RJ, Chavez MA, Vu C, Lilly MB, Mallya S, Ong ST, Konopleva M, Martin MB, Ren P, Liu Y, Rommel C, Fruman DA. Effective and selective targeting of leukemia cells using a TORC1/2 kinase inhibitor. Nat Med. 2010;2:205–13.
Sparks C, Guertin DA. Targeting mTOR: prospects for mTOR complex 2 inhibitors in cancer therapy. Oncogene. 2010;29:3733–44.
Kim S, Kang J, Qiao J, Thomas RP, Evers BM, Chung DH. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibition down-regulates Survivin and facilitates TRAIL-mediated apoptosis in neuroblastomas. J Pediatr Surg. 2004;4:516–21.
Hezel A, Kimmelmann A, Stanger B, Bardeesy N, DePinho R. Gentics and biology of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Genes Dev. 2006;20:1218–49.
Zhao P, Meng Q, Liu LZ, You YP, Liu N, Jiang BH. Regulation of Survivin by PI3K/Akt/p70S6K1 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;395:219–24.
Liu BB, Wang WH. Survivin and pancreatic cancer. World J Clin Oncol. 2011;2:164–8.
Samm N, Werner K, Rückert F, Saeger H, Grützmann R, Pilarsky. The role of apoptosis in the pathology of pancreatic cancer. Review. Cancers. 2011;3:1–16.
Minn A, Rudin C, Boise L, Thompson C. Expression of Bcl-xL can confer a multidrug resistance phenotype. Blood. 1995;5:1903–10.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Detlef Hübner Stiftung, Hochheim; Alfons und Gertrud Kassel-Stiftung, Frankfurt am Main; Senckenbergische-Stiftung, Frankfurt am Main, Tumorzentrum Rhein-Main e. V. and the Research Support Foundation, Vaduz/Liechtenstein.
Conflicts of interest
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glienke, W., Maute, L., Wicht, J. et al. The dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor NVP-BGT226 induces cell cycle arrest and regulates Survivin gene expression in human pancreatic cancer cell lines. Tumor Biol. 33, 757–765 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-011-0290-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-011-0290-2