Abstract
Background
Our previous study had shown the effectiveness of vestibular rehabilitation (VR) in improving balance in elderly patients, assessed immediately afterwards.
Aims
The main goal of the present study is to consider whether this improvement in balance assessment turns out in a reduction of the number of falls.
Methods
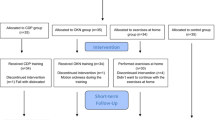
139 elderly patients with high risk of falls were included and randomized to one of the following study arms: computerized dynamic posturography (CDP) training, optokinetic stimulus, exercises at home or control group. Patients were assessed with objective outcome measures (sensorial organization test and limits of stability of CDP, number of falls and number of hospital admissions due to falls) and subjective outcome measures (dizziness handicap inventory and short falls efficacy scale-international) during a 12-month follow-up period.
Results
Average number of falls significantly declined from 10.96 (before VR) to 3.03 (12-month follow-up) in the intervention group (p < 0.001); meanwhile, in the control group, the average number of falls changed from 3.36 to 2.61 during a 12-month follow-up period (p = 0.166).
Discussion
The present study provides evidence that VR can decisively improve balance in elderly patients with instability, which can lead in turn to a significant reduction of falls.
Conclusion
We recommend performing VR in any older person with high risk of falls.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ungar A, Rafanelli M, Iacomelli I et al (2013) Fall prevention in the elderly. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab 10:91–95
Tinneti ME (2003) Clinical practice preventing falls in elderly persons. N Engl J Med 348:42–49
Anson E, Jeka J (2016) Perspectives on aging vestibular function. Front Neurol 6:269
Gadkaree SK, Sun DQ, Li C et al (2016) Does sensory function decline independently or concomitantly with age? Data from the baltimore longitudinal study of aging. J Aging Res 2016:1865038
Rossi-Izquierdo M, Soto-Varela A, Santos-Pérez S et al (2009) Vestibular rehabilitation with computerised dynamic posturography in patients with Parkinson’s disease: improving balance impairment. Disabil Rehabil 31:1907–1916
Rossi-Izquierdo M, Santos-Pérez S, Soto-Varela A (2011) What is the most effective vestibular rehabilitation technique in patients with unilateral peripheral vestibular disorders? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 268:1569–1574
Rossi-Izquierdo M, Santos-Pérez S, Rubio-Rodríguez JP et al (2014) What is the optimal number of treatment sessions of vestibular rehabilitation? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 271:275–280
McDonell MN, Hillier SL (2015) Vestibular rehabilitation for unilateral peripheral vestibular dysfunction. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 1:CD005397
Kao C-L, Chen L-K, Chern C-M et al (2010) Rehabilitation outcome in home-based versus supervised exercise programs for chronically dizzy patients. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 51:264–267
Kristinsdottir EK, Baldursdottir B (2014) Effect of multi-sensory balance training for unsteady elderly people: pilot study of the ‘‘Reykjavik model’’. Disabil Rehabil 36:1211–1218
Martins E, Silva DC, Bastos VH et al (2016) Effects of vestibular rehabilitation in the elderly: a systematic review. Aging Clin Exp Res 28:599–606
Vitte E, Sémont A, Berthoz A (1994) Repeated optokinetic stimulation in conditions of active standing facilitates recovery from vestibular deficits. Exp Brain Res 102:141–148
Macias JD, Massingale S, Gerkin RD (2005) Efficacy of vestibular rehabilitation therapy in reducing falls. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 133:323–325
Rossi-Izquierdo M, Gayoso-Diz P, Santos-Pérez S et al (2017) Short-term effectiveness of vestibular rehabilitation in elderly patients with postural instability: a randomized clinical trial. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274:2395–2403
Soto-Varela A, Gayoso-Diz P, Rossi-Izquierdo M et al (2015) Reduction of falls in older people by improving balance with vestibular rehabilitation (ReFOVeRe study): design and methods. Aging Clin Exp Res 27:841–848
Podsiadlo D, Richardson S (1991) The timed “Up & Go”: a test of basic functional mobility for frail elderly persons. J Am Geriatr Soc 39:142–148
Rossi M, Soto A, Santos S et al (2009) A prospective study of alteration of balance among patients with Parkinson’s disease: protocol of the postural evaluation. Eur Neurol 61:171–176
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) “Mini-mental state”: a practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12:189–198
Pérez N, Garmendia I, Martín E et al (2000) Adaptación cultural de dos cuestionarios de medida de la salud en pacientes con vértigo. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp 51:572–580
Kempen GI, Yardley L, van Haastregt JC et al (2008) The Short FES-I: a shortened version of the falls efficacy scale-international to assess fear of falling. Age Ageing 37:45–50
Lomas-Vega R, Hita-Contreras F, Mendoza N et al (2012) Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Falls Efficacy Scale International in Spanish postmenopausal women. Menopause 19:904–908
Nashner LM (2011) Computerized dynamic posturography. In: Goebel JA (ed) Practical management of the dizzy patient. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 143–170
Cawthorne T (1944) The physiological basis for head exercises. J Chart Soc Physiother 30:106
Cooksey FS (1946) Rehabilitation in vestibular injuries. Proc R Soc Med 39:273
Wrisley DM, Stephens MJ, Mosley S et al (2007) Learning effects of repetitive administrations of the sensory organization test in healthy young adults. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 88:1049–1054
Pierchała K, Lachowska M, Morawski K et al (2014) Does effect of rehabilitation based on sensory conflicts in patients with vestibular deficits exceed learning effect? NeuroRehabilitation 34:343–353
Semont A, Vitte E, Freyss G (1992) Falls in the elderly: a therapeutic approach by optokinetic reflex stimulations. In: Vellas B, Toupet M, Rubenstein L, Albarède JL, Christen Y (eds) Falls balance and gait disorders in the elderly. Elsevier, Paris, pp 153–159
Whitney SL, Wrisley DM, Brown KE et al (2004) Is perception of handicap related to functional performance in persons with vestibular dysfunction? Otol Neurotol 25:139–143
Rossi-Izquierdo M, Santos-Pérez S, Del-Río-Valeiras M et al (2015) Is there a relationship between objective and subjective assessment of balance in elderly patients with instability? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 272:2201–2206
Dumville JC, Torgerson DJ, Hewitt CE (2006) Reporting attrition in randomized controlled trials. BMJ 332:969–971
Meldrum D, Herdman S, Vance R et al (2015) Effectiveness of conventional versus virtual reality-based balance exercises in vestibular rehabilitation for unilateral peripheral vestibular loss: results of a randomized controlled trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 96:1319–1328
Trinidad Ruiz G, Pedroso MD, de la Piedad EC et al (2010) Guided home-based vestibular rehabilitation assisted by audiovisual media. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp 61:397–404
Stigler SM (1997) Regression towards the mean, historically considered. Stat Methods Med Res 6:103–114
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the project PI11/01328, integrated into the State Plan for R + D + I 2008–2011 and funded by the ISCIII—Subdirección General de Evaluación y Fomento de la Investigación and the European Regional Development Fund: “Reduction of falls in the elderly by improving balance through vestibular rehabilitation”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
The study was performed according to the protocol approved by the Independent Ethics Committee of Galicia (Protocol 2010/139).
Informed consent
Signed informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Financial disclosure
No commercial party having a direct financial interest in the results of the research supporting this article has or will confer a benefit on the authors or on any organization with which the authors are associated.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rossi-Izquierdo, M., Gayoso-Diz, P., Santos-Pérez, S. et al. Vestibular rehabilitation in elderly patients with postural instability: reducing the number of falls—a randomized clinical trial. Aging Clin Exp Res 30, 1353–1361 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-018-1003-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-018-1003-0