Abstract
Purpose. To examine the disposition of fexofenadine in the isolated perfused rat liver and the influence of erythromycin and dibromosulphthalein (DBSP) on the hepatic uptake and biliary excretion of fexofenadine.
Methods. Livers from four groups of rats were perfused in a recirculatory manner with fexofenadine HCl added as a bolus (125, 250, 500, or 1000 μg) to perfusate. Livers from another three groups of rats were perfused with 250 μg of fexofenadine HCl. With one group as control, erythromycin (4.0 μg/ml) or DBSP (136 μg/ml) was added to the perfusate of the other groups. In all experiments, perfusate and bile were collected for 60 min; in addition, livers from the second experiment were retained for assay. Fexofenadine was determined in perfusate, bile, and homogenized liver by HPLC.
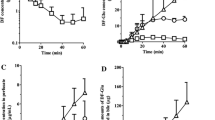
Results. The area under the curve (AUC) of fexofenadine was linearly related to concentration. It was unchanged from control (12,800 ± 200 ng·h/ml) by erythromycin (14,400 ± 2000 ng·h/ml), but was increased 95% by DBSP (25,000 ± 2600 ng·h/ml, P <0.001). The ratios of the concentrations of fexofenadine in liver/perfusate were decreased significantly by DBSP; those for bile/liver were increased by erythromycin.
Conclusions. Erythromycin reduced the canalicular transport of fexofenadine into bile, whereas DBSP reduced uptake across the sinusoidal membrane.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
T. Russell, M. Stoltz, and S. Weir. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and tolerance of single-and multiple-dose fexofenadine hydrochloride in healthy male volunteers. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 64:612–621 (1998).
C. M. Pratt, J. Mason, T. Russell, R. Reynolds, and R. Ahlbrandt. Cardiovascular safety of fexofenadine HCl. Am. J. Cardiol. 83: 1451–1454 (1999).
C. Lippert, J. Ling, P. Brown, S. Burmaster, M. Eller, L. Cheng, R. Thompson, and S. Weir. Mass balance and pharmacokinetics of MDL 16,455A in healthy male volunteers. Pharm. Res. 13(suppl. 9):S-390 (1996).
K. T. Kivisto, P. J. Neuvonen, and U. Klotz. Inhibition of terfenadine metabolism. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic consequences. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 27:1–5 (1994).
P. K. Honig, D. C. Wortham, R. Hull, K. Zamani, J. E. Smith, and L. R. Cantilena. Itraconazole affects single-dose terfenadine pharmacokinetics and cardiac repolarization pharmacodynamics. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 33:1201–1206 (1993).
P. K. Honig, D. C. Wortham, K. Zamani, J. C. Mullin, D. P. Conner, and L. R. Cantilena. The effect of fluconazole on the steady-state pharmacokinetics and electrocardiac pharmacodynamics of terfenadine in humans. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 53:630–636 (1993).
M. Takano, R. Hasegawa, T. Fukuda, R. Yumoto, J. Nagai, and T. Murakami. Interaction with P-glycoprotein and transport of erythromycin, midazolam and ketoconazole in Caco-2 cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 358:289–294 (1998).
R. B. Kim, C. Wandel, B. Leake, M. Cvetkovic, M. F. Fromm, P. J. Dempsey, M. M. Roden, F. Belas, A. K. Chaudhary, D. M. Roden, A. J. J. Wood, and G. R. Wilkinson. Interrelationship between substrates and inhibitors of human CYP3A and Pglycoprotein. Pharm. Res. 16:408–414 (1999).
A. Soldner, U. Christians, M. Susanto, V. J. Wacher, J. A. Silverman, and L. Z. Benet. Grapefruit juice exerts stimulatory effects on P-glycoprotein. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 65:205 (1999).
M. Cvetkovic, B. Leake, M. F. Fromm, G. R. Wilkinson, and R. B. Kim. OATP and P-glycoprotein transporters mediate the cellular uptake and excretion of fexofenadine. Drug Metab. Dispos. 27:866–871 (1999).
M. Müller and P. L. M. Jansen. Molecular aspects of hepatobiliary transport. Am. J. Physiol. 272:G1285–G1303 (1997).
H. M. J. Nijssen, T. Pijning, D. K. F. Meijer, and G. M. M. Groothuis. Mechanistic aspects of uptake and sinusoidal efflux of dibromosulfophthalein in the isolated perfused rat liver. Biochem. Pharmacol. 42:1997–2002 (1991).
Approved Product Information. Telfast Capsules. Hoechst Marion Roussel, Lane Cove, Australia.
A. M. Evans and K. Shanahan. The disposition of morphine and its metabolites in the in-situ rat isolated perfused liver. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 47:333–339 (1995).
R. A. Okerholm, D. L. Weiner, R. H. Hook, B. J. Walker, G. A. Leeson, S. A. Biedenbach, M. J. Cawein, T. D. Dusebout, and G. J. Wright. Bioavailability of terfenadine in man. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2:185–190 (1981).
D. A. Garteiz, R. H. Hook, B. J. Walker, and R. A. Okerholm. Pharmacokinetics and biotransformation studies of terfenadine in man. Arzneimittelforschung 32:1185–1190 (1982).
P. K. Honig, R. L. Woosley, K. Zamani, D. P. Conner, and L. R. Cantilena. Changes in the pharmacokinetics and electrocardiographic pharmacodynamics of terfenadine with concomitant administration of erythromycin. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 52:231–238 (1992).
P. K. Honig, D. C. Wortham, K. Zamani, D. P. Conner, J. C. Mullin, and L. R. Cantilena. Terfenadine-ketoconazole interaction. Pharmacokinetic and electrocardiographic consequences. JAMA 269:1513–1518 (1993).
C. D. Klaassen and G. L. Plaa. Hepatic disposition of phenoldibromphthalein disulfonate and sulfobromophthalein. Am. J. Physiol. 215:971–976 (1986).
M. Yamazaki, H. Suzuki, Y. Sugiyama, T. Iga, and M. Hanano. Uptake of organic anions by isolated rat hepatocytes. A classification in terms of ATP-dependency. J. Hepatol. 14:41–47 (1992).
H. Kouzuki, H. Suzuki, B. Stieger, P. J. Meier, and Y. Sugiyama. Characterization of the transport properties of organic anion transporting polypeptide 1 (oatp1) and Na+/taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (Ntcp): comparative studies on the inhibitory effects of their possible substrates in hepatocytes and cDNA-transfected COS-7 cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 292: 505–511 (2000).
K. Sathirakul, H. Suzuki, T. Tamada, M. Hanano, and Y. Sugiyama. Multiple transport systems for organic anions across bile canalicular membrane. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 268:65–73 (1994).
A. Blom, A. H. J. Scaf, and D. K. F. Meijer. Hepatic drug transport in the rat. A comparison between isolated hepatocytes, the isolated perfused liver and the liver in vivo. Biochem. Pharmacol. 31:1553–1565 (1982).
R. B. Kim, M. F. Fromm, C. Wandel, B. Leake, A. J. J. Wood, D. M. Roden, and G. R. Wilkinson. The drug transporter Pglycoprotein limits oral absorption and brain entry of HIV-1 protease inhibitors. J. Clin. Invest. 101:289–294 (1998).
J. D. Whisnant, G. H. Hurst, and K. I. R. Brouwer. Fexofenadine (Fex) disposition in the isolated perfused rat liver (IPL): effects of ketoconazole (Ket) and erythromycin (Ery). Pharm. Res. 14(suppl.):S-560 (1997).
E. G. Scheutz, K. Yasuda, K. Arimori, and J. D. Scheutz. Human MDR1 and mouse mdr1 P-glycoprotein alter the cellular retention and disposition of erythromycin, but not of retinoic acid and benzo(a)pyrene. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 350:340–347 (1998).
D. J. Birkett, R. A. Robson, N. Grgurinovich, and A. Tonkin. Single dose pharmacokinetics of erythromycin and roxithromycin and the effects of chronic dosing. Ther. Drug Monitoring 12:65–71 (1990).
M. M. Gottesman and I. Pastan. Biochemistry of multidrug resistance mediated by the multidrug transporter. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 62:385–427 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Milne, R.W., Larsen, L.A., Jørgensen, K.L. et al. Hepatic Disposition of Fexofenadine: Influence of the Transport Inhibitors Erythromycin and Dibromosulphothalein. Pharm Res 17, 1511–1515 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007609225851
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007609225851