Abstract
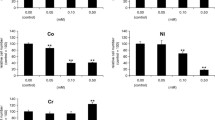
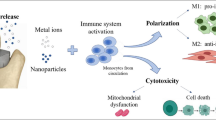
We have evaluated if the cytotoxic effects of metals released from implants are due to necrosis or apoptosis. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were exposed to different concentrations of chromium, nickel and cobalt extracts and the characteristics of both apoptosis and necrosis were evaluated by flow-cytometry at different culture endpoints. In order to define the prevalence of apoptosis or necrosis, the ratio cell death/apoptosis was calculated. A ratio of ≤1 means the prevalence of apoptotic events; a ratio >1 indicates the acute toxicity of the tested substance (necrosis). The extracts of chromium, cobalt and nickel had a cytotoxic effect on the mononuclear cells; high concentrations of cobalt and nickel produced cell necrosis, whereas by lowering the extract concentration apoptotic phenomena were observed. High chromium concentrations can induce cell death by apoptosis. Our data suggest that when large amounts of nickel and cobalt are released from implanted metal devices, necrosis is produced and consequently a strong inflammatory tissue reaction is likely to occur. The release of either chromium or limited amounts of nickel and cobalt induces toxicity characterized by apoptotic phenomena, which allows an adaptation of the tissue to the implant.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. D. Cook, R. L. Barrack, and A. J. T. Clemow, J. Bone Jt. Surg. 76–B (1994) 68.
F. F. Buechel, D. Drucker, M. Jasty, W. Jiranek and W. H. Harris, Clin. Orthop. Rel. Res. 298 (1994) 202.
D. Granchi, G. Ciapetti, L. Savarino, D. Cavedagna, M. E. Donati and A. Pizzoferrato. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 31 (1996) 183.
L. D. Tomei and F. O. Cope (eds), in “Current Commun. Cell and Mol. Biol.”, Vol. 3 (Cold Spring Harbor, NY, 1991) p. 410.
A. Bernelli-Zazzera, in “Patologia Generale.”, G. M. Pontieri (ed.) (Piccin Nuova Libraria, Padova, 1987) p. 216.
Z. Darzynkievicz, S. Bruno, G. del Bino, W. Gorczyca, M. A. Hotz, P. Lassota and F. Traganos, Cytometry 13 (1992) 795.
D. R. Haynes, S. D. Rogers, S. Hay, M. J. Pearcy and D. W. Howie, J. Bone Jt. Surg 75-A (1993) 825.
C. D. Brown, M. D. Lockshin, E. A. Salvati and P. G. Bullough, ibid 59-A (1977) 164.
ISO 10993 “Biological testing of medical devices — Part 12: Sample preparation and reference materials”, (1996).
A. Boyum Scand. J. Clin. Invest. 97 (1968) 1.
Z. Darzynkievicz, in “Flow cytometry and sorting”, M. R. Melamed, T. Lindmo, M. L. Mendelson (eds) (Wiley, New York, 1990) p. 291.
J. Gong, F. Traganos and Z. Darzynkievicz. Analy. Biochem. 218 (1994) 314.
C. M. Payne, L. Glasser, M. E. Tischler, D. Wycof, D. Cromey, R. Fiederlein and O. Bohnert, Micros. Res. Tech. 28 (1994) 327.
L. J. Blankenship, F. C. Manning, J. M. Orenstein and S. R. Patierno, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 126 (1994) 75.
R. Rajaram, B. U. Nair and T. Ramasami, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 16 (1995) 434.
A. Schedle, P. Samorapoompichit, X. H. Rausch fan, A. Franz, W. Fureder, W. R. Sper, W. Sperr, A. Ellinger, R. Slavicek, G. Boltz and G. Nitulescu, J. Dent. Res. 74 (1995) 1513.
A. Pizzoferrato, G. Ciapetti, S. Stea and A. Toni, Clinical Mater. 71 (1991) 51. ??
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
GRANCHI, D., CENNI, E., CIAPETTI, G. et al. Cell death induced by metal ions: necrosis or apoptosis?. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine 9, 31–37 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008878527233
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008878527233