Abstract
1. The responses of periphery (PNS) and central nervous systems (CNS) towards nerve injury are different: while injured mammalian periphery nerons can successfully undergo regeneration, axons in the central nervous system are usually not able to regenerate.
2. In the present study, the genes which were differentially expressed in the PNS and CNS following nerve injury were identified and compared by microarray profiling techniques.
3. Sciatic nerve crush and hemisection of the spinal cord of adult mice were used as the models for nerve injury in PNS and CNS respectively.
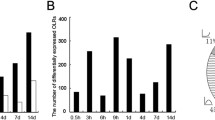
4. It was found that of all the genes examined, 14% (80/588) showed changes in expression following either PNS or CNS injury, and only 3% (18/588) showed changes in both types of injuries.
5. Among all the differentially expressed genes, only 8% (6/80) exhibited similar changes in gene expression (either up- or down-regulation) following injury in both PNS and CNS nerve injuries.
6. Our results indicated that microarray expression profiling is an efficient and useful method to identify genes that are involved in the regeneration process following nerve injuries, and several genes which are differentially expressed in the PNS and/or CNS following nerve injuries were identified in the present study.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Andersen, L. B., andSchreyer, D. J. (1999). Constitutive expression of GAP-43 correlates with rapid, but not slow regrowth of injured dorsal root axons in the adult rat. Exp. Neurol. 155: 157-164.
Bray, G. M.,Villegas-Perez, M. P.,Vidal-Sanz, M.,Carter, D. A., andAguayo, A. J. (1991). Neuronal and nonneuronal influences on retinal ganglion cell survival, axonal regrowth, and connectivity after axotomy. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 633: 214-228.
Brown, P. O., andBotstein, D. (1999). Exploring the new world of the genome with DNA microarrays. Nat. Genet. 21: 33-37.
Cassar-Malek, I.,Marchal, S.,Rochard, P.,Cases, F.,Wrutiniak C.,Samarut, J., andCabello, G. (1996). Induction of c-ErbA-AP-1 interactions and c-ErbA transcriptional activity in myoblasts by RXR. Consequences for muscle differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 271: 11392-11399.
Chao, M. V. (1992). Growth factor signaling:Where is the specificity? Cell 68: 995-997.
David, S., andAguayo, A. J. (1981). Axonal elongation in peripheral nervous system bridges after central nervous system injury in adult rats. Science 214: 391-393.
De Leon, M.,Welcher, A. A.,Suter, U., andShooter, E. M. (1991). Identification of transcriptionally regulated genes after sciatic nerve injury. J. Neurosci. Res. 29: 437-448.
Donoghue, J. P.,Kerman, K. L., andEbner, E. F. (1979). Evidence for two organizational plans within the somatic sensory-motor cortex of the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 183: 647-664.
Epstein, C. B., andButow, R. A. (2000). Microarray technology-enhanced versitility, persistent challenge. Curr. Opin. Biotech. 11: 36-41.
Flamant, F., andSamarut, J. (1998). Involvement of thyroid hormone and its α receptor in avian neurulation. Dev. Biol. 197: 1-11.
Fournier, A. E., andStrittmatter, S.M. (2001). Repulsive factors and axon regeneration in the CNS. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 11: 89-94.
Fu, S. Y., andGordon, T. (1997). The cellular and molecular basis of peripheral nerve regeneration. Mol. Neurobiol. 14: 67-116.
Funakoshi, H.,Risling, M.,Carlstedt, T.,Lendahl, U.,Timmusk, T.,Metsis, M.,Yamamoto, Y., andIbáñez, C. F. (1998). Targeted expression of a multifunctional chimeric neurotrophin in the lesioned sciatic nerve accelerates regeneration of sensory and motor axons. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95: 5269-5274.
Gillen, C.,Gleichmann, M.,Spreyer, P., andMuller, H. W. (1995). Differentially expressed genes after peripheral nerve injury. J. Neurosci. Res. 42: 159-171.
Goldberg, J. L., andBarres, B. A. (1998). Neural regeneration: Extending axons from bench to brain. Curr. Biol. 8: 310-312.
Goldberg, J. L., andBarres, B. A. (2000). The relationship between neuronal survival and regeneration. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 23: 579-612.
Greenberg, M. E.,Greene, L. A., andZiff, E. B. (1985). Nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor induce rapid transient changes in proto-oncogene transcription in PC12 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 260: 14101-14110.
Iglesias, T.,Llanos, S.,Lopez-Barahona, M.,Seliger, B.,Rodriguez-Pena, A.,Bernal, J., andMunoz, A. (1995). Induction of platelet-derived growth factor B/c-sis by the v-erbA oncogene in glial cells. Oncogene 10: 1103-1110.
Ishida, T.,Yamauchi, K.,Ishikawa, K., andYamamoto, T. (1993). Molecular cloning and characterization of the promoter region of the human c-erbA alpha gene. Biochem. Biophy. Res. Comm. 191: 831-839.
Koibuchi, N.,Yamaoka, S., andSuzuki, M. (1995). In situ hybridization histochemistry of c-erbA alpha 2 mRNA in the hypothalamus and its surrounding structures in the adult male rat. Endocr. J. 42: 49-55.
Laudet, V.,Vanacker, J. M.,Adelmant, G.,Begue, A., andStehelin, D. (1993). Characterization of a functional promoter for the human thyroid hormone receptor alpha (c-erbA-1) gene. Oncogene 8: 975-982.
Mi, R.,Kim, S., andFan, M. (1994). The changes of expression of neuronal β-, γ-actins in the spinal cord during regeneration. Chin. Sci. Bull. 39: 542-544.
Mi, R.,Kim, S.,Fan, M., andLau, S. (1996). The secondary amplification of the expression of neuronal c-fos mRNA in the spinal cord during regeneration following nerve injury. Chin. Sci. Bull. 41: 79-81.
Munoz, A.,Wrighton, C.,Seliger, B.,Bernal, J., andBeug, H. (1993). Thyroid hormone receptor/c-erbA: Control of commitment and differentiation in the neuronal/chronmaffin progenitor line PC12. J. Cell Biol. 121: 423-438.
Murphy, P.,Tolpilko, P.,Schneider-Maunoury, S.,Seitanidou, T.,Baron-Van Evercooren, A., andCharnay, P. (1996). The regulation of Krox-20 expression reveals important steps in the control of peripheral glial cell development. Development 122: 2847-2857.
Sambrook, J.,Fritsch, E. F., andManiatis, T. (1989). Molecular Cloning, a Laboratory Manual, 2nd Edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, pp. 7.3-7.87.
Schena, M.,Shalon, D.,Heller, R.,Chai, A.,Brown, P. O., andDavis, R. W. (1996). Parallel human genome analysis: Microarray-based expression monitoring of 1000 genes. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93: 10614-10619.
Schneider-Maunoury, S.,Gilardi-Hebenstreit, P., andCharnay, P. (1998). How to build a vertebrate hindbrain. Lesson from genetics. Comptes Rendus de l Academie des Sciences-Serie Iii, Sciences de la Vie 321: 819-834.
Schneider-Maunoury, S.,Topilko, P.,Seitandou, T.,Levi, G.,Cohen-Tannoudji, M.,Pournin, S.,Babinet, C., andCharnay, P. (1993). Disruption of Krox-20 results in alteration of rhombomeres 3 and 5 in the developing hindbrain. Cell 75: 1199-1214.
Swiatek, P. J., andGridley, T. (1993). Perinatal lethality and defects in hindbrain development in mice homozygous for a targeted mutation of the zinc finger gene Krox-20. Genes Dev. 7: 2071-2084.
van Hal, N. L. W.,Vorst, O.,van Houwelingen A. M. M. L.,Kok, E. J.,Peijnenburg A.,Aharoni A.,van Tunen A. J., andKeijer J. (2000). The application of DNA microarrays in gene expression analysis. J. Biotech. 78: 271-280.
Zilles, K., andWree, A. (1985). Cortex: Areal and laminar structure. In Paxinos, G. (ed.), The Rat Nervous System, Vol. 1, Academic Press, Sydney, pp. 375-415.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, M., Mi, R., Yew, D.T. et al. Analysis of Gene Expression Following Sciatic Nerve Crush and Spinal Cord Hemisection in the Mouse by Microarray Expression Profiling. Cell Mol Neurobiol 21, 497–508 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013867306555
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013867306555