Abstract
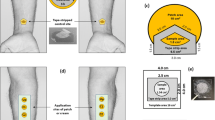
Purpose: Tape stripping the outermost skin layer, the stratum corneum (sc), is a popular method for assessing the rate and extent of dermal absorption in vivo. Results from tape strip (TS) experiments can be affected significantly by chemical diffusion into the sc during the time required to apply and remove all of the TSs, tTS. Here, we examine the effects of this problem on the interpretation of TS experimental results.
Methods: Dermal absorption of 4-cyanophenol (4CP) in humans was studied using TS experiments to assess conditions in which diffusion alters TS results. Mathematical models were developed to assess the effects of diffusion on parameter estimation.
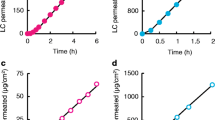
Results: For an experiment with tTS > tlag (i.e., the lag time for a chemical to cross the sc), the permeability coefficient for 4CP, Psc,v, calculated including tTS, was consistent with values from the literature (i.e., 0.0019 cm/h). When diffusion during stripping was not included in the model, Psc,v was 70% smaller.
Conclusions: Calculations show that chemical concentrations in TSs can be affected by diffusion during tape stripping, but if tTS < 0.2 tlag and the exposure time is > 0.3 tlag, TS concentrations are not significantly affected by tTS.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
A. L. Stinchcomb, F. Pirot, G. D. Touraille, A. L. Bunge, and R. H. Guy. Chemical uptake into human stratum corneum in vivo from volatile and nonvolatile solvents. Pharm. Res. 16:1288–1293 (1999).
F. P. Schwarb, B. Gabard, T. Rufli, and C. Surber. Percutaneous absorption of salicylic acid in man after topical administration of three different formulations. Dermatology 198:44–51 (1999).
K. Tojo and A.-R. C. Lee. A method for predicting steady-state rate of skin penetration in vivo. J. Invest. Dermatol. 92:105–108 (1989).
F. Pirot, Y. N. Kalia, A. L. Stinchcomb, G. Keating, A. L. Bunge, and R. H. Guy. Characterization of the permeability barrier of human skin in vivo. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 94:1562–1567 (1997).
V. P. Shah, G. L. Flynn, A. Yacobi, H. I. Maibach, C. Bon, N. M. Fleischer, T. J. Frantz, S. A. Kaplan, J. Kawamoto, L. J. Lesko, J. P. Marty, L. K. Pershing, H. Schaefer, J. A. Sequeira, S. P. Shrivastava, J. Wilkin and R. L. Williams. Bioequivalence of topical dermatological dosage forms-methods of evaluation of bioequivalence. Pharm. Res. 15:167–171 (1998).
M. S. Islam, L. Zhao, J. N. McDougal, and G. L. Flynn. Uptake of chloroform by skin on brief exposures to the neat liquid. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 60:5–15 (1999).
N. Higo, A. Naik, D. B. Bommannan, R. O. Potts, and R. H. Guy. Validation of reflectance infrared spectroscopy as a quantitative method to measure percutaneous absorption in vivo. Pharm. Res. 10:1500–1506 (1993).
H. Weigmann, J. Lademann, H. Meffert, H. Schaefer, and W. Sterry. Determination of the horny layer profile by tape stripping in combination with optical spectroscopy in the visible range as a prerequisite to quantify percutaneous absorption. Skin Pharmacol. Appl. Skin Physiol. 12:34–45 (1999).
F. Pirot, E. Berardesca, Y. N. Kalia, M. Singh, H. I. Maibach, and R. H. Guy. Stratum corneum thickness and apparent water diffusivity: facile and noninvasive quantitation in vivo. Pharm. Res. 15:492–494 (1998).
R. J. Scheuplein and R. L. Bronaugh. Percutaneous absorption. In L. A. Goldsmith (ed), Biochemistry and Physiology of the Skin, vol. II, Oxford University Press, New York, 1983, pp. 1255–1295.
J. Crank. The Mathematics of Diffusion, 2nd ed., Clarendon Press, Oxford, United Kingdom, 1975.
Y. N. Kalia, F. Pirot, and R. H. Guy. Homogenous transport in a heterogeneous membrane: water diffusion across human stratum corneum in vivo. Biophys. J. 71:2692–2700 (1996).
M. B. Reddy. Examining Issues in Percutaneous Transport Using Mathematical Models, PhD thesis, Colorado School of Mines, 2000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reddy, M.B., Stinchcomb, A.L., Guy, R.H. et al. Determining Dermal Absorption Parameters in Vivo From Tape Strip Data. Pharm Res 19, 292–298 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014443001802
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014443001802