Abstract
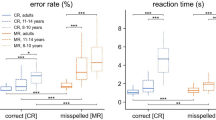
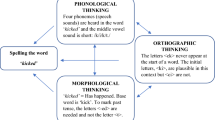
The correlates of spelling impairment wereexamined in children with histories of earlyspeech sound disorders. The spelling errors of52 children with histories of speech sounddisorders were analyzed to predict theassociation between weaknesses in expressivelanguage skills in early childhood andschool-age spelling abilities. Resultsrevealed that children with preschool speechsound and language problems became poorerspellers at school age than did children withpreschool speech sound disorders only. However, even children with isolated speechsound disorders demonstrated a weakness inspelling skills relative to their reading andlanguage abilities and Weschler Performance IQ.Measures of phonological awareness were highlycorrelated with spelling skills, suggestingthat phonological processing abilities arerelated to the ability to spell phoneticallypredictable words. Analysis of spelling errorsbased on level of phonological awareness skillrevealed that children with preschool speechsound disorders utilize phonetic strategies inspelling phonetically predictable words. Familial aggregation of spelling disorderssuggests a possible genetic component that ismodified by gender.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ball, E.W. & Blachman, B.A. (1991). Does phoneme awareness training in kindergarten make a difference in early word recognition and developmental spelling?, Reading Research Quarterly 26: 49-69.
Bird, J., Bishop, D.V.M. & Freeman, N.H. (1995). Phonological awareness and literacy development in children with expressive phonological impairments, Journal of Speech and Hearing Research 38: 446-462.
Bishop, D.V.M. & Adams, C. (1990). A prospective study of the relationship between specific language impairment, phonological disorders, and reading retardation, Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 31: 1027-1057.
Bishop, D.V.M., Bishop, S.J., Bright, P., James, C., Delaney, T. & Tallal, P. (1999). Different origin of auditory and phonological processing problems in children with language impairment-evidence from a twin study, Journal of Speech and Hearing Research 42: 155-168.
Catts, H.W. (1986). Speech production/phonological deficits in reading disordered children, Journal of Learning Disabilities 19: 504-508.
Catts, H.W. (1993). The relationship between speech-language impairments and reading disabilities, Journal of Speech and Hearing Research 36: 948-958.
Clarke-Klein, S.M. (1994). Expressive phonological deficiencies: Impact on spelling development, Topics in Language Disorders 14(2): 40-55.
Clarke-Klein, S. & Hodson, B.W. (1995). A phonologically based analysis of misspellings by third graders with disordered-phonology histories, Journal of Speech and Hearing Research 38: 839-849.
DeFries, J.C., Stevenson, J., Gillis, J.J. & Wadsworth, S.J. (1991). Genetic aetiology of spelling deficits in the Colorado and London twin studies of reading disability, Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal 3: 271-283.
DeFries, J.C., Alarcon, M. & Olson, R.K. (1997). Genetic aetiologies of reading and spelling deficits: Developmental differences. In: C. Hulme & M. Snowling (eds.), Dyslexia: biology, cognition, and intervention (pp. 20-37). San Diego, California: Singular Publishing Group, Inc.
Ehri, L. (1989). The development of spelling skill and its role in reading acquisition and reading disability, Journal of Learning Disability 22: 356-365.
Ehri, L. (1992a). Reconceptualizing the development of sight word reading and its relationship to recoding. In: P.B. Gough, L.C. Ehri & R. Treiman (eds.), Reading acquisition (pp. 145-174). Hillsdale, New Jersey: Erlbaum.
Ehri, L. (1992b). Review and commentary: Stages of spelling development. In: S. Templeton & D.R. Bear (eds.), Development of orthographic knowledge and foundation of literacy (pp. 307-332). Hillsdale, New Jersey: Erlbaum.
Felsenfeld, S., McGue, M. & Broen, P.A. (1995). Familial aggregation of phonological disorders: Results from a 28 year follow-up, Journal of Speech and Hearing Research 38: 1091-1107.
Fowler, A. (1991). How early phonological development might set the stage for phoneme awareness. In: S.A. Brady & D.P. Shankweiler (eds.), Phonological processes in literacy: A tribute to Isabelle Lieberman (pp. 97-117). Hillsdale, New Jersey: Erlbaum.
Frith, U. (1980). Unexpected spelling problems. In: U. Frith (ed.), Cognitive processes in spelling (pp. 495-515). New York/London: Academic Press.
Gentry, J.R. (1982). An analysis of developmental spelling in GYNS AT WRK, The Reading Teacher 36: 192-200.
Goldman, R. & Fristoe, M. (1986). The Goldman-Fristoe test of articulation. Circle Pines, Minnesota: American Guidance Service.
Goldman, R., Fristoe, M. & Woodcock, R.W. (1974). Goldman-Fristoe-Woodcock auditory skills test battery. Circle Pines, Minnesota: American Guidance Service.
Gopnik, M. & Crago, M.B. (1991). Familial aggregation of a developmental language disorder, Cognition 39: 1-50.
Hall, P.K. & Tomblin, J.B. (1978). A follow-up study of children with articulation and language disorders, Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders 43: 227-241.
Henderson, E.H. & Beers, J.W. (1980). Developmental and cognitive aspects of learning to spell: A reflection of word knowledge. Newark, Delaware: International Reading Association.
Hoffman, P.R. & Norris, J.A. (1989). On the nature of phonological development: Evidence from normal children's spelling errors, Journal of Speech and Hearing Research 32: 787-794.
Hollingshead, A.B. (1975). Four factor index of social class. Unpublished manuscript (available from A.B. Hollingshead, Department of Sociology, Yale University, New Haven, CT 06520, USA).
Kamhi, A. & Catts, H.W. (1986). Toward an understanding of developmental language disorders and reading disorders, Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders 51: 337-347.
Khan, L. & Lewis, N. (1986). Khan-Lewis phonological analysis. Circle Pines, Minnesota: American Guidance Service.
Kroese, J.M., Hynd, G.W.& Knight, D. (1998). Impact of phonological processing on spelling abilities. Paper presented at the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association Annual Convention, San Antonio, Texas.
Lahey, M. & Edwards, J. (1995). Specific language impairment: Preliminary investigation of factors associated with family history and patterns of language performance, Journal of Speech and Hearing Research 38: 643-657.
Larsen, S.C. & Hammill, D.D. (1994). Test of written spelling third edition examiner's manual. Austin, Texas: Pro-Ed.
Levi, G., Capozzi, F., Fabrizi, A. & Sechi, E. (1982). Language disorders and prognosis for reading disabilities in developmental age, Perceptual and Motor Skills 54: 1119-1122.
Lewis, B.A. (1992). Pedigree analysis of children with phonology disorders, Journal of Learning Disabilities 25: 586-597.
Lewis, B.A. & Freebairn, L. (1993). A clinical tool for evaluating the familial basis of speech and language disorders, American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology 2: 38-43.
Lewis, B.A., Freebairn, L. & Taylor, H.G. (2000). Follow-up of children with early expressive phonology disorders, Journal of Learning Disabilities 33: 433-444.
Lombardino, L.J., Bedford, T., Fortier, C., Carter, J. & Brandi, J. (1997). Invented spellings: developmental patterns in kindergarten children and guidelines for early literacy intervention, Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools 28: 333-343.
Marcel, T. (1980). Phonological awareness and phonological representation: Investigation of a spelling problem. In: U. Frith (ed.), Cognitive processes in spelling (pp. 373-403). New York/London: Academic Press.
Menyuk, P., Chesnick, M., Liebergott, J.W., Korngold, B., D'Agostino, R. & Belanger, A. (1991). Predicting reading problems in at-risk children, Journal of Speech and Hearing Research 34: 893-903.
Nation, K & Hulme, C. (1997). Phonemic segmentation, not onset-rime segmentation, predicts early reading and spelling skills, Reading Research Quarterly 32: 154-167.
Neils, J. & Aram, D.M. (1986). Family history of children with developmental language disorders, Perceptual and Motor Skills 63: 655-658.
Newcomer, P.L. & Hammill, D.D. (1988). Test of language development-primary, 2nd edn. Austin, Texas: Pro-Ed.
Olson, R., Wise, B., Connors, F. & Rack, J. (1989). Specific deficits in component reading and language skills: Genetic and environmental influences, Journal of Learning Disabilities 22: 339-348.
Pennington, B.F. (1999). Toward an integrated understanding of dyslexia: Genetic, neurological, and cognitive mechanisms, Developmental and Psychopathology 11: 629-654.
Rice, M.L., Haney, K.R. & Wexler, K. (1998). Family histories of children with SLI who show extended optional infinitives, Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research 41: 419-432.
Richgels, D. (1995). Invented spelling ability and printed word learning in kindergarten., Reading Research Quarterly 30: 96-109.
Robbins, J. & Klee, T. (1987). Clinical assessment of oropharyngeal motor development in young children, Journal of Speech and Hearing Research 52: 271-277.
Sawyer, D.J., Wade, S. & Kim, J.K. (1999). Spelling errors as a window on variations in phonological deficits among students with dyslexia, Annals of Dyslexia 49: 137-159.
Scarborough, H.S. (1990). Very early language deficits in dyslexic children, Child Development 61: 1728-1743.
Semel, E., Wiig, E.H. & Secord, W. (1987). Clinical evaluation of language fundamentals-revised. San Antonio, Texas: The Psychological Corporation.
Shriberg, L.D. & Kwiatkowski, J. (1988). A follow-up of children of phonological disorders of unknown origin, Journal of Speech and Hearing Research 53: 144-155.
Shriberg, L.D., Tomblin, J.B. & McSweeny, J.L. (1999). Prevalence of speech delay in 6-yearold children and comorbidity with language impairment, Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research 42: 1461-1481.
Snowling, M.J. (1985). Children's written language difficulties. Windsor, UK: NFER-Nelson.
Spitz, R.V., Tallal, P., Flax, J. & Benasich, A.A. (1997). Look who's talking: A prospective study of familial transmission of language impairments, Journal of Speech and Hearing Research 40: 990-1001.
Stackhouse, J. (1996). Speech, spelling, and reading: who is at risk and why? In: M. Snowling & J. Stackhouse (eds.), Dyslexia, speech, and language: A practitioner's handbook (pp. 12-30). San Diego, California: Singular Publishing Group.
Stanovich, K.E. & Seigel, L.S. (1994). The phenotypic performance profile of reading disabled children: A regression-based test of the phonological-core variable difference model, Journal of Educational Psychology 86: 24-53.
Stevenson, J., Graham, P., Fredman, G. & McLoughlin, V. (1987). A twin study of genetic influence on reading and spelling ability and disability, Journal of Child Psychology 28: 229-247.
Studdert-Kennedy, M. (1987). The phoneme as a perceptumotor structure. In: A. Allport, D. Mackay, W. Prinz & E. Scheerer (eds.), Language perception and production (pp. 67-84). New York: Academic Press.
Tallal, P., Ross, P. & Curtiss, S. (1989). Familial aggregation in specific language impairment, Journal of Speech and Hearing Research 54: 167-173.
Tomblin, J.B. (1989). Familial concentration of developmental language impairment, Journal of Speech and Hearing Disorders 54: 287-295.
Tomblin, J.B., Records, N.L., Buckwalter, P., Zhang, X., Smith, E. & O'Brien, M. (1997). Prevalence of specific language impairment in kindergarten children, Journal of Speech and Hearing Research 40: 1245-1260.
Torgesen, J.K. & Wagner, R.K. (1994). Comprehensive tests of phonological processing-experimental version. Unpublished tests, Florida State University.
Treiman, R. (1985). Phonemic awareness and spelling: Children's judgements do not always agree with adults, Journal of Experimental Child Psychology 39: 161-181.
Treiman, R. & Cassar, M. (1996). Effects of morphology on children's spelling of final consonant clusters, Journal of Experimental Child Psychology 63: 141-170.
Wadsworth, S.J., Gillis, J.J., DeFries, J.C. & Fulker, D.W. (1989). Differential genetic aetiology of reading disability as a function of age, Irish Journal of Psychology 10: 509-520.
Webster, P.E., Plante, A.S. & Couvillion, L.M. (1997). Phonological impairment and prereading: update on a longitudinal study, Journal of Learning Disabilities 30: 365-375.
Wechsler, D. (1991). Wechsler intelligence scale for children-third edition. San Antonio, Texas: The Psychological Corporation.
Wechsler individual achievement test (1992). San Antonio, Texas: The Psychological Corporation.
Woodcock, R.W. (1987). Woodcock reading mastery tests-revised. Circle Pines, Minnesota: American Guidance Service.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lewis, B.A., Freebairn, L.A. & Taylor, H.G. Correlates of spelling abilities in children with early speech sound disorders. Reading and Writing 15, 389–407 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015237202592
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015237202592