Abstract
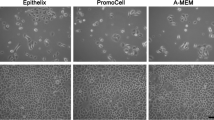
A human nasal epithelial cell culture model has been adapted to observe transport and metabolism of drugs, e.g., peptides. Human nasal epithelial cells, isolated by protease treatment of human nasal conchae, grew to confluency after 6-8 days using DMEM supplemented with 1% nonessential amino acids, 1% glutamine, 10% FCS and 1% antibiotics. These cultures expressed microvilli and actively beating cilia as documented by light microscopy and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Tight junctions were confirmed by dome formation and positive actin staining using FITC-labelled phalloidin. Preliminary transport studies, carried out with FITC-labelled Dex-tran (FD 4, MW 4400) and Sulforhodamine (SR 101, MW 607), demonstrated the intact barrier function of the cultured monolayer, grown on filter membranes. In addition, the cultured cells metabolized Leu-Enkephalin to Des-Tyr-Leu-Enkephalin demonstrating the presence of aminopeptidase, a naturally occurring enzyme in the human nasal mucosa.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
M.J.M. Deurloo, W.A.J.J. Hermens, S.G. Romeyn, J.C. Verhoef and F.W.H.M. Merkus. Absorption enhancement of intranasally administered insulin by sodium taurodihydrofusidate (STDHF) in rabbits and rats. Pharm. Res. 6, 853–856 (1989).
F.W.H.M. Merkus, J.C. Verhoef, S.G. Romeijn and N.G.M. Schipper. Absorption enhancing effect of cyclodextrins on intranasally administered insulin in rats. Pharm. Res. 8, 588–592 (1991)
W.A.J.J. Hermens, M.J.M. Deurloo, S.G. Romeyn, J.C. Verhoef and F.W.H.M. Merkus. Nasal absorption enhancement of 17β-estradiol by dimethyl-β-cyclodextrin in rabbits and rats. Pharm. Res. 7, 500–503 (1990)
P.A. Baldwin, C.K. Klingbeil, C.J. Grimm and J.P. Longenecker. The effect of sodium tauro-24,25-dihydrofusidate on the nasal absorption of human growth hormone in three animal models. Pharm. Res. 7, 547–552
D.T. O'Hagan, H. Critchley, N.F. Farraj, A.N. Fisher, B.R. Johansen, S.S. Davis and L. Illum. Nasal absorption enhancers for biosynthetic human growth hormone in rats. Pharm. Res. 7, 772–776 (1990)
K. Morimoto, H. Yamaguchi, Y. Iwakura, M. Miyazaki, E. Nakatani, T. Iwamoto, Y. Ohashi and Y. Nakai. Effects of proteolytic enzyme inhibitors on the nasal absorption of vasopressin and an analogue. Pharm. Res. 8, 1175–1179 (1991)
T. Kissel, J. Drewe, S. Bantle, A. Rummelt and C. Beglinger. Tolerability and absorption enhancement of intranasally administered octreotide by sodium taurodihydrofusidate in healthy subjects. Pharm. Res. 9, 52–57 (1992)
J.A. Faraj, A.A. Hussain, Y. Aramaki, K. Iseki, M. Kagoshima and L.W. Dittert. Mechanism of nasal absorption of drugs. III: Nasal absorption of leucine enkephalin. J. Pharm. Sci. 79, 698–702 (1990)
A. Hussain, J. Faraj, Y. Aramaki and J.E. Truelove. Hydrolysis of leucine enkephalin in the nasal cavity of the rat — A possible factor in the low bioavailability of nasally administered peptides. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 133, 923–928 (1985)
S. Hirai, T. Yashiki, T. Matsuzawa and H. Mima. Absorption of drugs from the nasal mucosa of rat. Int. J. Pharm. 7, 317–325 (1981)
T.C. Lee, R. Wu, A.R. Brody, J.C. Barrett and P. Nettesheim. Growth and differentiation of hamster tracheal epithelial cells in culture. Exp. Lung. Res. 6, 27–45 (1984)
J.F. Lechner, A. Haugen, H. Autrup, I.A. McClendon, B.F. Trump and C.C. Harris. Clonal growth of epithelial cells from normal adult human bronchus. Cancer Res. 41, 2294–2304 (1981)
D.C. Gruenert, C.B. Basbaum and J.H. Widdicombe. Long-term culture of normal and cystic fibrosis epithelial cells under serum-free conditions. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 26, 411–418 (1990)
D.P. Chopra, J. Sullivan, J.J. Wille and K.M. Siddiqui. Propagation of differentiating normal human tracheobronchial epithelial cells in serum-free medium. J. Cell. Phys. 130, 173–181 (1987)
R. Wu, J. Yankaskas, E. Cheng, M.R. Knowles and R. Boucher. Growth and differentiation of human nasal epithelial cells in culture. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 132, 311–320 (1985)
J.R. Yankaskas, C.U. Cotton, M.R. Knowles, J.T. Gatzy and R.C. Boucher. Culture of human nasal epithelial cells on collagen matrix supports. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 132, 1281–1287 (1985)
M. Jorissen, B. Van der Schueren, H. Van den Berghe and J.-J. Cassiman. The preservation and regeneration of cilia on human nasal epithelial cells cultured in vitro. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 246, 308–314 (1989)
F. Böhm, M. Wenzel and H.J. Gerhardt. Cultivation of ethmoidal sinus ciliated epithelia. Acta Otolaryngol. (Stockh) 108, 136–141 (1989)
J.R. Kennedy and J.R. Ranyard. Morphology and quantitation of ciliated outgrowth from cultured rabbit tracheal explants. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 29, 200–208 (1983)
E.K. Anderberg, T. Lindmark and P. Artursson. Sodium caprate elicits dilatations in human intestinal tight junctions and enhances drug absorption by the paracellular route. Pharm. Res. 10, 857–864 (1993)
U. Werner and T. Kissel. Cultivation and characterisation of human nasal cells in primary culture. Pharm. Pharmacol. Lett. 3, 249–252 (1994)
K.L. Audus, R.L. Bartel, I.J. Hidalgo and R.T. Borchardt. The use of cultured epithelial and endothelial cells for drug transport and metabolism studies. Pharm. Res. 7, 435–451 (1990)
X.H. Zhou and A. Li Wan Po. Comparison of enzyme activities of tissues lining portals of absorption of drugs: Species differences. Int. J. Pharm. 70, 271–283 (1991)
E. Walter and T. Kissel. Metabolic differences in subclones of a human intestinal cell line (Caco-2): Presystemic cleavage of leu-and met-enkephalin. Pharm. Pharmacol. Lett. 3, 221–224 (1994)
C. McMartin, L.E.F. Hutchinson, R. Hyde and G.E. Peters. Analysis of structural requirements for the absorption of drugs and macromolecules from the nasal cavity. J. Pharm. Sci. 76, 535–540 (1987)
A. Yamamoto, T. Morita, M. Hashida and H. Sezaki. Effect of absorption promoters on the nasal absorption of drugs with various molecular weights. Int. J. Pharm. 93, 91–99 (1993)
C.S. Schasteen, M.G. Donovan and J.N. Cogburn. A novel in vitro screen to discover agents which increase the absorption of molecules across the intestinal epithelium. J. Control. Rel. 21, 49–62 (1992)
L. Jørgensen and E. Bechgaard. Intranasal permeation of thyrotropin-releasing hormone: in vitro study of permeation and enzymatic degradation. Int. J. Pharm. 107, 231–237 (1994)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Werner, U., Kissel, T. Development of a Human Nasal Epithelial Cell Culture Model and Its Suitability for Transport and Metabolism Studies Under in Vitro Conditions. Pharm Res 12, 565–571 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016210231121
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016210231121