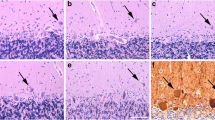
Abstract
There is growing interest in the cerebellum as a site of neuropathological changes in schizophrenia. Reports showing that schizophrenics have higher nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activity and MAPKinase levels in the vermis, point to possible aberrations in the cerebellar signal transduction of schizophrenics. It has been speculated that Ca2+-dependent extracellular to intracellular signal transduction may be disrupted in the cerebellum of schizophrenics. We decided to test this hypothesis by studying the nitrergic system and markers of the Ca2+-triggered signal cascade in the cerebellum of schizophrenics, depressives and controls. The cellular distribution of two calcium sensor proteins (VILIP-1 and VILIP-3) and of neuronal NOS immunoreactivity was studied morphometrically in the flocculonodulus, the inferior vermis and the dentate nucleus of 9 schizophrenics, 7 depressive patients and 9 matched controls. In comparison to controls and depressed patients there were fewer Nissl-stained neurons in the dentate nucleus of schizophrenics. The number of NOS-expressing Purkinje neurons was however strongly increased. In the flocculonodulus and the vermis no differences between the groups were found with regard to the density of Nissl-stained Purkinje cells. The number of NOS-expressing Purkinje neurons was increased in schizophrenics, however. No differences between schizophrenics, depressives and controls were found in the number of VILIP-1 immunoreactive dentate nucleus neurons and VILIP-3 immunoreactive vermal and flocculonodular Purkinje cells. Our data provide further histochemical evidence in favor of structural abnormalities in discrete cerebellar regions of schizophrenics. They confirm and extend earlier reports of increased cerebellar NOS immunoreactivity in schizophrenia and point to possible neurodevelopmental disturbances. Our failure to show an altered expression of two calcium sensor proteins possibly points to a less important role of calcium signaling in cerebellar pathology of the disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbarian, S., Vinuela, A., Kim, J. J., Potkin, S. G., Bunney, W. E. Jr. & Jones, E. G. (1993) Distorted distribution of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phophate-diaphorase neurons in temporal lobe of schizophrenics implies anomalous cortical development. Archives of General Psychiatry 50, 178–187.
Andersen, B. B., Korbo, L. & Pakkenberg, B. (1992) A quantitative study of the human cerebellum with unbiased stereological techniques. Journal of Comparative Neurology 326, 549–560.
Andreasen, N. C. (2000) Schizophrenia: The fundamental questions. Brain Research Brain Research Reviews 31, 106–112.
Andreasen, N. C., Paradiso, S. & O'Leary, D. S. (1998) “Cognitive dysmetria” as an intergrative theory of schizophrenia: A dysfunction in cortical-subcorticalcerebellar circuitry? Schizophenia Bulletin 24, 203–218.
Bayer, T. A., Schramm, M., Feldmann, N., Knable, M. B. & Falkai, P. (2000) Antidepressant drug exposure is associated with mRNA levels of tyrosine receptor kinase B in major depressive disorder. Progress in Neuropsychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry 24, 881–888.
Bernstein, H.-G., Baumann, B., Danos, P., Diekmann, S., Bogerts, B., Gundelfinger, E. D. & Braunewell, K.-H. (1999) Regional and cellular distribution of neural visinin-like protein immunoreactivities (VILIP-1 and VILIP-3) in human brain. Journal of Neurocytology 28, 655–662.
Bernstein, H.-G., Braunewell, K.-H., Spilker, C., Danos, P., Baumann, B., Funke, S., Diekmann, S., Gundelfinger, E. D. & Bogerts, B. (2002) Hippocampal expression of the calcium sensor protein VILIP-1 in schizophrenia. NeuroReport 13, 393–396.
Bernstein, H.-G., Stanarius, A., Baumann, B., Henning, H., Krell, D., Danos, P., Falkai, P. & Bogerts, B. (1998) Nitric oxide synthasecontaining neurons in the human hypothalamus: Reducednumberofimmunoreactive cells in the paraventricular nucleus of depressive patients and schizophrenics. Neuroscience 83, 867–875.
Black, M. D., Selk, D. E., Hitchcock, J. M., Wettstein, J. G. & Sorensen, S. M. (1999) On the effect of neonatal nitric oxide synthase inhibition in rat: A potential neurodevelopmental model of schizophrenia. Neuropharmacology 38, 1299–1306.
Blum-Degen, D., Heinemann, T., Lan, J., Pedersen, V., Leblhuber, F., Paulus, W., Riederer, P. & Gerlach, M. (1999) Characterization and regional distribution of nitric oxide synthase in the human brain during normal ageing. Brain Research 834, 128–135.
Braunewell, K.-H., Brackmann, M. M. S., Spilker, C. & Gundelfinger, E. (2001) Intracellular neuronal sensor (NCS) protein VILIP-1 modulates cGMP signalling pathways in transfected neural cells and cerebellar granule neurons. Journal of Neurochemistry 78, 1277–1286.
Braunewell, K.-H., Riederer, P., Spilker, C., Gundelfinger, E. D., Bogerts, B. & Bernstein, H.-G. (2000) Abnormal localization of two neuronal calcium sensor proteins, visinin-like proteins (VILIPs)-1 and-3, in neocortical brain areas of Alzheimer disease patients}. Dementia and Other Geriatric Cognitive Disorders 12, 110–116.
Breen, G., Fox, P., Glen, I., Collier, D., Shaw, D. & St. Clair, D. (1999) Association of the CACN1A4 (SCA6) triplet repeat arm with schizophrenia. Psychiatric Genetics 9, 111–113.
Das, I., Khan, N. S., Puri, B. K., Sooranna, S. R., de Belleroche, J. & Hirsch, S. R. (1995) Elevated platelet calcium mobilization and nitric oxide synthase activity may reflect abnormalities in schizophrenic brain. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 212, 375–380.
Doyle, C. A. & Slater, P. (1995) Application of [3H]LN( G)-nitro-arginine labelling to measure cerebellar nitric oxide synthase in patients with schizophrenia. Neuroscience Letters 202, 49–52.
Durany, N., Michel, T., ZÖchling, R., Boissl, K. W., Cruz-Sanchez, F. F., Riederer, P. & Thome, J. (2001) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin 3 in schizophrenic psychoses. Schizophrenia Research 52, 76–86.
Eastwood, S. L., Burnet, P. W., Gittins, R., Baker, K. & Harrison, P. J. (2001) Expression of serotonin 5-HAT (A) receptors in the human cerebellum and alterations in schizophrenia. Synapse 42, 104–114.
Egberongbe, Y. L., Gentleman, S. M., Falkai, P., Bogerts, B., Polak, J. M. & Roberts, G. W. (1994) The distribution of nitric oxide synthase immunoreactivity in the human brain. Neuroscience 59, 561–578.
Gaser, C., Volz, H. P., Kiebel, S., Riehemann, S. & Sauer, H. (1999) Detecting structural changes in whole brain based on nonlinear deformations—application to schizophrenia research. Neuroimage 10, 107–113.
Hara, H., Waeber, P. L., Huang, P. L., Fujii, M., Fishman, M. C. & Moskowitz, M. A. (1996) Brain distribution of nitric oxide synthase in neuronal and endothelial nitric oxide synthase mutant mice using [3H] LNω-nitro-arginine autoradiography. Neuroscience 75, 93–102.
Heath, R. G., Franklin, D. E., Walker, C. & Keating, J. W. Jr. (1982) Cerebellar vermis atrophy in psychiatric patients. Biological Psychiatry 17, 569–583.
Helmkamp, C. E., Bigelow, L. B., Paltan-Ortiz, J. D., Torrey, E. F., Kleiman, J. E. & Herman, M. M. (1999) Evaluation of superior vermal Purkinje cell placement in mental illness. Biological Psychiatry 45, 1370–1375.
Hirai, H. & Launey, T. (2000) The regulatory connection between the activity of granule cellNMDAreceptors and dendritic differentiation of cerebellar Purkinje cells. Journal of Neuroscience 20, 5217–5224.
Hsu, S. M. & Soban, E. (1982) Color modification of diaminobenzidine (DAB) precipitation by metallic ions and its application for double immunohistochemistry. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 30, 1079–1082.
Hudson, C., Gotowiec, A., Seemann, M., Warsh, J. & Ross, B. M. (1999) Clinical subtyping reveals significant differences in calcium-dependent phopspholipase A2 activity in schizophrenia. Biological Psychiatry 46, 401–405.
Ichimiya, T., Okubo, Y., Suhara, T. & Sudo, Y. (2001) Reduced volume of the cerebellar vermis in neuroleptic-naive schizophrenia. Biological Psychiatry 49, 20–27.
Impagnatiello, F., Guidotti, A. R., Pesold, C., Dwivedi, Y., Caruncho, H., Pisu, M. G., Uzunow, D. P., Smalmeiser, N. R., Davis, J. M., Pandey, G. N., Pappas, G. D., Tueting, P., Sharma, R. P. & Costa, E. (1998) A decrease of reelin expression as a putative vulnerability factor in schizophrenia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 95, 15718–15723.
Karson, C. N., Griffin, W. S., Mrak, R. E., husain, M., Dawson, T. M., Snyder, S. H., Moore, N. C. & Sturmer, W. Q. (1996) Nitric oxide synthase (NOS) in schizophrenia: Increases in cerebellar vermis. Molecular and Chemical Neuropathology 27, 275–284.
Katsetos, C. D., Hyde, T. M. & Herman, M. M. (1997) Neuropathology of the cerebellum in schizophrenia—an update: 1996 and future directions. Biological Psychiatry 42, 213–224.
Kim, J. J., Mohamed, S., Andreasen, N. C., O'Leary, D. S., Watkins, G. L., Boles Ponto, L. L. & Hichwa, R. D. (2000) Regional neural dysfunctions in chronic schizophrenia studied by positron emission tomography. American Journal of Psychiatry 157, 542–548.
Kuroda, S., Schweighofer, N. & Kawato, M. (2001) Exploration of signal transduction pathways in cerebellar long-term depression by kinetic stimulation. Journal of Neuroscience 21, 5693–5702.
Kyosseva, S. V., Elbein, A. D., Hutton, T. L., Griffin, S. T., Mrak, R. E., Sturner, W. Q. & Karson, C. N. (2000) Increased levels of transcription factors Elk-1, cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding protein, and activating transcription factor 2 in the cerebellar of schizophrenic patients. Archives of General Psychiatry 57, 685–691.
Loeber, R. T., Cintron, C. M. B. & Yurgeluntodd, D. A. (2001) Morphometry of individual cerebellar lobules in schizophrenia. American Journal of Psychiatry 158, 952–954.
Lohr, J. B. & Jeste, D. V. (1986) Cerebellar pathology in schizophrenia? A neuronometric study. Biological Psychiatry 21, 865–875.
Martin, P. & Albers, M. (1995) Cerebellum and schizophrenia: A selective review. Schizophrenia Bulletin 21, 241–250.
Mathisen, P. M., Johnson, J. M., Kawcak, J. A. & Tuohy, V. K. (1998) Visinin-like protein (VILIP) is a neuron-specific calcium-dependent double-stranded RNA-binding protein. Journal of Biological Chemistry 274, 31571–31576.
Middleton, F. A. & Strick, P. L. (1994) Anatomic evidence for cerebellar and basal ganglia involvement in higher cognitive function. Science 266, 458–461.
Middleton, F. A. & Strick, P. L. (2000) Basal ganglia and cerebellar loops: Motor and cognitive circuits. Brain Research Reviews 31, 236–250.
Nagao, S. & Kitazawa, H. (2000) Subdural applications of NO scaenger or NO blocker to the cerebellum depress the adaptation of monkey post-saccadic smooth pursuit eye movements. NeuroReport 17, 131–134.
Nasrallah, H. A., Jacoby, C. G. & McCalley-Whitters, M. (1981) Cerebellar atrophy in schizophrenia and mania. Lancet i(8229), 1102.
Ohyu, J. & Takashima, S. (1998) Developmental characteristics of neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) immunoreactive neurons in fetal to adolescent human brains. Brain Research Developmental Brain Research 110, 193–202.
Poeggel, G., MÜller, M., Seidel, I., Rechardt, L. & Bernstein, H.-G. (1992) Histochemistry of guanylate cyclase, phosphodiesterase, and NADPH-diaphorase (nitric oxide synthase) in rat brain vasculature. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 20, S76–S79.
Post, R. M. (1999) Comparative pharmacology of bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research 39, 153–158.
Reyes, M. & Gordon, A. (1981) Cerebellar vermis in schizophrenia. Lancet ii(8248), 700–701.
Rodrigo, J., Alonso, D., Fernandez, A. P., Serrano, J., Richart, A., Lopez, J. C., Martinez-Murillo, R., Bentura, M. L., Ghilione, M. & Uttenthal, L. O. (2001) Neuronal and inducible nitric oxide synthase and nitration after oxygen and glucose deprivation. Brain Research 3, 20–45.
Sachdev, P. S. & Brodaty, H. (1999) Mid-sagittal anatomy in late-onset schizophrenia. Psychological Medicine 29, 963–970.
Schmahmann, J. D. & Sherman, J. C. (1998) The cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome. Brain 121, 561–579.
Sears, L. L., Andreasen, N. C. & Leary D. S. (2000) Cerebellar functional abnormalities in schizophrenia are suggested by classical eyeblink conditioning. Biological Psychiatry 48, 204–209.
Slater, P., Doyle, C. A. & Deakin, J. F. W. (1998) Abnormal persistence of cerebellar serotonin-1A receptors in schizophrenia suggests failure of regress in neonates. Journal of Neural Transmission 105, 305–315.
Stevens, J. R. (1982) Neurology and neuropathology of schizophrenia. In: Schizophrenia as a Brain Disease (edited by Henn, F. A. & Nasrallah, H. S.) pp. 112–147. New York: Oxford University Press.
Sullivan, E. V., Desmukh, A., Desmond, J. E., Mathalon, D. H., Rosenbloom, K. O. & Pfefferbaum, A. (2000) Contribution of alcohol abuse to cerebellar volume deficits in schizophrenia. Archives of General Psychiatry 57, 894–902.
Supprian, T., Ulmar, G., Bauer, M., Schuler, M., Puschel, K., Retz-Junginger, P., Schmitt, H. P. & Heinsen, H. (2000) Cerebellar vermis area in schizophrenic patients—a postmortem study. Schizophrenia Research 42, 19–28.
Takahishi, M., Shirakawa, O., Toyoka, K., Kitamura, N., Hashimoto, T., Maeda, K., Koizumi, S., Wakabayashi, K., Takahashi, H., Someya, T. & Nawa, H. (2000) Abnormal expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its receptor in the corticolimbic system of schizophrenic patients. Molecular Psychiatry 5, 293–300.
Toledano, A., Alvarez, M. I., Rrivaz, L., La Cruz, C. & Martinez-Rodrigez, R. (1999) Amyloid precursor proteins in the cerebellar cortex of Alzheimer's disease patients devoid of cerebellar ß-amyloid deposits: Immunocytochemical study of five cases. Journal of Neural Transmission 106, 1151–1169.
Tran, K. D., Smutzer, G. S., Doty, R. L. & Arnold, S. E. (1998) Reduced Purkinje cell size in the cerebellar vermis of elderly schizophrenics. American Journal of Psychiatry 155, 1288–1290.
Vincent, S. R. (1996) Nitric oxide and synaptic plasticity:NO news from the cerebellum. Behavioral and Brain Sciences 19, 362–367.
von Santha, K. (1930) Über die Entwicklungsstörungender Purkinjezellen. Archiv der Psychiatrie 91, 373–410.
Wassink, T. H., Andreasen, N. C., Nopoulos, P. & Flaum, M. (1999) Cerebellar morphology as a predictor of symptoms and psychosocial outcome in schizophrenia. Biological Psychiatry 45, 41–48.
Weinberger, D. R., Kleinman, J. E., Luchins, D. J., Bigelow, L. B. & Wyatt, R. J. (1980) Cerebellar pathology in schizophrenia:Acontrolled postmortem study. American Journal of Psychiatry 137, 359–361.
Yan, X. X., Jen, L. S. & Garey L. J. (1995) Spatial periodicity of NADPH-diaphorase and synaptophysin, but not SNAP-25, reactivity in the monkey cerebellar cortex. Brain Research 669, 285–290.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bernstein, HG., Krell, D., Braunewell, KH. et al. Increased number of nitric oxide synthase immunoreactive Purkinje cells and dentate nucleus neurons in schizophrenia. J Neurocytol 30, 661–670 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016520932139
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016520932139