Abstract
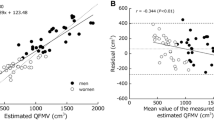
The maximum anatomical muscle cross-sectional areas and volumes of the muscles in the lower part of the body, thigh, and shank were measured by magnetic resonance imaging. The largest cross-sectional areas were 145.65 and 63 cm2 in m. gluteus maximus and m. vastus, respectively, referred to as mm. adductors. In the thigh, m. vastus had the largest volume, 1505 ± 271 cm3, and in the shank, m. soleus had the largest volume, 552 ± 64 cm3. Close correlations (0.50 < R < 0.75) between the maximum areas of the lower extremity muscles were evidence for a certain relationship between the muscle cross-sections. A multiple regression equation was formulated to calculate the maximum anatomical cross-sectional areas and volumes in the muscles of the lower extremities with respect to some anthropometric parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Voronov, A.V. and Lavrovskii, E.K., Determination of Lower Extremity Mass-Inertia Characteristics in Humans, Fiziol. Chel., 1998, vol. 24, no 2, p. 91.
Prilutskii, B.I. and Shafranova, E.I., The Use of Mag-netic Resonance Imaging for Measuring Morphometric Parameters of Locomotor Apparatus in Humans, Fiziol. Chel., 1990, vol. 16, no 6, p. 103.
Always, S.E., Grumbt, W.H., Stray-Gunderson, J., and Goney, W.J., Effects of Resistance Training on Elbow Flexors of Highly Competitive Bodybuilders, J. Appl. Physiol., 1992, vol. 72, p. 151.
Beneke, R., Neuerburg, J., and Bohndorf, K., Muscle Cross-Section Measurement by Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Eur. J. Appl. Physiol., 1991, vol. 63, p. 424.
Decarvalho, A., Jorgensen, B., Schibye, K., et al., Con-trolled Ultrasonographic Measurements of Cross-Sectional Areas of the Quadriceps Muscle Submitted to Dynamic Strength Training, J. Sports Med. Physiol. Fitness, 1985, vol. 25, p. 251.
Hakkinen, K. and Keskinen, K., Muscle Cross-Sectional Area and Voluntary Force Production Characteristics in Elite Strength-and Endurance-Trained Athletes and Sprinters, Eur. J. Appl. Physiol., 1989, vol. 59, p. 215.
Maugahn, R.J., Watson, J.S., and Weir, J. Muscle Strength and Cross-Sectional Area in Man: A Compari-son of Strength-Trained and Untrained Subjects, Brit. J. Sports Med., 1984, vol. 18, p. 149.
Narici, M.V., Rot, G.S., and Landoni, L., Force of Knee Extensor and Flexor Muscles and Cross-Sectional Area Determined by Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Eur. J. Appl. Physiol., 1988, vol. 57, p. 39.
Young, A.I., Hughes, P., Russell, M., et al., Measurement of Quadriceps Muscle Wasting by Ultrasonography, Rheumatol. Rehab., 1980, vol. 19, p. 141.
Martirosov, E.G., Metody issledovanii v sportivnoi antropologii (Investigation Methods in Sports Anthro-pology), Moscow: Fizk. Sport, 1982.
Brand, R.A., Crowninshield, R.D., Wittstock, C.E., et al., Model of Lower Extremity Muscular Anatomy, J. Biomed. Engineer., 1982, vol. 104, p. 304.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Voronov, A.V. Anatomical Cross-Sectional Areas and Volumes of the Muscles of the Lower Extremities. Human Physiology 29, 201–211 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022954929403
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022954929403