Abstract
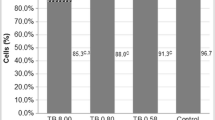
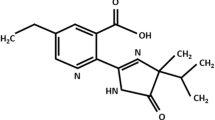
Terbutryn, as-triazine herbicide, is extensively used in agriculture as a selective pre- and postemergence control agent for most grasses and many annual broadleaf weeds in cereal and legume fields, and under fruit trees. Terbutryn was reported to degrade slowly, with half-lives of 240 and 180 days in pond and river sediment, respectively. The tendency of this herbicide to move from treated soils to water compartments through water runoff and leaching was demonstrated and residual amounts of terbutryn and its metabolites have been found in drinking water, and industrial food products, long after application. Although this herbicide may be regarded as a contaminant of our environment, only limited and inconsistent data exist concerning its genotoxic properties. In this study, the DNA-damaging ability of the herbicide was evaluated in the alkaline single-cell microgel-electrophoresis ("comet") assay by testing terbutryn in the presence of S9mix (rat liver homogenate containing microsomal enzymes plus cofactors) prepared with liver homogenate from both uninduced (basal) and aroclor 1254-induced rats. DNA damage was recorded in freshly isolated human peripheral blood leukocytes. A statistically significant increase in the extent of primary DNA damage, more pronounced in the absence of S9mix, took place only when terbutryn concentrations were high (100 and 150 μg/ml), in the presence of a concomitant mild cytotoxic effect.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams NH, Levi PE, Hodgson E. In vitro studies of the metabolism of atrazine, simazine, and terbutryn in several vertebrate species. J Agr Food Chem. 1990;38:1411-7.
Ashby J, Tinwell H, Lefevre PA, Browne MA. The single cell gel electrophoresis assay for induced DNA damage (comet assay): measurement of tail length and moment. Mutagenesis. 1995;10:85-90.
Bacci E. Studio del destino ambientale di alcuni presidi sanitari con particolare riferimento alle s-triazine, fenossiacidi e piretroidi artificiali. Quad Ig Pubb Vet. 1993;4:113-38.
Bester K, Hühnerfuss H. Triazine herbicide concentrations in the German Wadden sea. Chemosphere. 1996;32:1919-28.
Brendler-Schwaab SY, Schmezer P, Liegibel U, et al. Cells of diffferent tissues for in vitro and in vivo studies in toxicology: compilation of isolation methods. Toxicol In Vitro. 1994;8: 1285-302.
Brewster JD, Laightfield AR. Rapid biorecognition assay for herbicides in biological matrices. Anal Chem. 1993;65: 2415-9.
European Community. EEC Drinking water guideline. 80, 79, EEC, EEC no. L229/11-29. Brussels: EEC, 30 August 1980.
Fránek M, Kolár W, Eremin SA. Enzyme immunoassays for s-triazines herbicides and their application in environmental and food analysis. Anal Chim Acta. 1995;311:349-56.
Galassi S, Mingazzini M, Battegazore M. The use of biological methods for pesticide monitoring. Sci Total Environ. 1993; 132:399-414.
Hellman B, Vaghef H, Boström B. The concepts of tail moment and tail inertia in the single cell gel electrophoresis assay. Mutat Res. 1995;336:123-31.
IARC. Monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. Vol. 53. Occupational exposure in insecticide application, and some pesticides. Lyon: IARC; 1991:441.
IARC. Monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans.Vol. 73. Some chemicals that cause tumours of the kidney or urinary bladder in rodents and some other substances. Lyon: IARC; 1999:59.
Italian Health Ministry. D.M. 705/475, Rome; 1991.
Kaya B, Yanikoglu A, Creus A, Marcos R. Genotoxicity testing of five herbicides in the Drosophila wing spot test. Mutat Res. 2000;465:77-84.
Kenneth HJ, Senft JA. An improved method to determine cell viability by simultaneous staining with fluorescein diacetate-propidium iodide. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985; 33:77-9.
Krivankova L, Bocek P, Takel J, Kovacicova J. Isotachoforethic determination of herbicides prometryne, desmetryne, terbutryn and hydroxy-derivatives of atrazine and simazine in extracts of milk. Electrophoresis 1989;10:731-4.
Lang DH, Rettie A, Böcker RH. Identification of enzymes involved in the metabolism of atrazine, terbuthylazine, ametryne, and terbutryne in human liver microsomes. Chem Res Toxicol. 1997;10:1037-44.
Larsen GL, Bakke JE. Mass spectral characterization of the glucuronide conjugates of terbutryn (2-(t-butylamino)-4-(ethylamino)-6-methylthio)-s-triazine). Metabolites from rats and goats. Biomed Mass Spectrom. 1978;5:382-90.
Lippens R, Claeys M., Wildemauwe C, Van Larebeke N. Mutagenicity studies on 10 pesticides, on trichloroethane and on diaminobenzidine. Mutat Res. 1983;113:277-8.
Maron DM, Ames BN. Revised method for the Salmonella mutagenicity test. Mutat Res. 1983;113:173-215.
Moore DS. Statistics. Concepts and controversies. New York: Freeman; 1996:201-83.
Moretti M, Villarini M, Scassellati-Sforzolini G, Santroni AM, Fedeli D, Falcioni G. Extent of DNA damage in density-separated trout erythrocytes assessed by the ‘comet’ assay. Mutat Res. 1998;397:353-60.
Mucci N, Camoni I. Guidelines of the Italian CCTN for the classification of some effects of chemical substances. Rome: National Health Institute (Report series 96/2); 1996.
Muir DC. Determination of terbutryn and its degradation products in water sediments, aquatic plants, and fish. J Agr Food Chem. 1980;28:714-9.
Nilson EL, Unz RF. Antialgal substances for iodine-disinfected swimming pools. Appl Environ Microb. 1977;34:815-22.
Raju GS, Millette JA, Khan SU. Pollution potential of selected pesticides in soils. Chemosphere. 1993;26:1429-42.
Readman JW, Albanis TA, Barcelo D, Galassis S, Tronczynski J, Gabrielides GP. Herbicide cantamination of Mediterranean estuarine waters. Mar Pollut Bull. 1993;26:614-9.
Ribas G, Frenzilli G, Barale R, Marcos R. Herbicide-induced DNA damage in human lymphocytes evaluated by the single-cell gel electrophoresis (SCGE) assay. Mutat Res. 1995;344:41-54.
Rojas E, Lopez MC, Valverde M. Single cell gel electrophoresis assay: methodology and applications. Mutat Res. 1999;722: 225-54.
Saez A, Gomez de Barreda D, Gamon M, Garcia de la Cuadra J, Lorenzo E, Peris C. UV detection of triazine herbicides and their hydroxylated and dealkylated degradation products in well water. J Chromatogr A. 1996;721:107-12.
Singh NP, McCoy MT, Tice RR, Schneider EL. A simple technique for quantitation of low levels of DNA damage in individual cells. Exp Cell Res. 1988;175:184-91.
Tekel J, Farkas P, Schultzova K, Kovacicova J, Szokolay A. Analysis of triazine herbicides residues in butter and pasteurized milk. Z Lebensm Unter Forsch. 1988;186:319-22.
Thurman EM, Meyer M, Pomes M, Perry CA, Schwab AB. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay compared with gas chromatography/mass spectrometry for the determination of triazine herbicides in water. Anal Chem. 1990;62:2043-8.
Tomlin CDS. The pesticide manual. 11th edn. Farnham: British Crop Protection Council; 1997.
Tripathy NK, Routray PK, Kumar AA, Sahu CP. Genotoxicity to two triazine herbicides tested in the Drosophila wing spot and sex-linked recessive lethal tests. Biol Zentralbl. 1995; 114:279-84.
Villarini M, Moretti M, Pasquini R, et al. In vitro genotoxic effects of the insecticide deltamethrin in human peripheral blood leukocytes: DNA damage ('comet’ assay) in relation to the induction of sister-chromatid exchanges and micro-nuclei. Toxicology. 1998;130:129-39.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Villarini, M., Scassellati-Sforzolini, G., Moretti, M. et al. In vitro genotoxicity of terbutryn evaluated by the alkaline single-cell microgel-electrophoresis "comet" assay. Cell Biol Toxicol 16, 285–292 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026794213308
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026794213308