Abstract
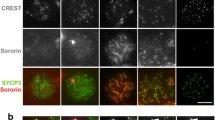
Cohesins are chromosomal proteins that form complexes involved in the maintenance of sister chromatid cohesion during division of somatic and germ cells. Three meiosis-specific cohesin subunits have been reported in mammals, REC8, STAG3 and SMC1β; their expression in mouse spermatocytes has also been described. Here we studied the localization of different meiotic and mitotic cohesin components during prophase I in human and murine female germ cells. In normal and atretic human fetal oocytes, from leptotene to diplotene stages, REC8 and STAG3 colocalize in fibers. In murine oocytes, SMC1β, SMC3 and STAG3 are localized along fibers that correspond first to the chromosome axis and then to the synaptonemal complex in pachytene. Mitotic cohesin subunit RAD21 is also found in fibers that decorate the SC during prophase I in mouse oocytes, suggesting a role for this cohesin in mammalian sister chromatid cohesion in female meiosis. We observed that, unlike human oocytes, murine synaptonemal complex protein SYCP3 localizes to nucleoli throughout prophase I stages, and centromeres cluster in discrete locations from leptotene to dictyate. At difference from meiosis in male mice, the cohesin axis is progressively lost during the first week after birth in females with a parallel destruction of the axial elements at dictyate arrest, demonstrating sexual dimorphism in sister chromatid cohesion in meiosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buonomo SB, Clyne RK, Fuchs J, Loidl J, Uhlmann F, Nasmyth K (2000) Disjunction of homologous chromosomes in meiosis I depends on proteolytic cleavage of the meiotic cohesin Rec8 by separin. Cell 103: 387-398.
Dietrich AJ, Kok E, Offenberg HH, Heyting C, de Boer P, Vink AC (1992) The sequential appearance of components of the synaptonemal complex during meiosis of the female rat. Genome 35: 492-497.
Eijpe M, Offenberg H, Jessberger R, Revenkova E, Heyting C (2003) Meiotic cohesin REC8 marks the axial elements of rat synaptonemal complexes before cohesins SMC1beta and SMC3. J Cell Biol 160: 657-670.
Hartshorne GM, Barlow AL, Child TJ, Barlow DH, Hultén MA (1999) Immunocytogenetic detection of normal and abnormal oocytes in human fetal ovarian tissue in culture. Hum Reprod 14: 172-182.
Hassold T, Hunt P (2001) To err (meiotically) is human: the genesis of human aneuploidy. Nat Rev Genet 2: 280-291.
Hodges CA, LeMarire-Adkins R, Hunt P (2001) Coordinating the segregation of sister chromatids during the first meiotic division: evidence for sexual dimorphism. J Cell Sci 114: 2417-2426.
Hultén M, Barlow AL, Tease C (2001) Meiotic studies in humans. In: Rooney DE, ed. Human Cytogenetics: Constitutional Analysis: A Practical Approach. 3rd edn. Oxford: Oxford University Press, pp 211-236.
Hunt PA, Hassold TJ (2002) Sex matters in meiosis. Science 216: 2181-2183.
Kitajima TS, Yokobayashi S, Yamamoto M, Watanabe Y (2003) Distinct cohesin complexes organize meiotic chromosome domains. Science 300: 1152-1155.
Lammers JH, Offenberg HH, van Aalderen M, Vink AC, Dietrich AJ, Heyting C (1994) The gene encoding a major component of the lateral elements of synaptonemal complexes of the rat is related to X-linked lymphocyte-regulated genes. Mol Cell Biol 14: 1137-1146.
Lee J, Iwai T, Yokota T, Yamashita M (2003) Temporally and spatially selective loss of Rec8 protein from meiotic chromosomes during mammalian meiosis. J Cell Sci 116: 2781-2790.
Nasmyth K (2001) Disseminating the genome: joining, resolving, and separating sister chromatids during mitosis and meiosis. Annu Rev Genet 35: 673-745.
Ortega S, Prieto I, Odajima J et al. (2003) Cyclin dependent kinase 2 is essential for meiosis but not for mitotic cell division in mice. Nat Genet 35: 25-31.
Page J, Suja JA, Santos JL, Rufas JS (1998) Squash procedure for protein immunolocalization in meiotic cells. Chromosome Res 6: 639-642.
Parisi S, McKay MJ, Molnar M et al. (1999) Rec8p, a meiotic recombination and sister chromatid cohesion phosphoprotein of the Rad21p family conserved from fission yeast to humans. Mol Cell Biol 19: 3515-3528.
Pasierbek P, Jantsch M, Melcher M, Schleiffer A, Schweizer D, Loidl J (2001) A Caenorhabditis elegans cohesion protein with functions in meiotic chromosome pairing and dysjunction. Genes Dev 15: 1349-1360.
Pelttari J, Hoja MR, Yuan L et al. (2001) A meiotic chromosomal core consisting of cohesin complex proteins recruits DNA recombination proteins and promotes synapsis in the absence of an axial element in mammalian meiotic cells. Mol Cell Biol 21: 5667-5677.
Pfeifer C, Scherthan H, Thomsen PD (2003) Sex-specific telomeres redistribution and synapsis initiation in cattle oogenesis. Dev Biol 255: 206-215.
Prieto I, Pezzi N, Buesa JM et al. (2002) STAG2 and Rad21 mammalian mitotic cohesins are implicated in meiosis. EMBO Rep 3: 543-550.
Prieto I, Suja JA, Pezzi N et al. (2001) Mammalian STAG3 is a cohesin specific to sister chromatid arms in meiosis I. Nat Cell Biol 3: 761-766.
Revenkova E, Eijpe M, Heyting C, Gross B, Jessberger R (2001) Novel meiosis-specific isoform of mammalian SMC1. Mol Cell Biol 21: 6984-6998.
Scherthan H, Weich S, Schwegler H, Heyting C, Harle M, Cremer T (1996) Centromere and telomere movements during early meiotic prophase of mouse and man are associated with the onset of chromosome pairing. J Cell Biol 134: 1109-1125.
Speed RM (1982) Meiosis in the fetal mouse ovary. I. An analysis at the light microscope level using surface spreading. Chromosoma 85: 427-437.
Speed RM (1988) The possible role of meiotic pairing anomalies in the atresia of human fetal oocytes. Hum Genet 78: 260-266.
Watanabe Y, Nurse P (1999) Cohesin Rec8 is required for reductional chromosome segregation at meiosis. Nature 400: 461-464.
Wolstenholme J, Angell RR (2000) Maternal age and trisomy-a unifying mechanism of formation. Chromosoma 109: 435-438.
Yokobayashi S, Yamamoto M, Watanabe Y (2003) Cohesins determine the attachment manner of kinetochores to spindle microtubules at meiosis I in fission yeast. Mol Cell Biol 23: 3965-3973.
Yuan L, Liu JG, Zhao J, Brundell E, Daneholt B, Höög C (2000) The murine SCP3 gene is required for synaptonemal complex assembly, chromosome synapsis, and male fertility. Mol Cell 5: 73-83.
Yuan L, Liu JG, Hoja MR, Wilbertz J, Nordqvist K, Hoog C (2002) Female germ cell aneuploidy and embryo death in mice lacking the meiosis-specific protein SCP3. Science 296: 1115-1118.
Zickler D, Kleckner N (1999) Meiotic chromosomes: integrating structure and function. Annu Rev Genet 33: 603-754.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prieto, I., Tease, C., Pezzi, N. et al. Cohesin component dynamics during meiotic prophase I in mammalian oocytes. Chromosome Res 12, 197–213 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CHRO.0000021945.83198.0e
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CHRO.0000021945.83198.0e