Abstract
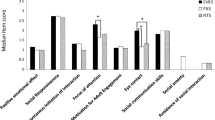
Social skills impairment in children with Turner or fragile X syndrome has been documented using parental reports. Anxiety, shyness, and difficulty understanding social cues have been reported for females with Turner syndrome; whereas social withdrawal, avoidance of social interactions, and anxiety are often reported for females with fragile X syndrome. Social interaction anxiety in these two populations may be a framework for understanding the difficulty these children experience in social situations. In the present study, 29 females with Turner syndrome and 21 females with fragile X syndrome ages 6–22 years were compared to females in a comparison group, on a videotaped role-play interaction. Behavioral indices examined included eye-contact maintenance, duration of speech, and body discomfort as observed during the brief interaction. Three of eight such behavioral measures of social skills differentiated the participant groups from each other. Specifically, participants with fragile X required more time to initiate interactions than did participants in either of the remaining groups; and females with Turner syndrome made fewer facial movements than did females in the fragile X or comparison group. Self-report and parental ratings did not suggest higher levels of anxiety in females with Turner or fragile X syndrome, but did reflect higher levels of social difficulty. The authors discuss these findings in terms of understanding the nature of social dysfunction in females with Turner or fragile X syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach, T. M. (1991). Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist/4–18 and 1991 profile. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
American Psychiatric Association. 1994. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed). Washington, DC: APA.
Asendorf, J. B. (1991). Development of inhibited children's coping with unfamiliarity. Child Development, 62, 1460-1474.
Bailey, D. B., Jr., Hatton, D. D., & Skinner, M. (1998). Early developmental trajectories of males with fragile X syndrome. American Journal of Mental Retardation, 1, 29-39.
Beidel, D. C., Turner, S. M., & Morris, T. L. (1998). Social phobia and anxiety inventory for children. New York: Multi-Health Systems, Inc..
Belser, R. C., & Sudhalter, V. (1995). Arousal difficulties in males with fragile X syndrome: A preliminary report. Development and Brain Dysfunction, 8, 270-279.
Bender, B. G., Puck, M., Salbenblatt, J., & Robinson, A. (1984). Cognitive development of unselected girls with complete and partial X monosmy. Pediatrics, 73, 175-182.
Bernstein, G. A., Borchardt, C. M., & Perwien, A. R. (1996). Anxiety disorders in children and adolescents: A review of the past 10 years. Journal of American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 35, 1110-1119.
Coplan, J. C., Rubin, K. H., Fox, N. A., Calkins, S. D., & Stewart, S. L. (1994). Being alone, playing alone, and acting alone: Distinguishing among reticence and passive and active solitude in young children. Child Development, 65, 129-137.
Downey, J. I. Ehrhardt, E. A., Gruen, R., Bell, J. J., & Morishima, A. (1989). Psychopathology and social functioning in women with Turner syndrome. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 177, 191-196.
Fisch, G. S. (1993). What is associated with the fragile X syndrome? American Journal of Medical Genetics, 48, 112-121.
Freund, L. S., Reiss, A. L., Abrams, M. T. (1993). Psychiatric disorders associated with fragile X in the young female. Pediatrics, 91, 321-329.
Fydrich, T., Chambless, D. L., Perry, K. J., Buergener, F., & Beazley, M. B. (1998). Behavioral assessment of social performance: A rating system for social phobia. Behavior Research and Therapy, 36, 995-1010.
Hagerman, R. J. (1999). Clinical and molecular aspects of fragile X syndrome. In Tager-Flusberg (Ed.), Neurodevelopmental Disorders (pp. 25-42). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Hagerman, R. J., & Sobesky, W. E. (1989). Psychopathology in fragile X syndrome. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 59, 142-152.
Herbert, J. D., Bellack, A. S., & Hope, D. A. (1991). Concurrent validity of the social phobia and anxiety inventory. Journal of Psychopathology and Behavioral Assessment, 13, 357-368.
Herbert, J. D., Hope, D. A., & Bellack, A. S. (1992). Validity of the distinction between generalized social phobia and avoidant personality disorder. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 101, 332-339.
Holmes, C. S., Karlsson, J. A., & Thompson, R. G. (1985). Social and school competencies in children with short stature: Longitudinal patterns. Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics, 6, 263-267.
Keysor, C. S., Mazzocco, M. M. M., McLeod, D. R., & Hoehn-Saric, R. (2002). Physiological arousal in females with fragile X or Turner syndrome. Developmental Psychobiology, 41, 133-146.
Kovar, C. G. (1993). The neurocognitive phenotype of fragile X girls. Unpublished master's thesis. University of Denver, Denver, Colorado.
Lachiewicz, A. M. (1992). Abnormal behaviors of young girls with fragile X syndrome. American Journal of Medical Genetics, 43, 72-77.
Lachiewicz, E. M., & Dawson, D. V. (1994). Behavioral problems of young girls with fragile x syndrome: Factor scores on the Conners' Parent's Questionnaire. American Journal of Medical Genetics, 51, 364-369.
Last, C. G., Perrin, S., Hersen, M., & Kazdin, A. E. DSM-III-R anxiety disorders in children: Sociodemografic and clinical characteristics. American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 31, 1070-1076.
Lesniak-Karpiak, K., Barakat, L. P., & Ross, J. L. Selective attention and children with Turner Syndrome. Manuscript submitted (in 2001) for publication.
Mazzocco, M. M. M. (2000). Advances in research on the fragile X syndrome. Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews, 6, 96-106.
Mazzocco, M. M. M., Baumgardner, T., Freund, L. S., & Reiss, A. L. (1998). Social functioning among girls with fragile X or Turner syndrome and their sisters. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 28, 509-517.
Mazzocco, M. M. M., Pennington, B. F., & Hagerman, R. J. (1993). The neurocognitive phenotype of female carriers of fragile X: Further evidence for specificity. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics, 14, 328-335.
Mazzocco, M. M. M., Pennington, B. F., & Hagerman, R. J. (1994). Social cognition skills in females with fragile X. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 24, 473-485.
McCauley, E., Ito, J., & Kay, T. (1986). Psychosocial functioning in girls with Turner's syndrome and short stature: Social skills, behavior problems, and self-concept. Journal of the American Academy of Child Psychiatry, 25, 105-112.
McCauley, E., Kay, T., Ito, J., & Treder, R. (1987). The Turner syndrome: Cognitive deficits, affective discrimination, and behavior problems. Child Development, 58, 464-473.
McCauley, E., Feuillan, P., Kushner, H., & Ross, J. L. (2001). Psychosocial development in adolescents with Turner syndrome. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics, 22, 360-365.
Monti, P. M., Boice, R., Fingeret, A. L., Zwick, W. R., Kolko, D., Munroe, S., & Grunberger, A. (1984). Midi-level measurement of social anxiety in psychiatric and non-psychiatric samples. Behavior Research and Therapy, 22, 651-660.
Perry, B. D. (1998). Anxiety disorder. In R. A. Brumbach & C. E. Coffey (Eds.), Textbook of pediatric neuropsychiatry (pp. 579-595). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Press.
Pope, A. W., McHale, S. M., & Craighead, W. E. (1988). Self-esteem enhancement with children and adolescents. Needham Heights, MA: Allyn and Bacon.
Reiss, A. L., & Freund, L. (1990). Fragile X syndrome. Biological Psychiatry, 27, 223-240.
Reynolds, C., & Richmond, B. (1978). What I think and feel: A revised measure of children's manifest anxiety. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 6, 271-280.
Roberts, J. E., Boccia, M. L., Bailey, D. B., Hatton, D. D., & Skinner, M. (2001). Cardiovascular indices of physiological arousal in boys with fragile X Syndrome. Developmental Psychobiology, 39, 107-123.
Ross, J. L., McCauley, E., Roeltgen, D., Long, L., Kushner, H., Feuillian, P., & Cutler, G. B. (1996). Self-concept and behavior in adolescent girls with Turner syndrome: Potential estrogen effects. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 81, 926-931.
Ross, J. L., & Zinn, A. (1999). Turner syndrome: Potential hormonal and genetic influences on the neurocognitive profile. In Tager-Flusberg (Ed.), Neurodevelopmental disorders (pp. 251-268). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Rousseau, F., Heitz, D., Tarleton, J., MacPherson, J., Malmgren, H., Dahl, N., Barnicoat, A., Mathew, C., Mornet, E., Tejada, I., Maddalena, A., Spiegel, R., Schinzel, A., Marcos, J. A. G., Schwartz, C., & Mandel, J. L. (1994) A multicenter study on genotype-phenotype correlations in the fragile X syndrome, using direct diagnosis with probe StB12.3: The first 2,253 cases. American Journal of Human Genetics, 55, 225-237.
Rovet, F. J. (1993). The psychoeducational characteristics of children with Turner syndrome. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 26, 333-341.
Rovet, J., & Buchanan, L. (1999). Turner syndrome: A cognitive neuroscience approach. In Tager-Flusberg (Ed.), Neurodevel-opmental disorders (pp. 223-249). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Rovet, J., & Ireland, L. (1994). Behavioral phenotype in children with Turner Syndrome. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 19, 779-790.
Safren, S. A., Heimberg, R. G., Horner, K. J., Justar, H. R., Schneider, F. R., & Liebowitz, M. R. (1999). Factor structure of social fears: The Liebowitz Social Anxiety Scale, Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 13, 253-270.
Skuse, D., Percy, E. L., & Stevensen, J. (1994). Psychosocial functioning in the Turner syndrome: A national survey. In B. Stabler & L. Underwood (Eds.), Growth, stature and adaptation (pp. 151-164). Chapel Hill, NC: The University of Northern Carolina at Chapel Hill.
Sobesky, W. E., Pennington, B. F., Porter, D., Hull, C. E., & Hagerman, R. J. (1994). Emotional and neurocognitive deficits in fragile X. American Journal of Medical Genetics, 51, 378-385.
Spinelli, M., de OliveiraRocha, A. C., Giacheti, C. M., & Richieri-Costa, A. (1995). Word-finding difficulties, verbal paraphasia, and verbal dyspraxia in ten individuals with fragile X syndrome. American Journal of Medical Genetics, 60, 39-43.
Stravynski, A., & Greenberg, D. (1989). Behavioral psychotherapy for social phobia and dysfunction. International Review of Psychiatry, 3, 207-217.
Sudhalter, V., Cohen, I. I., Silverman, W., & Wolf-Schein, E. G. (1990). Conversational analyses of males with fragile X, Down syndrome, and autism: Comparison of the emergence of deviant language. American Journal of Mental Retardation, 94, 431-441.
Tsatsanis, K. D., & Rourke, B. P. (1995). Syndrome of nonverbal learning disabilities: Neurodevelopmental manifestations. In B. P. Rourke (Ed.), Conclusions and future directions (pp. 476-496). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Turk, J. (1992). The fragile-X syndrome: On the way to a behavioral phenotype. British Journal of Psychiatry, 160, 24-35.
Turner, S. M., Beidel, D. C., & Dancu, C. V. (1996). Social Phobia and Anxiety Inventory. North Tonwanada: Multi-Health Systems, Inc.
Verkerk, A. J., Pieretti, M., Sutcliffe, J. S., Fu, Y. H., Kuhl, D. P., Pizzuti, A., Reiner, O., Richards, S., Victoria, M. F., Fuping Zhang, M. F. V., Eussen, B. E., van Ommen, G. J. B., Blonden, L. A. J., Riggins, G. J., Chastain, J. L., Kunst, C. B., Galjaard, H., Caskey, C. T., Nelson, D. L., Oostra, B. A., & Warren, S. T. (1991). Identification of a gene (FMR-1) containing a CGG repeat coincident with a breakpoint cluster region exhibiting length variation in fragile X syndrome. Cell, 65, 905-914.
Waber, D. P. (1979). Neuropsychological aspects of Turner's syndrome. Developmental Medical Child Neurology, 21, 58-70.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lesniak-Karpiak, K., Mazzocco, M.M.M. & Ross, J.L. Behavioral Assessment of Social Anxiety in Females with Turner or Fragile X Syndrome. J Autism Dev Disord 33, 55–67 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022230504787
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022230504787