Abstract
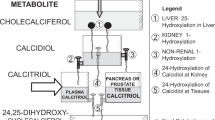
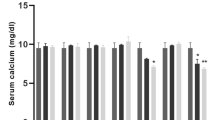
LACTATION represents a challenge to regulation of calcium metabolism. Because of the high rate of calcium transfer to the milk, the lactating rat consuming a commercial stock diet maintains a reduced serum Ca level1. The increased need for Ca seems to be met primarily by increased intestinal absorption of Ca (ref. 1). Since vitamin D is important for regulation of Ca metabolism, particularly during lactation2, and since the circulating level of the active metabolite lα,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1α,25-(OH)2D3) seems to be regulated according to Ca needs3, we determined by radioreceptor binding assay the serum levels of 1α,25-(OH)2D3 in vitamin D-fed lactating rats. We report here that these levels are two- to fourfold higher than those of non-lactating controls. Rats deprived of vitamin D during lactation fail to show elevated metabolite blood levels and develop marked hypocalcaemia, thus indicating the importance of the elevated blood level of 1α,25-(OH)2D3 for Ca metabolism during lactation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Toverud, S. U., Harper, C. & Munson, P. L. Endocrinology 99, 371–378 (1976).
Toverud, S. U. Transfer of Calcium and Strontium Across Biological Membranes (ed. Wasserman, R. H.) 341–358 (Academic, New York, 1963).
Hughes, M. R., Brumbaugh, P. F., Haussler, M. R., Wergedal, J. E. & Baylink, D. J. Science 190, 578–580 (1975).
Lawson, D. E. M., Fraser, D. R., Kodicek, E., Morris, H. R. & Williams, D. H. Nature 230, 228–230 (1971).
Hughes, M. R., Baylink, D. J., Jones, P. G. & Haussler, M. R. J. clin. Invest. 58, 61–70 (1976).
Hughes, M. R. et al. Endocrinology 100, 799–806 (1977).
MacIntyre, I. et al. Clin. Endocrinol. 5, Suppl. 85S–95S (1976).
Tanaka, Y. & DeLuca, H. F. Archs Biochem. Biophys. 154, 566–574 (1973).
Fraser, D. R. & Kodicek, E. Nature new Biol. 241, 163–166 (1973).
Garabedian, M., Holick, M. F., DeLuca, H. F. & Boyle, I. T. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 69, 1673–1676 (1972).
Chen, P. S., Toribara, T. Y. & Warner, H. Analyt. Chem. 28, 1756–1758 (1956).
Spanos, E. et al. Life Sci. 19, 1751–1756 (1976).
Pike, J. W., Toverud, S. U., Boass, A., McCain, T. & Haussler, M. R. Proc. 3rd Workshop Vitamin D, Pacific Grove, California (1977).
Schneider, L. E., Haussler, M. R., Schedl, H. P. & McCain, T. A. Clin. Res. 24, 567A (1976).
Spanos, E. et al. Molec. cell. Endocrinol. 5, 163–167 (1976).
Toverud, S. U. Acta physiol. scand. 62 Suppl. 234, 1–31 (1964)
Shah, B. G. & Draper, H. H. Am. J. Physiol. 211, 963–966 (1966).
Mainoya, J. R. Endocrinology 96, 1165–1170 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BOASS, A., TOVERUD, S., MCCAIN, T. et al. Elevated serum levels of 1α, 25-dihydroxycholecalciferol in lactating rats. Nature 267, 630–632 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1038/267630a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/267630a0
This article is cited by
-
Acromegaly and non‐parathyroid hormone‐dependent hypercalcemia: a case report and literature review
BMC Endocrine Disorders (2021)
-
Vitamin D metabolism in pregnant and pseudopregnant rats: Identification of 25-hydroxycholecalciferol-1-hydroxylase in decidual tissue
Calcified Tissue International (1988)
-
Normal milk composition in lactating X-linked hypophosphatemic mice despite continued hypophosphatemia
Calcified Tissue International (1983)
-
Reduction of lead-induced hypercalcemia by calcitonin: Comparison between thyroid-intact and thyroidectomized rats
Calcified Tissue International (1982)
-
An ultrastructural study of postprandial changes in bone lining cells of lead-injected thyroidectomized and thyroid-intact rats
Calcified Tissue International (1982)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.