Abstract
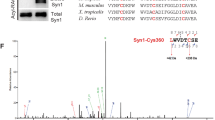
DYNAMIN is a microtubule-binding protein with a microtubule-activated GTPase activity1,3. The gene encoding dynamin is mut-ated in shibire4,5, a Drosophila mutant defective in endocytosis in nerve terminals and other cells6–9. These observations place dyna-min into two distinct functional contexts, suggesting roles in microtubule-based motility or in endocytosis. We report here that dynamin is identical to the neuronal phosphoprotein dephosphin (P96), originally identified by its stimulus-dependent dephosphorylation in nerve terminals10–13. Dynamin is a protein doublet of Mr 94 and 96K arising by alternative splicing of its primary transcript. In the nerve terminal, both forms of dynamin are phosphorylated by protein kinase C (PKC) and are quantitatively dephosphoryla-ted on excitation. In vitro, dynamin is also phosphorylated by casein kinase II which inhibits PKC phosphorylation. Phosphory-lation by PKC but not by casein kinase II enhances the GTPase activity of dynamin 12-fold. The dynamins are therefore a group of nerve terminal phosphoproteins whose GTPase is regulated by phosphorylation in parallel with synaptic vesicle recycling. The regulation of dynamin GTPase could serve as the trigger for the rapid endocytosis of synaptic vesicles after exocytosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Obar, R. A., Collins, C. A., Hammarback, J. A., Shpetner, H. S. & Vallee, R. B. Nature 347, 256–261 (1990).
Shpetner, H. S. & Vallee, R. B. Nature 355, 733–735 (1992).
Maeda, K., Nakata, T., Noda, Y., Sato-Yoshitake, R. & Hirokawa, N. Molec. Biol. Cell 3, 1181–1194 (1992).
van der Bliek, A. M. & Meyerowitz, E. M. Nature 351, 411–414 (1991).
Chen, M. S. et al. Nature 351, 583–586 (1991).
Kosaka, T. & Ikeda, K. J. Neurobiol. 14, 207–225 (1983).
Kosaka, T. & Ikeda, K. J. Cell Biol. 97, 499–507 (1983).
Kessell, I., Holst, G. D. & Roth, T. F. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 4968–4972 (1989).
Koenig, J. H. & Ikeda, K. J. Neurosc. 9, 3844–3860 (1989).
Robinson, P. J. FEBS Lett. 282, 388–392 (1991).
Robinson, P. J., Hauptschein, R., Lovenberg, W. & Dunkley, P. R. J. Neurochem. 48, 187–195 (1987).
Sihra, T. S., Bogonez, E. & Nicholls, D. G. J. biol. Chem. 267, 1983–1989 (1992).
Robinson, P. J. J. biol. Chem. 267, 21637–21644 (1992).
Faire, K., Trent, F., Tepper, J. M. & Bonder, E. M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 8376–8380 (1992).
Matsudaira, P. J. biol. Chem. 262, 10035–10038 (1987).
Harlow, E. & Lane, D. Antibodies: A Laboratory Manual (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 1988).
Südhof, T. C. et al. Science 245, 1474–1480 (1989).
Johnston, P. A., Jahn, R. & Südhof, T. C. J. biol. Chem. 264, 1268–1273 (1989).
Lincoln, T. M. Meth. Enzym. 99, 62–71 (1983).
Reimann, F. M. & Beham, R. A. Meth. Enzym. 99, 51–55 (1983).
Pascal, B. M., Shpetner, H. S. & Vallee, R. B. Meth. Enzym. 196, 181–191 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robinson, P., Sontag, JM., Liu, JP. et al. Dynamin GTPase regulated by protein kinase C phosphorylation in nerve terminals. Nature 365, 163–166 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/365163a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/365163a0
This article is cited by
-
Neural circuitry for maternal oxytocin release induced by infant cries
Nature (2023)
-
A deep intronic variant in DNM1 in a patient with developmental and epileptic encephalopathy creates a splice acceptor site and affects only transcript variants including exon 10a
neurogenetics (2023)
-
Proteomic Changes in Female Rat Hippocampus Following Exposure to a Terrified Sound Stress
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (2014)
-
Crystal structure of nucleotide-free dynamin
Nature (2011)
-
Prominent synaptic and metabolic abnormalities revealed by proteomic analysis of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder
Molecular Psychiatry (2008)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.